Abstract
Main conclusion
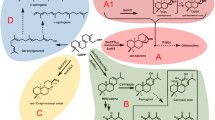
An alkenal double-bond reductase enzyme (CaDBR1) was cloned from Colchicum autumnale L. The encoded enzyme catalysed 4-coumaraldehyde to 4-hydroxydihydrocinnamaldehyde (4-HDCA). Its functional characterization increased the understanding of colchicine biosynthesis.
Abstract
As a traditional medical plant, Colchicum autumnale L. is famous for producing colchicine, a widely used drug for alleviating gout attacks. The biosynthetic pathway of colchicine was revealed most recently, and 4-hydroxydihydrocinnamaldehyde (4-HDCA) has been verified as a crucial intermediate derived from L-phenylalanine. However, the functional gene that catalyses the formation of 4-HDCA remains controversial. In this study, the alkenal double-bond reductase (DBR) gene member CaDBR1 was cloned and characterized from C. autumnale. Bioinformatics analysis predicted and characterized the basic physicochemical properties of CaDBR1. Recombinant CaDBR1 protein was heterologously expressed in Escherichia coli and purified by a Ni-NTA column. In vitro enzyme assays indicated that CaDBR1 could catalyse 4-coumaraldehyde to form 4-HDCA but could not generate 4-HDCA by taking cinnamaldehyde as a substrate. Stable transformation into tobacco BY-2 cells revealed that CaDBR1 localized in the cytoplasm, and tissue-specific expression results showed that CaDBR1 had the highest expression in bulbs. All these results verify and confirm the participation and contribution of CaDBR1 in the biosynthesis pathway of 4-HDCA and colchicine alkaloids in C. autumnale.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- DBR:
-
Alkenal double-bond reductase
- C. autumnale :
-
Colchicum autumnale L.
- 4-HDCA:
-
4-Hydroxydihydrocinnamaldehyde
- qRT-PCR:
-
The quantitative real-time PCR
- MDR family:
-
Medium-chain reductase/dehydrogenase family
- LB:
-
Luria–Bertani
- IPTG:
-
Isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactoside
- UPLC:
-
Ultrahigh-pressure liquid chromatography
- UPLC–MS:
-
Ultra-performance liquid chromatograph–mass spectrometry
- Ox:
-
Overexpression
References
Anastasia S, Binita S, Pillinger MH, Svetlana K (2015) Colchicine: old and new. Am J Med 128(5):461–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2014.12.010
Bader J, Kim MA, Simon H (1981) The reduction of allyl alcohols by clostridium species is catalyzed by the combined action of alcohol dehydrogenase and enoate reductase. Hoppe-Seyler’s Zeitschrift Fur Physiologische Chemie. https://doi.org/10.1515/bchm2.1981.362.1.809
Baldockl C, Rafferty JB, Stuitje AR, Slabas AR, Rice DW (1998) The X-ray structure of Escherichia coli enoyl reductase with bound NAD+at 2.1 a resolution. J Mol Biol 284(5):1529–1546. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1998.2271
Buschmann H, Green P, Sambade A, Doonan JH, Lloyd CW (2011) Cytoskeletal dynamics in interphase, mitosis and cytokinesis analyzed through Agrobacterium-mediated transient transformation of tobacco BY-2 cells. New Phytol 190(1):258–267. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2010.03587.x
Caliandro R, Polsinelli I, Demitri N, Musiani F, Martens S, Benini S (2021) The structural and functional characterization of Malus domestica double bond reductase MdDBR provides insights towards the identification of its substrates. Int J Biol Macromol 171:89–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.12.190
Cronstein BN, Sunkureddi P (2013) Mechanistic aspects of inflammation and clinical management of inflammation in acute gouty arthritis. JCR-J Clin Rheumatol 19(1):19–29. https://doi.org/10.1097/RHU.0b013e31827d8790
Gao N, Wadhwani P, Mühlhäuser P, Liu Q, Riemann M, Ulrich AS, Nick P (2016) An antifungal protein from Ginkgo biloba binds actin and can trigger cell death. Protoplasma 253(4):1159–1174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-015-0876-4
He Y, Zhong X, Jiang X, Cong H, Sun H, Qiao F (2020) Characterisation, expression, and functional analysis of PAL gene family in Cephalotaxus hainanensis. Plant Physiol Bioch 156:461–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.09.030
Herbert RB, Kattah AE, Knagg E (1990) The biosynthesis of the phenethylisoquinoline alkaloid colchicine. Early and intermediate stages. Tetrahedron 46(20):7119–7138. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4020(01)87895-9
Hu J, Li W, Liu Z, Zhang G, Luo Y (2021a) Molecular cloning and functional characterization of tyrosine decarboxylases from galanthamine-producing Lycoris radiata. Acta Physiol Plant 43(6):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-021-03258-6
Hu W, Xia P, Liang Z (2021b) Molecular cloning and structural analysis of key enzymes in Tetrastigma hemsleyanum for resveratrol biosynthesis. Int J Biol Macromol 190:19–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.08.178
Jahanzeb M, Nismat J, Uzma I, Khan U, Talha L (2020) Is there a role for colchicine in acute coronary syndromes? A literature review. Cureus. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.8166
Jiang D, Li P, Yin Y, Ren G, Liu C (2021) Molecular cloning and functional characterization of UGTs from Glycyrrhiza uralensis flavonoid pathway. Int J Biol Macromol 192:1108–1116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.09.136
Jung LS, Winter S, Eckstein RL, Kriechbaum M, Karrerc G, Welk E, Elsasser M, Donath TW (2011) Colchicum autumnale L., perspectives in plant ecology. Evol Syst 13(3):227–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ppees.2011.04.001
Kasahara H, Jiao Y, Bedgar DL, Kim S, Patten AM, Xia Z, Davin LB, Lewis NG (2006) Pinus taeda phenylpropenal double-bond reductase: purification, cDNA cloning, heterologous expression in Escherichia coli, and subcellular localization in P. Taeda. Phytochemistry 67(16):1765–1780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2006.07.001
Lange U, Schumann C, Schmidt KL (2002) Aspects of colchicine therapy. 1: pharmacology, toxicology, classic indications. Zeitschrift fur Arztliche Fortbildung und Qualitatssicherung 96(1):59–63. https://europepmc.org/article/MED/11876051
Lau W, Sattely ES (2015) Six enzymes from mayapple that complete the biosynthetic pathway to the etoposide aglycone. Science 349:1224–1228. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aac7202
Mano J, Torii Y, Hayashi S, Takimoto K, Matsui K, Nakamura K, Inze D, Babiychuk E, Kushnir S, Asada K (2002) The NADPH: quinone oxidoreductase P1-crystallin in Arabidopsis catalyzes the α, β-hydrogenation of 2-alkenals: detoxication of the lipid peroxide-derived reactive aldehydes. Plant Cell Physiol 43(12):1445–1455. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcf187
Mano J, Belles-Boix E, Babiychuk E, Inzé D, Torii Y, Hiraoka E, Takimoto K, Slooten L, Asada K, Kushnir S (2005) Protection against photooxidative injury of tobacco leaves by 2-Alkenal reductase. Detoxication of lipid peroxide-derived reactive carbonyls. Plant Physiol 139(4):1773–1783. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.105.070391
Mansell DJ, Toogood HS, Waller J, Hughes JMX, Levy CW, Gardiner JM, Scrutton NS (2013) Biocatalytic asymmetric alkene reduction: crystal structure and characterization of a double bond reductase from Nicotiana tabacum. ACS Catal 3(3):370–379. https://doi.org/10.1021/cs300709m
Nett RS, Sattely ES (2021) Total biosynthesis of the Tubulin-Binding alkaloid colchicine. J Am Chem Soc 143(46):19454–19465. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.1c08659
Nett RS, Lau W, Sattely ES (2020) Discovery and engineering of colchicine alkaloid biosynthesis. Nature 584(7819):148–153. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2606-0
Olofsson L, Engström A, Lundgren A, Brodelius PE (2011) Relative expression of genes of terpene metabolism in different tissues of Artemisia annua L. BMC Plant Biol. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-11-45
Paul P, Halder M, Jha S (2013) Alkaloids derived from tyrosine: penethylisoquinoline (autumnaline, colchicine). Natural Products 10:978–983. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-22144-6_16
Rajabi F, Heene E, Maisch J, Nick P (2017) Combination of plant metabolic modules yields synthetic synergies. PLoS ONE 12(1):e169778. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0169778
Schlesinger N (2010) New agents for the treatment of gout and hyperuricemia: febuxostat, puricase, and beyond. Curr Rheumatol Rep 12(2):130–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-010-0093-2
Sivakumar G (2018) Upstream biomanufacturing of pharmaceutical colchicine. Crit Rev Biotechnol 38(1):83–92. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388551.2017.1312269
Stuermer R, Hauer B, Hall M, Faber K (2007) Asymmetric bioreduction of activated C=C bonds using enoate reductases from the old yellow enzyme family. Curr Opin Chem Biol 11(2):203–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2007.02.025
Tong DC, Wilson AM, Layland J (2016) Colchicine in cardiovascular disease: an ancient drug with modern tricks. Heart 102(13):995–1002. https://doi.org/10.1136/heartjnl-2015-309211
Wallace WL (1973) Colchicum: the panacea. Bull NY Acad Med 49:130–135. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/4567271/
Weng J (2020) How the flame lily synthesizes a therapeutic natural product. Nature 584(7819):49–50. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-01675-0
Wu Y, Zheng H, Liu X, Cheng A, Lou H (2018) Molecular diversity of alkenal double bond reductases in the liverwort Marchantia paleacea. Molecules 23(7):1630. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071630
Youn B, Kim S, Moinuddin SGA, Lee C, Bedgar DL, Harper AR, Davin LB, Lewis NG, Kang C (2006) Mechanistic and structural studies of apo form, binary, and ternary complexes of the arabidopsis alkenal double bond reductase At5g16970. J Biol Chem 281(52):40076–40088. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M605900200
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32070364), the Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (319MS084 and 2019RC309), and the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund for the Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences (1630032019038).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Communicated by Anastasios Melis.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, Z., Wang, L., Sun, J. et al. Functional characterization of a Colchicum autumnale L. double-bond reductase (CaDBR1) in colchicine biosynthesis. Planta 256, 95 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-022-04003-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-022-04003-0