Abstract
Main conclusion
Exogenous application of dsRNA molecules targeting MYMV genes offers a promising approach to effectively mitigate yellow mosaic disease in blackgram, demonstrating potential for sustainable plant viral disease management.
Abstract
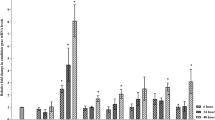
The exogenous application of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) molecules to control plant viral diseases is gaining traction due to its advantages over conventional methods, such as target specificity, non-polluting nature, and absence of residue formation. Furthermore, this approach does not involve genome modification. In this study, dsRNA molecules targeting the coat protein gene (dsCP) and replication initiator protein gene (dsRep) of mungbean yellow mosaic virus (MYMV) were synthesised using an in vitro transcription method. To evaluate the effectiveness of dsRNA treatment, blackgram plants exhibiting MYMV symptoms at the first trifoliate stage were subjected to exogenous application of dsRNA. Second, third, and fourth trifoliate leaves, which emerged at 7, 15, and 21 days after dsRNA application, respectively, were monitored for MYMV symptoms. Remarkably, a significant reduction in yellow mosaic disease (YMD) symptoms was observed in the newly emerged trifoliate leaves of MYMV-infected blackgram plants after treatment with dsRNA targeting both gene regions. This reduction was evident as a decrease in the intensity of yellow mosaic coverage on the leaf lamina compared to control. dsCP effectively reduced the MYMV titre in the treated plants for up to 15 days. However, dsRep demonstrated greater efficiency in conferring resistance to MYMV at 15 days post-application. These findings were supported by quantitative real-time PCR analysis, where the observed Ct values for DNA extracted from dsRep-treated plants were significantly higher compared to the Ct values of DNA from dsCP-treated plants at 15 days post-application. Similarly, higher viral copy numbers were observed in dsCP-treated plants 15 days after dsRNA treatment, in contrast to plants treated with dsRep.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data supporting the results reported in the paper are included within the manuscript provided.
Change history
25 October 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-023-04264-3
Abbreviations
- DPA:
-
Days post application
- dsCP:
-
dsRNA molecule targeting the coat protein gene
- dsREP:
-
dsRNA molecule targeting the replication initiator protein gene
- dsRNA:
-
Double-stranded RNA
- YMD:
-
Yellow mosaic disease
References
Balaji V, Vanitharani R, Karthikeyan AS, Anbalagan S, Veluthambi K (2004) Infectivity analysis of two variable DNA B components of Mungbean yellow mosaic virus-Vigna in Vigna mungo and Vigna radiata. J Biosci 29(3):297–308
Baulcombe D (2004) RNA silencing in plants. Nature 431:356–363
Borah M, Berbati M, Reppa C, Holeva M, Nath PD, Voloudakis A (2018) RNA-based vaccination of Bhut Jolokia pepper (Capsicum chinense Jacq.) against cucumber mosaic virus. Virus Dis 29(2):207–211
Borges F, Martienssen RA (2015) The expanding world of small RNAs in plants. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 16(12):727–741
Cerutti H, Ibrahim F (2010) Turnover of mature miRNAs and siRNAs in plants and algae. In: Madame Curie Bioscience Database [Internet]. Landes Bioscience, Austin (TX), 2000–2013. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK28486/
Chatterjee BN, Bhattacharyya KK (1986) Principles and practices of grain legume production. In: Oxford and IBH Publishing Co. pp. 492, New Delhi
Dubelman S, Fischer J, Zapata F, Huizinga K, Jiang C, Uffman J, Carson D (2014) Environmental fate of double-stranded RNA in agricultural soils. PLoS ONE 9(3):0093155
Holeva MC, Sklavounos A, Rajeswaran R, Pooggin MM, Voloudakis AE (2021) Topical application of double-stranded RNA targeting 2b and CP genes of Cucumber mosaic virus protects plants against local and systemic viral infection. Plants 10(5):963
Kaldis A, Berbati M, Melita O, Reppa C, Holeva M, Otten P, Voloudakis A (2018) Exogenously applied dsRNA molecules deriving from the Zucchini yellow mosaic virus (ZYMV) genome move systemically and protect cucurbits against ZYMV. Mol Plant Pathol 19(4):883–895
Khalid A, Zhang Q, Yasir M, Li F (2017) Small RNA based genetic engineering for plant viral resistance: application in crop protection. Front Microbiol 8:43
Kim H, Shimura H, Masuta C (2019) Advancing toward commercial application of RNA silencing-based strategies to protect plants from viral diseases. J Gen Plant Pathol 85(5):321–328
Konakalla NC, Kaldis A, Berbati M, Masarapu H, Voloudakis AE (2016) Exogenous application of double-stranded RNA molecules from TMV p126 and CP genes confers resistance against TMV in tobacco. Planta 244(4):961–969
Malathi VG, John P (2009) Mungbean yellow mosaic viruses. In: van Regenmortel MHV, Mahy BWJ (eds) Desk encyclopedia of plant and fungal virology. Elsevier, pp 217–226
Melita O, Kaldis A, Berbati M, Reppa C, Holeva M, Lapidot M, Gelbart D, Otten P, Voloudakis A (2021) Topical application of double-stranded RNA molecules deriving from Tomato yellow leaf curl virus reduces cognate virus infection in tomato. Biol Plant 65:100–110
Nagamani S, Ankita T, Mandal B, Jain RK (2020) Effect of temperature on systemic infection and symptom expression induced by Soybean yellow mottle mosaic virus in leguminous hosts. Austr Plant Pathol 49(5):579–589
Namgial T, Kaldis A, Chakraborty S, Voloudakis A (2019) Topical application of double-stranded RNA molecules containing sequences of Tomato leaf curl virus and Cucumber mosaic virus confers protection against the cognate viruses. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 155:1345–1352
Napoli C, Lemieux C, Jorgensen R (1990) Introduction of a chimeric chalcone synthase gene into petunia results in reversible co-suppression of homologous genes in trans. Plant Cell 2(4):279–289
Pooggin M, Shivaprasad PV, Veluthambi K, Hohn T (2003) RNAi targeting of DNA virus in plants. Nat Biotechnol 21(2):131–132
Rego-Machado CM, Nakasu YET, Silva JMF, Lucinda N, Nagata T, Inoue-Nagata AK (2020) siRNA biogenesis and advances in topically applied dsRNA for controlling virus infections in tomato plants. Sci Rep 10(1):22277
Rouhibakhsh A, Priya J, Periasamy M, Haq QMI, Malathi VG (2008) An improved DNA isolation method and PCR protocol for efficient detection of multicomponents of begomovirus in legumes. J Virol Methods 147(1):37–42
Singh S, Awasthi LP (2004) Varietal screening of urdbean against Mungbean yellow mosaic virus under field conditions. Ann Plant Prot Sci 12(1):225–226
Voloudakis AE, Holeva MC, Sarin LP, Bamford DH, Vargas M, Poranen MM, Tenllado F (2015) Efficient double-stranded RNA production methods for utilization in plant virus control. Methods Mole Biol 1236:255–274
Werner BT, Gaffar FY, Schuemann J, Biedenkopf D, Koch AM (2020) RNA-spray-mediated silencing of Fusarium graminearum AGO and DCL genes improve barley disease resistance. Front Plant Sci 11:476
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Dorothea Bartels.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: Author affiliation, Abbreviation text, Figure 1 and 4 were corrected in the original version.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kamesh Krishnamoorthy, K., Malathi, V.G., Renukadevi, P. et al. Exogenous delivery of dsRNA for management of mungbean yellow mosaic virus on blackgram. Planta 258, 94 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-023-04253-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-023-04253-6