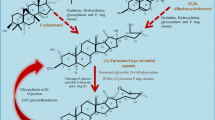
Main conclusion
This work reviews recent advances in the pathways and key enzymes of steroidal saponins biosynthesis and sets the foundation for the biotechnological production of these useful compounds through transformation of microorganisms.
Abstract
Steroidal saponins, due to their specific chemical structures and active effects, have long been important natural products and that are irreplaceable in hormone production and other pharmaceutical industries. This article comprehensively reviewed the previous and current research progress and summarized the biosynthesis pathways and key biosynthetic enzymes of steroidal saponins that have been discovered in plants and microoganisms. On the basis of the general biosynthetic pathway in plants, it was found that the starting components, intermediates and catalysing enzymes were diverse between plants and microorganisms; however, the functions of their related enzymes tended to be similar. The biosynthesis pathways of steroidal saponins in microorganisms and marine organisms have not been revealed as clearly as those in plants and need further investigation. The elucidation of biosynthetic pathways and key enzymes is essential for understanding the synthetic mechanisms of these compounds and provides researchers with important information to further develop and implement the massive production of steroidal saponins by biotechnological approaches and methodologies.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Abbreviations
- IPP:
-
Isopentenyl diphosphate
- CAS:
-
Cycloartenol synthase
- CPI1:
-
Cyclopropylsterol isomerase
- CYP51, ERG11:
-
Sterol C-14 demethylase
- DMAPP:
-
Dimethylallyl diphosphate
- DWF1, ERG4:
-
Delta 24-sterol reductase
- DWF5:
-
7-Dehydrocholesterol reductase
- DWF7, ERG3:
-
Sterol C-5 desaturase
- ERG5:
-
Sterol C-22 desaturase
- ERG6:
-
Sterol C-24 methylase
- FK, ERG24:
-
Sterol C-14 reductase
- FPPS:
-
Farnesyl diphosphate synthase
- GPPS:
-
Geranyl diphosphate synthase
- HYD1, ERG2:
-
Sterol 8,7 isomerase
- LAS:
-
Lanosterol synthetase
- SMO, ERG25:
-
Sterol 4α-methyl oxidase
- SMT:
-
Sterol C-24 methyltransferase
- SQE:
-
Squalene epoxidase
- UGTs:
-
Uridine diphosphate-dependent glycosyltransferases
References
Abdelrahman M et al (2017) RNA-sequencing-based transcriptome and biochemical analyses of steroidal saponin pathway in a complete set of Allium fistulosum—A. cepa monosomic addition lines. PLoS One 12:e0181784. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0181784
Adham NZ, Zaki RA, Naim N (2009) Microbial transformation of diosgenin and its precursor furostanol glycosides. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:481–487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9913-1
Arthan D, Kittakoop P, Esen A, Svasti J (2006) Furostanol glycoside 26-O-β-glucosidase from the leaves of Solanum torvum. Phytochemistry 67:27–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2005.09.035
Bai Y, Yin H, Bi H, Zhuang Y, Liu T, Ma Y (2016) De novo biosynthesis of Gastrodin in Escherichia coli. Metab Eng 35:138–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2016.01.002
Bard M et al (1996) Cloning and characterization of ERG25, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene encoding C-4 sterol methyl oxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:186–190. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.93.1.186
Basu S, Jha TB (2013) In vitro root culture : an alternative source of bioactives in the rare aphrodisiac herb Chlorophytum borivilianum Sant et Fern. Plant Tissue Cult Biotechnol 23:133–145. https://doi.org/10.3329/ptcb.v23i2.17505
Behrman E, Gopalan V (2005) Cholesterol and plants. J Chem Educ. https://doi.org/10.1021/ed082p1791
Blunden G, Patel AV, Crabb TA (1990) Microbiological transformation of hecogenin and diosgenin by Cunninghamella elegans. Phytochemistry 29:1771–1780. https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9422(90)85013-6
Bouvier P, Rohmer M, Benveniste P, Ourisson G (1976) Delta 8(14)-steroids in the bacterium Methylococcus capsulatus. Biochem J 159:267–271. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj1590267
Cao XD, Zhou LG, Xu LJ, Tan ML (2005) Biological characters of the endophytic fungi from Paris polyphylla var.yunnanensis and their steroidal content. J Northwest A F Univ 033:125–128. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1671-9387.2005.z1.034
Chaudhary S et al (2015) Elicitation of diosgenin production in Trigonella foenum-graecum (Fenugreek) seedlings by Methyl Jasmonate. Int J Mol Sci 16:29889–29899. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226208
Chauhan R, Keshavkant S, Quraishi A (2018) Enhanced production of diosgenin through elicitation in micro-tubers of Chlorophytum borivilianum Sant et Fernand. J Industrial Crops 113:234–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.01.029
Chauhan HK (2020) The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020: e.T175617476A176257430. https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T175617476A176257430.en
Chen ND, Zhang J, Liu JH, Yu BY (2009) Microbial conversion of ruscogenin by Gliocladium deliquescens NRRL1086: glycosylation at C-1. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:491–497. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2315-y
Chen M, Chen JJ, Luo N, Qu RD, Guo ZF, Lu SY (2018a) Cholesterol accumulation by suppression of SMT1 leads to dwarfism and improved drought tolerance in herbaceous plants. Plant Cell Environ. https://doi.org/10.1111/pce.13168
Chen Y, Dong Y, Chi YL, He Q, Wu H, Ren Y (2018b) Eco-friendly microbial production of diosgenin from saponins in Dioscorea zingiberensis tubers in the presence of Aspergillus awamori. Steroids. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.steroids.2018.05.005
Cheng J, Chen J, Liu XN, Li XC, Ma YH (2020) The origin and evolution of diosgenin biosynthetic pathway in yam. Plant Commun 2:100079. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.xplc.2020.100079
Cheong S, Clomburg JM, Gonzalez R (2016) Energy- and carbon-efficient synthesis of functionalized small molecules in bacteria using non-decarboxylative Claisen condensation reactions. Nat Biotechnol 34:556–561. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3505
Ciura J, Szeliga M, Grzesik M, Tyrka M (2017a) Changes in fenugreek transcriptome induced by methyl jasmonate and steroid precursors revealed by RNA-Seq. Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2017.10.006
Ciura J, Szeliga M, Grzesik M, Tyrka M (2017b) Next-generation sequencing of representational difference analysis products for identification of genes involved in diosgenin biosynthesis in fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum). Planta 245:977–991. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-017-2657-0
Corsello MA, Garg NK (2015) Synthetic chemistry fuels interdisciplinary approaches to the production of artemisinin. Nat Prod Rep 32:359–366. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4np00113c
Cunningham AB, Brinckmann JA, Bi YF, Pei SJ, Schippmann U, Luo P (2018) Paris in the spring: a review of the trade, conservation and opportunities in the shift from wild harvest to cultivation of Paris polyphylla (Trilliaceae). J Ethnopharmacol 222:208–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2018.04.048
Dai Z et al (2014) Producing aglycons of ginsenosides in bakers’ yeast. Sci Rep 4:3698. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep03698
Darnet S, Rahier A (2004) Plant sterol biosynthesis: identification of two distinct families of sterol 4α-methyl oxidases. Biochem J 378:889–898. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20031572
Darnet S, Bard M, Rahier A (2001) Functional identification of sterol-4α-methyl oxidase cDNAs from Arabidopsis thaliana by complementation of a yeast erg25 mutant lacking sterol-4α-methyl oxidation. FEBS Lett 508:39–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-5793(01)03002-2
de Oliveira JVA et al (2019) Saponin-rich fraction from Agave sisalana: effect against malignant astrocytic cells and its chemical characterisation by ESI-MS/MS. Nat Prod Res 33:1769–1772. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2018.1434633
Desmond E, Gribaldo S (2009) Phylogenomics of sterol synthesis: insights into the origin, evolution, and diversity of a key eukaryotic feature. Genome Biol Evol 1:364–381. https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evp036
Desta M, Wang WW, Zhang LG, Xu P, Tang HZ (2019) Isolation, characterization, and genomic analysis of Pseudomonas sp. strain SMT-1, an efficient fluorene-degrading bacterium. Evol Bioinform Online 15:1176934319843518. https://doi.org/10.1177/1176934319843518
Diener AC, Li H, Zhou W, Whoriskey WJ, Nes WD, Fink GR (2000) Sterol methyltransferase 1 controls the level of cholesterol in plants. Plant Cell 12:853–870. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.12.6.853
Ding CH et al (2014) Screening for differentially expressed genes in endophytic fungus strain 39 during co-culture with herbal extract of its host Dioscorea nipponica makino. Curr Microbiol 69:517–524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-014-0615-7
Dong M, Feng XZ, Wang BX, Ikejima T, Wu LJ (2004) Microbial metabolism of pseudoprotodioscin. Planta Med 70:637–641. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2004-827187
Dong XR, Gao ZH, Hu HX, Gao RR, Sun D (2016) Microbial transformation of pseudoprotodioscin by Chaetomium olivaceum. J Mol Catal B Enzym. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2016.05.001
Dutch Medicines Evaluation Board (2012) First Authorisation of Traditional Herbal Medicine from outside the European Union. http://www.cbg-meb.nl/CBG/en/human-medicines/actueel/First_Authorisation_of_Traditional_Herbal_Medicine_from_outside_the_European_Union/. Accessed 21 July 2013
Espinosa-Leal CA, Puente-Garza CA, Garcia-Lara S (2018) In vitro plant tissue culture: means for production of biological active compounds. Planta 248:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-018-2910-1
Fabris M et al (2014) Tracking the sterol biosynthesis pathway of the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. New Phytol. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12917
Fan B, Chen TY, Zhang S, Wu B, He BF (2017) Mining of efficient microbial UDP-glycosyltransferases by motif evolution cross plant kingdom for application in biosynthesis of salidroside. Sci Rep 7:463. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-00568-z
Feng B, Ma BP, Kang LP, Xiong CQ, Wang SQJC (2005) The microbiological transformation of steroidal saponins by Curvularia Lunata. Tetrahedron 61:11758–11763
Feng S, Song W, Fu RR, Zhang H, Xu AR, Li JR (2018) Application of the CRISPR/Cas9 system in Dioscorea zingiberensis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult (PCTOC) 135:133–141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-018-1450-5
Fernández-Cabezón L, Galán B, García JL (2018) New insights on steroid biotechnology. Front Microbiol 9:958. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.00958
Fontaine J, Grandmougin-Ferjani A, Hartmann MA, Sancholle M (2002) Sterol biosynthesis by the arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus intraradices. Lipids 36:1357–1363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-001-0852-z
Fujita S et al (2006) Arabidopsis CYP90B1 catalyses the early C-22 hydroxylation of C27, C28 and C29 sterols. Plant J 45:765–774. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02639.x
Galanie S, Thodey K, Trenchard IJ, Interrante MF, Smolke CD (2015) Complete biosynthesis of opioids in yeast. Science 349:1095–1100. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aac9373
Ganapathy K, Jones CW, Stephens CM, Vatsyayan R, Marshall JA, Nes WD (2008) Molecular probing of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae sterol 24-C methyltransferase reveals multiple amino acid residues involved with C2-transfer activity. Biochem Biophys Acta 1781:344–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2008.04.015
Gao RR, Gao ZH, Dong XR, Hu HX, Qiao Y, Sun AD (2017) Microbial transformation of gracillin by Penicillium Lilacinum ACCC 31890. China Pharmacist 020:988–993
Garagounis C et al (2020) A hairy-root transformation protocol for Trigonella foenum-graecum L. as a tool for metabolic engineering and specialised metabolite pathway elucidation. Plant Physiol Biochem 154:451–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.06.011
González-Lamothe R, Mitchell G, Gattuso M, Diarra MS, Malouin F, Bouarab K (2009) Plant antimicrobial agents and their effects on plant and human pathogens. Int J Mol Sci 10:3400–3419. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms10083400
Grandmougin-Ferjani A, Dalpé Y, Hartmann M-A, Laruelle F, Sancholle M (1999) Sterol distribution in arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Phytochemistry 50:1027–1031. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(98)00636-0
Guan HY et al (2017) Molecular cloning and functional identification of sterol C24-methyltransferase gene from Tripterygium wilfordii. Acta Pharmaceutica Sin B 7:603–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2017.07.001
Guan HY et al (2018) Cloning and functional analysis of two sterol-C24-methyltransferase 1 (SMT1) genes from Paris polyphylla. J Asian Nat Prod Res 20:595–604. https://doi.org/10.1080/10286020.2016.1271791
Güçlü-Ustündağ O, Mazza G (2007) Saponins: properties, applications and processing. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 47:231–258. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408390600698197
Haubrich BA et al (2014) Characterization, mutagenesis and mechanistic analysis of an ancient algal sterol C24-methyltransferase: implications for understanding sterol evolution in the green lineage. Phytochemistry 113:64–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2014.07.019
Hayakawa S, Sato Y (1963) Microbiological transformation of diosgenin. J Org Chem 28:2742–2743. https://doi.org/10.1021/jo01045a059
He XJ, Liu B, Wang GH, Wang XL, Su L, Qu GX, Yao XS (2006) Microbial metabolism of methyl protodioscin by Aspergillus niger culture—A new androstenedione producing way from steroid. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 100:87–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2006.03.007
Hedden P, Phillips AL, Rojas MC, Carrera E, Tudzynski B (2002) Gibberellin biosynthesis in plants and fungi: a case of convergent evolution? J Plant Growth Regul 20:319–331. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003440010037
Heinig U, Scholz S, Jennewein S (2013) Getting to the bottom of Taxol biosynthesis by fungi. Fungal Div 60:161–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13225-013-0228-7
Holmberg N et al (2002) Sterol C-24 methyltransferase type 1 controls the flux of carbon into sterol biosynthesis in tobacco seed. Plant Physiol 130:303–311. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.004226
Hu YM, Yu ZL, Fong WF (2011) Stereoselective biotransformation of timosaponin A-III by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:582–589. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1101.12041
Hu HX, Gao RR, Gao ZH, Qiao Y, Dong XR, Ding G, Sun DA (2018) Microbial transformation of pseudoprotodioscin by Gibberella fujikuroi. J Asian Nat Prod Res 20:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/10286020.2018.1468438
Huang FC, Giri A, Daniilidis M, Sun G, Hartl K, Hoffmann T, Schwab W (2018) Structural and functional analysis of UGT92G6 suggests an evolutionary link between mono- and disaccharide glycoside-forming transferases. Plant Cell Physiol 59:857–870. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcy028
Husselstein T, Gachotte D, Desprez T, Bard M, Benveniste P (1996) Transformation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae with a cDNA encoding a sterol C-methyltransferase from Arabidopsis thaliana results in the synthesis of 24-ethyl sterols. FEBS Lett 381:87–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(96)00089-0
Inoue K, Ebizuka Y (1996a) Purification and characterization of a β-glucosidase which converts furostanol glycosides to spirostanol glycosides from Costus speciosus. Adv Exp Med Biol 404:57–69. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4899-1367-8_6
Inoue K, Ebizuka Y (1996b) Purification and characterization of furostanol glycoside 26-O-β-glucosidase from Costus speciosus rhizomes. FEBS Lett 378:157–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/0014-5793(95)01447-0
Iorrizzi M, De Marino S, Zollo F (2001) Steroidal oligoglycosides from the asteroidea. Curr Org Chem 5:951–973. https://doi.org/10.2174/1385272013374978
Jaramillo-Madrid AC, Ashworth J, Fabris M, Ralph PJ (2019) Phytosterol biosynthesis and production by diatoms (Bacillariophyceae). Phytochemistry 163:46–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2019.03.018
Jiang X et al (2017) Panax ginseng genome examination for ginsenoside biosynthesis. GigaScience. https://doi.org/10.1093/gigascience/gix093
Kim M et al (2017) Optimal fermentation conditions of hyaluronidase inhibition activity on Asparagus cochinchinensis merrill by Weissella cibaria. J Microbiol Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1611.11051
Kumar A, Fogelman E, Weissberg M, Tanami Z, Veilleux RE, Ginzberg I (2017) Lanosterol synthase-like is involved with differential accumulation of steroidal glycoalkaloids in potato. Planta. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-017-2763-z
Lata R, Chowdhury S, Gond SK, White JF (2018) Induction of abiotic stress tolerance in plants by endophytic microbes. Lett Appl Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.12855
Lee AK, Banta AB, Wei JH, Kiemle DJ, Feng J, Giner J-L, Welander PV (2018) C-4 sterol demethylation enzymes distinguish bacterial and eukaryotic sterol synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 115:201802930. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1802930115
Lees ND, Skaggs B, Kirsch DR, Bard M (1995) Cloning of the late genes in the ergosterol biosynthetic pathway of Saccharomyces cerevisiae–a review. Lipids 30:221–226. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02537824
Li PQ, Mao ZL, Lou JF, Mou Y, Lu SQ, Peng YL, Zhou LG (2011) Enhancement of diosgenin production in Dioscorea zingiberensis cell cultures by oligosaccharides from its endophytic fungus Fusarium oxysporum Dzf17. Molecules 16:10631–10644. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules161210631
Li XW, Chen YN, Lai YF, Yang Q, Hu H, Wang YT (2015) Sustainable utilization of traditional Chinese medicine resources: systematic evaluation on different production modes. Evid Based Complement Altern Med 2015:218901. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/218901
Li H, Wang XD, Ma Y, Yang NN, Zhang XJ, Xu ZH, Shi JS (2016) Purification and characterization of a glycosidase with hydrolyzing multi-3-O-glycosides of spirostanol saponin activity from Gibberella intermedia. J Mol Catal B Enzym. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcatb.2016.03.003
Li YB, Lin L, Liao QH, Yang SC, Liu T (2019) Screening of endophytic fungi for promote the accumulation of active components of saponins from Pairs polyphylla var yunnanensis. J Yunnan Agric Univ 34:132–137
Liao P, Hemmerlin A, Bach TJ, Chye ML (2016) The potential of the mevalonate pathway for enhanced isoprenoid production. Biotechnol Adv 34:697–713. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2016.03.005
Liu L, Dong YS, Qi SS, Wang H, Xiu ZL (2010) Biotransformation of steriodal saponins in Dioscorea zingiberensis C. H. Wright to diosgenin by Trichoderma harzianum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:933–940. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2098-1
Liu TQ et al (2013a) Preparation of progenin III from total steroidal saponins of Dioscorea nipponica Makino using a crude enzyme from Aspergillus oryzae strain. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 40:427–436. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-013-1246-x
Liu TQ et al (2013b) Protodioscin-glycosidase-1 hydrolyzing 26-O-β-D-glucoside and 3-O-(1 → 4)-α-L-rhamnoside of steroidal saponins from Aspergillus oryzae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:10035–10043. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-013-4791-3
Liu JY et al (2015) Selective glycosylation of steroidal saponins by Arthrobacter nitroguajacolicus. Carbohyd Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2014.07.006
Louveau T et al (2018) Analysis of two new arabinosyltransferases belonging to the carbohydrate-active enzyme (CAZY) glycosyl transferase family1 provides insights into disease resistance and sugar donor specificity. Plant Cell 30:3038–3057. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00641
Lu Q et al (2018) Saponins from Paris forrestii (Takht) H. Li display potent activity against acute myeloid leukemia by suppressing the RNF6/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00673
Luo M, Tan KL, Xiao ZY, Hu MY, Liao P, Chen KJ (2008) Cloning and expression of two sterol C-24 methyltransferase genes from upland cotton (Gossypium hirsuturm L.). J Genet Genomics 35:357–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1673-8527(08)60052-1
Madoui MA, Bertrand-Michel J, Gaulin E, Dumas B (2009) Sterol metabolism in the oomycete Aphanomyces euteiches, a legume root pathogen. New Phytol 183:291–300. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.02895.x
Mehrafarin A, Qaderi A, Rezazadeh S, Badi HN, Zand E (2010) Bioengineering of important secondary metabolites and metabolic pathways in fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.). J Med Plants 9:1–18
Messner B, Thulke O, Schäffner AR (2003) Aradiposis glucosyltransferases with activities toward both endogenous and xenobiotic substrates. Planta 217:138–146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-002-0969-0
Mimaki Y, Kuroda M, Kameyama A, Sashida Y, Hirano T, Oka K (1997) Cholestane glycosides with potent cytostatic activities on various tumor cells from Ornithogalum saundersiae bulbs. BioorgMedChemLett 7:633–636. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0960-894X(97)00071-1
Moreau RA, Nyström L, Whitaker BD, Winkler-Moser JK, Baer DJ, Gebauer SG, Hicks KB (2018) Phytosterols and their derivatives: structural diversity, distribution, metabolism, analysis, and health-promoting uses. Prog Lipid Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2018.04.001
Moses T, Papadopoulou KK, Osbourn A (2014) Metabolic and functional diversity of saponins, biosynthetic intermediates and semi-synthetic derivatives. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 49:1–24. https://doi.org/10.3109/10409238.2014.953628
Nakagawa A et al (2016) Total biosynthesis of opiates by stepwise fermentation using engineered Escherichia Coli. Nat Commun 7:10390. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10390
Nakayasu M, Kawasaki T, Lee HJ, Sugimoto Y, Mizutani M (2015) Identification of furostanol glycoside 26-O-β-glucosidase involved in steroidal saponin biosynthesis from Dioscorea esculenta. Plant Biotechnol 32:299–308. https://doi.org/10.5511/plantbiotechnology.15.1023b
Nakayasu M et al (2017) A Dioxygenase catalyzes steroid 16α-hydroxylation in steroidal glycoalkaloid biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 175:120–133. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.17.00501
Nazir R, Kumar V, Gupta S, Dwivedi P, Pandey DK, Dey A (2021) Biotechnological strategies for the sustainable production of diosgenin from Dioscorea spp. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105:569–585. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-11055-3
Neelakandan AK et al (2009) Cloning, functional expression and phylogenetic analysis of plant sterol 24C-methyltransferases involved in sitosterol biosynthesis. Phytochemistry 70:1982–1998. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2009.09.003
Nes WD (2005) Enzyme redesign and interactions of substrate analogues with sterol methyltransferase to understand phytosterol diversity, reaction mechanism and the nature of the active site. Biochem Soc Trans 33:1189–1196. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20051189
Newman JD, Chappell J (1999) Isoprenoid biosynthesis in plants: carbon partitioning within the cytoplasmic pathway. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 34:95–106. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409239991209228
Nikam TD, Ebrahimi MA, Patil VA (2009) Embryogenic callus culture of Tribulus terrestris L. a potential source of harmaline, harmine and diosgenin. Plant Biotechnol Rep 3:243–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-009-0096-5
Ohnishi T, Yokota T, Mizutani M (2009) Insights into the function and evolution of P450s in plant steroid metabolism. Phytochemistry 70:1918–1929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2009.09.015
Ohyama K, Suzuki M, Kikuchi J, Saito K, Muranaka T (2009) Dual biosynthetic pathways to phytosterol via cycloartenol and lanosterol in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:725–730. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0807675106
Osbourn AE (1996) Preformed antimicrobial compounds and plant defense against fungal attack. Plant Cell 8:1821–1831. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.8.10.1821
Pal S, Rastogi S, Nagegowda DA, Gupta PM, Shasany AK, Chanotiya CS (2018) RNAi of sterol methyl transferase1 reveals its direct role in diverting intermediates towards withanolide/phytosterol biosynthesis in Withania somnifera. Plant Cell Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcy237
Pang X, Wen D, Zhao Y, Xiong CQ, Wang XQ, Yu LY, Ma BP (2014) Steroidal saponins obtained by biotransformation of total furostanol glycosides from Dioscora zingiberensis with Absidia coerulea. Carbohyd Res 402:236–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carres.2014.11.011
Pearson A, Budin M, Brocks JJ (2003) Phylogenetic and biochemical evidence for sterol synthesis in the bacterium Gemmata obscuriglobus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:15352–15357. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2536559100
Pereira M et al (2010) Cloning, mechanistic and functional analysis of a fungal sterol C24-methyltransferase implicated in brassicasterol biosynthesis. Biochem Biophys Acta 1801:1163–1174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2010.06.007
Podolak I, Galanty A, Sobolewska D (2010) Saponins as cytotoxic agents: a review. Phytochem Rev 9:425–474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11101-010-9183-z
Pompon D, Dumas B, Spagnoli R (2012) Cholesterol-producing yeast strains and uses thereof. US Patent 8211676, 7.3
Prawat H, Mahidol C, Kaweetripob W, Intachote P, Pisutjaroenpong S, Ruchirawat S (2016) Cytotoxic steroidal glycosides from the whole plant of Calamus acanthophyllus. Planta Med 82:1117–1121. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0042-106972
Puente-Garza CA, Espinosa-Leal CA, García-Lara S (2021) Effects of saline elicitors on saponin production in Agave Salmiana plants grown in vitro. Plant Physiol Biochem 162:476–482. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2021.03.017
Rahim MA, Jung HJ, Afrin KS, Lee J-H, Nou I-S (2018) Comparative transcriptome analysis provides insights into dwarfism in cherry tomato (Solanum lycopersicum var. Cerasiforme). PLoS One 13:e0208770. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0208770
Rizvi MZ, Kukreja AK, Bisht NS (2010) In vitro propagation of an endangered medicinal herb Chlorophytum borivilianum Sant. et Fernand. through somatic embryogenesis. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 16:249–257. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-010-0026-6
Sah B, Subban K, Chelliah J (2017) Cloning and sequence analysis of 10-deacetylbaccatin III-10-O-acetyl transferase gene and WRKY1 transcription factor from taxol producing endophytic fungus Lasiodiplodia theobromea. FEMS Microbiol Lett. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fnx253
Saunders R, Cheetham PSJ, Hardman R (1986) Microbial transformation of crude fenugreek steroids. Enzyme Microb Technol 8:549–555. https://doi.org/10.1016/0141-0229(86)90040-2
Sawai S, Saito K (2011) Triterpenoid biosynthesis and engineering in plants. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2011.00025
Shen L, Xu J, Luo L, Hu H, Meng XX, Li XW, Chen SL (2018) Predicting the potential global distribution of diosgenin-contained Dioscorea species. Chin Med 13:58. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13020-018-0215-8
Sidana J, Singh B, Sharma OP (2016) Saponins of agave: chemistry and bioactivity. Phytochemistry 130:22–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2016.06.010
Singh P, Singh G, Bhandawat A, Singh G, Parmar R, Seth R, Sharma RK (2017) Spatial transcriptome analysis provides insights of key gene(s) involved in steroidal saponin biosynthesis in medicinally important herb Trillium govanianum. Sci Rep 7:45295. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep45295
Singh G, Dhar YV, Asif MH, Misra P (2018) Exploring the functional significance of sterol glycosyltransferase enzymes. Prog Lipid Res 69:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2017.11.001
Sonawane PD et al (2016) Plant cholesterol biosynthetic pathway overlaps with phytosterol metabolism. Nat Plants 3:16205. https://doi.org/10.1038/nplants.2016.205
Song CK, Gu L, Liu JY, Zhao S, Hong XT, Schulenburg T, Schwab W (2015) Functional characterization and substrate promiscuity of UGT71 glycosyltransferases from strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa). Plant Cell Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcv151
Song XY, Han FY, Chen JJ, Wang W, Zhang Y, Yao GD, Song SJ (2019) Timosaponin AIII, a steroidal saponin, exhibits anti-tumor effect on taxol-resistant cells in vitro and in vivo. Steroids 146:57–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.steroids.2019.03.009
Souza CM et al (2011) A stable yeast strain efficiently producing cholesterol instead of ergosterol is functional for tryptophan uptake, but not weak organic acid, resistance. Metab Eng 13:555–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2011.06.006
Sparg SG, Light ME, van Staden J (2004) Biological activities and distribution of plant saponins. J Ethnopharmacol 94:219–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2004.05.016
Sun W et al (2017) Weighted gene co-expression network analysis of the dioscin rich medicinal plant Dioscorea nipponica. Front Plant Sci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.00789
Suthangkornkul R et al (2016) A Solanum torvum GH3 β-glucosidase expressed in Pichia pastoris catalyzes the hydrolysis of furostanol glycoside. Phytochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2016.03.015
Suza WP, Chappell J (2015) Spatial and temporal regulation of sterol biosynthesis in Nicotiana benthamiana. Physiol Plant 157:120–134. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12413
Suzuki M et al (2006) Lanosterol synthase in dicotyledonous plants. Plant Cell Physiol 47:565–571. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcj031
Tang GH, Lu N, Li W, Wu M, Chen YY, Zhang HY, He SY (2020) Mannosylxylarinolide, a new 3,4-seco-ergostane-type steroidal saponin featuring a β-d-mannose from the endophytic fungus Xylaria sp. J Asian Nat Prod Res 22:397–403. https://doi.org/10.1080/10286020.2018.1563075
Tenon M, Feuillère N, Roller M, Birtić S (2017) Rapid, cost-effective and accurate quantification of Yucca schidigera Roezl. steroidal saponins using HPLC-ELSD method. Food Chem 221:1245–1252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.11.033
Tian LW, Zhang Z, Long HL, Zhang YJ (2017) Steroidal saponins from the genus smilax and their biological activities. Nat Prod Bioprospect 7:283–298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13659-017-0139-5
Torres S et al (2017) Steroidal composition and cytotoxic activity from fruiting body of Cortinarius xiphidipus. Nat Prod Res 31:473–476. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2016.1185717
Tsukagoshi Y, Suzuki H, Seki H, Muranaka T, Ohyama K, Fujimoto Y (2016) Ajuga Δ24-sterol reductase catalyzes the direct reductive conversion of 24-methylenecholesterol to campesterol. J Biol Chem 291:8189–8198. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M115.703470
Upadhyay S, Phukan UJ, Mishra DS, Shukla RK (2014) De novo leaf and root transcriptome analysis identified novel genes involved in Steroidal sapogenin biosynthesis in Asparagus racemosus. BMC Genomics. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-746
Venkatramesh M, Guo DA, Harman JG, Nes WD (1996a) Sterol specificity of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae ERG6 gene product expressed in Escherichia coli. Lipids 31:373–377. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02522922
Venkatramesh M, Guo DA, Jia ZH, Nes WD (1996b) Mechanism and structural requirements for transformation of substrates by the (S)-adenosyl-L-methionine:Δ24(25)sterol methyl transferase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Acta 1299:313–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2760(95)00218-9
Venugopalan A, Potunuru UR, Dixit M, Srivastava S (2016) Effect of fermentation parameters, elicitors and precursors on camptothecin production from the endophyte Fusarium solani. Biores Technol 206:104–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.01.079
Visbal G, Alvarez A, Moreno B, San-Blas G (2003) S-Adenosyl-L-methionine inhibitors delta(24)-sterol methyltransferase and delta(24(28))-sterol methylreductase as possible agents against Paracoccidioides brasiliensis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47:2966–2970. https://doi.org/10.1128/aac.47.9.2966-2970.2003
Wang FQ, Li B, Wang Y, Zhang CG, Wei DZ (2007) Biotransformation of diosgenin to nuatigenin-type steroid by a newly isolated strain, Streptomyces virginiae IBL14. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 77:771–777. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1216-1
Wang LW, Xu BG, Wang JY, Su ZZ, Lin FC, Zhang CL, Kubicek CP (2012) Bioactive metabolites from Phoma species, an endophytic fungus from the Chinese medicinal plant Arisaema erubescens. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93:1231–1239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3472-3
Wang YC, Li X, Sun H, Yi KX, Zheng JL, Zhang J, Hao ZB (2014) Biotransformation of steroidal saponins in sisal ( Agave sisalana Perrine) to tigogenin by a newly isolated strain from a karst area of Guilin, China. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 28:1024–1033. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2014.978199
Wang LS, Ma T, Zheng YP, Lv SQ, Li Y, Liu SX (2015) Diosgenin inhibits IL-1beta-induced expression of inflammatory mediators in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Int J Clinic Exp Pathol 8:4830–4836
Wang Q, Huiju Z, Min Y, Hua Z, Zhou N, Li Y (2018) Effects of 28 species of AM fungi on diosgenin contents in Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis. J Dali Univ 2:22–25. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.2096-2266.2018.10.005
Weete JD, Abril M, Blackwell M (2010) Phylogenetic distribution of fungal sterols. PLoS One 5:e10899. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0010899
Wei M, Bai Y, Ao MZ, Jin WW, Yu PP, Zhu M, Yu LJ (2013) Novel method utilizing microbial treatment for cleaner production of diosgenin from Dioscorea zingiberensis CH Wright (DZW). Bioresour Technol 146C:549–555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.07.090
Wilson AE, Tian L (2019) Phylogenomic analysis of UDP-dependent glycosyltransferases provides insights into the evolutionary landscape of glycosylation in plant metabolism. Plant J. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14514
Wriessnegger T, Pichler H (2013) Yeast metabolic engineering–targeting sterol metabolism and terpenoid formation. Prog Lipid Res 52:277–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2013.03.001
Wu GW, Gao JM, Shi XW, Zhang Q, Wei SP, Ding K (2011) Microbial transformations of diosgenin by the white-rot basidiomycete Coriolus versicolor. J Nat Prod 74:2095–2101. https://doi.org/10.1021/np2003484
Xiao X, Liu XK, Fu SB, Sun DA (2011) Microbial transformation of diosgenin by filamentous fungus Cunninghamella echinulata. J Asian Nat Prod Res 13:270–275. https://doi.org/10.1080/10286020.2010.551117
Xie YX, Sen B, Wang GY (2017) Mining terpenoids production and biosynthetic pathway in thraustochytrids. Bioresour Technol 244:1269–1280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.05.002
Xu M et al (2015) Microbial transformation of diosgenin by Cunninghamella blakesleana AS 3.970 and potential inhibitory effects on P-glycoprotein of its metabolites. RSC Adv 5:78081–78089. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ra12253h
Yang XD, Yang YY, Ouyang DS, Yang GP (2015) A review of biotransformation and pharmacology of ginsenoside compound K. Fitoterapia. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2014.11.019
Yang JC et al (2017a) Anti-trachea inflammatory effects of diosgenin from Dioscorea nipponica through interactions with glucocorticoid receptor α. Journal of International Medical Research 45:101–103. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060516676724
Yang R et al (2017b) Dioscin relieves endotoxemia induced acute neuro-inflammation and protect neurogenesis via improving 5-HT metabolism. Scientific Reports 7:40035. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep40035
Yang BY, Yin X, Liu Y, Zhao DY, Kuang HX (2018a) New steroidal saponins from the roots of Solanum melongena L. Fitoterapia 128:12–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2018.04.021
Yang XC, Li YB, Liao QH, Yang SC, Tao L (2018b) Isolation and screening of endophytic fungi that might produce saponins in Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis. Mol Plant Breed 16:665–669. https://doi.org/10.13271/j.mpb.016.000665
Yang ZY, Yang LF, Liu CK, Qin XJ, Liu HY, Chen JH, Ji YH (2019) Transcriptome analyses of Paris polyphylla var. chinensis, Ypsilandra thibetica, and Polygonatum kingianum characterize their steroidal saponin biosynthesis pathway. Fitoterapia 135:52–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2019.04.008
Yin Y, Gao LH, Zhang XN, Gao W (2018) A cytochrome P450 monooxygenase responsible for the C-22 hydroxylation step in the Paris polyphylla steroidal saponin biosynthesis pathway. Phytochemistry 156:116–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2018.09.005
Yoshida Y, Aoyama Y, Noshiro M, Gotoh O (2000) Sterol 14-demethylase P450 (CYP51) provides a breakthrough for the discussion on the evolution of cytochrome P450 gene superfamily. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 273:799–804. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.2000.3030
Youn JH et al (2015) ARF7 increases the endogenous contents of castasterone through suppression of BAS1 expression in Arabidopsis thaliana. Phytochemistry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2015.11.006
Youn JH et al (2018a) DWF1 functions as a C-24 reductase to convert 24-methylene brassinosteroids to 24-methyl brassinosteroids in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ery038
Youn JH et al (2018b) Function and molecular regulation of DWARF1 as a C-24 reductase in brassinosteroid biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 69:1873–1886. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ery038
Yu YN et al (2014) Comparative effectiveness of Di’ao Xin Xue Kang capsule and compound danshen tablet in patients with symptomatic chronic stable angina. Sci Rep 4:7058. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep07058
Yu SS et al (2017) Microbial transformation of ginsenoside Rb1, Re and Rg1 and its contribution to the improved anti-inflammatory activity of ginseng. Sci Rep 7:138. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-00262-0
Yuan WQ, Zhang RR, Wang J, Ma Y, Li WX, Jiang RW, Cai SH (2016) Asclepiasterol, a novel C21 steroidal glycoside derived from Asclepias curassavica, reverses tumor multidrug resistance by down-regulating P-glycoprotein expression. Oncotarget 7:31466–31483. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.8965
Yuan YL et al (2016b) Timosaponin B-II Ameliorates Palmitate-Induced Insulin Resistance and Inflammation via IRS-1/PI3K/Akt and IKK/NF-κB Pathways. The American Journal of Chinese Medicine 44:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0192415X16500415
Zhang XJ, Tang LL, Wang YD (2007) Isolating and screening of steroidal saponins-producing entophytic fungi, actinomycete from Paris Polyphylla var. Chinensis Franch. Prog Modern Biomed 7:358–360. https://doi.org/10.13241/j.cnki.pmb.2007.03.013
Zhang J et al (2016a) Galactosylation of steroidal saponins by β-galactosidase from Lactobacillus bulgaricus L3. Glycoconj J 33:53–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-015-9632-4
Zhang X et al (2016b) Sterol methyl oxidases affect embryo development via auxin-associated mechanisms. Plant Physiol 171:468–482. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.15.01814
Zhang Y et al (2016c) Anti-inflammatory steroids from the rhizomes of Dioscorea septemloba Thunb. Steroids 112:95–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.steroids.2016.05.007
Zhang TT, Gong T, Hu ZF, Gu AD, Yang JL, Zhu P (2018) Enzymatic synthesis of unnatural ginsenosides using a promiscuous UDP-glucosyltransferase from Bacillus subtilis. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23112797
Zhao M, He SR, Chen XJ, Huang CP, Wang YD (2005) Screening and identification of steroidal saponins-producing endophytes from Paris polyphylla var. Chinensis Franch. Acta Microbiol Sin 045:776–779
Zhao Y, Sun LM, Wang XN, Shen T, Ji M, Li X, Lou HX (2009) Microbial transformation of diosgenin by Syncephalastrum racemosum (Cohn) Schroeter. Chin Chem Lett 21:76–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2009.08.015
Zhao Y, Jiang TC, Han BQ, Lu L, Feng B (2015) Preparation of some metabolites of timosaponin BII by biotransformation in vitro. Process Biochem 50:2182–2187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2015.09.022
Zhao YZ et al (2018) Advances in the antitumor activities and mechanisms of action of steroidal saponins. Chin J Nat Med 16:732–748. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1875-5364(18)30113-4
Zhou LG, Cao XD, Yang CD, Wu XH, Zhang LQ (2004) Endophytic fungi of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis and steroid analysis in the fungi. Nat Product Res Dev 16:198–200. https://doi.org/10.16333/j.1001-6880.2004.03.003
Zhou WB et al (2010) Hydrolysis of timosaponin BII by the crude enzyme from Aspergillus niger AS 3.0739. J Asian Nat Prod Res 12:955–961. https://doi.org/10.1080/10286020.2010.510470
Zhu Q, Wu FT, Ding F, Ye D, Chen YQ, Li Y, Zhifan Y (2009) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Dioscorea zingiberensis Wright, an important pharmaceutical crop. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 96:317–324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-008-9489-3
Zhu SL, Tang SY, Su F (2017) Dioscin inhibits ischemic stroke-induced inflammation through inhibition of the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway in a rat model. Molecular Medicine Reports 17:660–666. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.7900
Zhu JH, Li HL, Guo D, Wang Y, Dai HF, Mei WL, Peng SQ (2018a) Identification, characterization and expression analysis of genes involved in steroidal saponin biosynthesis in Dracaena cambodiana. J Plant Res 131:555–562. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-017-1004-7
Zhu X, Wang K, Zhang K, Pan Y, Zhou FF, Zhu L (2018b) Polyphyllin I induces cell cycle arrest and cell apoptosis in human retinoblastoma Y-79 cells through targeting p53. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 18:875–881. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871520618666180108095148
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 81872967).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no confict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Gerhard Leubner.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Wu, J., Yu, D. et al. Advances in steroidal saponins biosynthesis. Planta 254, 91 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-021-03732-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-021-03732-y