Abstract
Main conclusion
TDIF and TDIF-like peptides in excess simultaneously facilitate primary root elongation and lateral root formation through regulating auxin distribution and transport.
Abstract
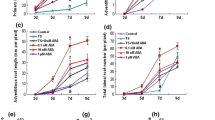
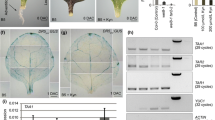
Tracheary element differentiation inhibitory factor (TDIF) plays key roles in mediating cell–cell communication and stem cell maintenance during vascular development. Recently, TDIF has also been linked to lateral root (LR) organogenesis through Brassinosteroid Insensitive 2 (BIN2) action. In this work, by comparing the in vitro and in vivo activities of AtCLE41-encoded TDIF and one poplar-derived TDIF-like peptide in Arabidopsis thaliana, we demonstrated that both TDIFs promoted primary root (PR) growth and stimulated LR formation. Without affecting auxin biosynthesis and catabolism, TDIFs suppressed the auxin maxima at PR apex but intensified the auxin accumulation at LR initiation sites along the longitudinal axis of PR. TDIF did not alter root sensitivity to exogenous auxin and mutants with varied endogenous auxin levels responded to TDIF peptides in a wild-type manner but to a lesser extent. Intriguingly, TDIF specifically upregulated the transcript abundance of PINs and multiple pin mutants displayed insensitivity to TDIF, demonstrating that PIN-mediated polar auxin transport (PAT) is indispensably required for the TDIF-induced root phenotypes. Taken together, our results revealed that TDIF might target PAT via mobilizing auxin efflux carriers to dynamically regulate the auxin signaling output and hence facilitate PR growth and LR formation.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BIN2:
-
Brassinosteroid Insensitive 2
- CLE:
-
CLAVATA3/embryo surrounding region
- LR:
-
Lateral root
- NPA:
-
N-1-Naphthylphthalamic acid
- PAT:
-
Polar auxin transport
- PR:
-
Primary root
- PXY/TDR:
-
Phloem intercalated with xylem/TDIF receptor
- QC:
-
Quiescent center
- TDIF:
-
Tracheary element differentiation inhibitory factor
References
Adamowski M, Friml J (2015) PIN-dependent auxin transport: action, regulation, and evolution. Plant Cell 27(1):20–32. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.114.134874
Araniti F, Bruno L, Sunseri F, Pacenza M, Forgione I, Bitonti MB, Abenavoli MR (2017) The allelochemical farnesene affects Arabidopsis thaliana root meristem altering auxin distribution. Plant Physiol Biochem 121:14–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.10.005
Benkova E, Michniewicz M, Sauer M, Teichmann T, Seifertova D, Jurgens G, Friml J (2003) Local, efflux-dependent auxin gradients as a common module for plant organ formation. Cell 115(5):591–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00924-3
Blilou I, Xu J, Wildwater M, Willemsen V, Paponov I, Friml J, Heidstra R, Aida M, Palme K, Scheres B (2005) The PIN auxin efflux facilitator network controls growth and patterning in Arabidopsis roots. Nature 433(7021):39–44. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03184
Casamitjana-Martinez E, Hofhuis HF, Xu J, Liu CM, Heidstra R, Scheres B (2003) Root-specific CLE19 overexpression and the sol1/2 suppressors implicate a CLV-like pathway in the control of Arabidopsis root meristem maintenance. Curr Biol 13(16):1435–1441. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0960-9822(03)00533-5
Casimiro I, Marchant A, Bhalerao RP, Beeckman T, Dhooge S, Swarup R, Graham N, Inze D, Sandberg G, Casero PJ, Bennett M (2001) Auxin transport promotes Arabidopsis lateral root initiation. Plant Cell 13(4):843–852. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.13.4.843
Cazzonelli CI, Vanstraelen M, Simon S, Yin K, Carron-Arthur A, Nisar N, Tarle G, Cuttriss AJ, Searle IR, Benkova E, Mathesius U, Masle J, Friml J, Pogson BJ (2013) Role of the Arabidopsis PIN6 auxin transporter in auxin homeostasis and auxin-mediated development. PLoS ONE 8(7):e70069. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0070069
Cho H, Ryu H, Rho S, Hill K, Smith S, Audenaert D, Park J, Han S, Beeckman T, Bennett MJ, Hwang D, De Smet I, Hwang I (2014) A secreted peptide acts on BIN2-mediated phosphorylation of ARFs to potentiate auxin response during lateral root development. Nat Cell Biol 16(1):66–76. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2893
Clark SE, Williams RW, Meyerowitz EM (1997) The CLAVATA1 gene encodes a putative receptor kinase that controls shoot and floral meristem size in Arabidopsis. Cell 89(4):575–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80239-1
Delarue M, Prinsen E, Onckelen HV, Caboche M, Bellini C (1998) sur2 mutations of Arabidopsis thaliana define a new locus involved in the control of auxin homeostasis. Plant J 14(5):603–611. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.1998.00163.x
Dhonukshe P, Grigoriev I, Fischer R, Tominaga M, Robinson DG, Hasek J, Paciorek T, Petrasek J, Seifertova D, Tejos R, Meisel LA, Zazimalova E, Gadella TW Jr, Stierhof YD, Ueda T, Oiwa K, Akhmanova A, Brock R, Spang A, Friml J (2008) Auxin transport inhibitors impair vesicle motility and actin cytoskeleton dynamics in diverse eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(11):4489–4494. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0711414105
Dubrovsky JG, Doerner PW, Colon-Carmona A, Rost TL (2000) Pericycle cell proliferation and lateral root initiation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 124(4):1648–1657. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.124.4.1648
Etchells JP, Turner SR (2010) The PXY-CLE41 receptor ligand pair defines a multifunctional pathway that controls the rate and orientation of vascular cell division. Development 137(5):767–774. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.044941
Fisher K, Turner S (2007) PXY, a receptor-like kinase essential for maintaining polarity during plant vascular-tissue development. Curr Biol 17(12):1061–1066. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2007.05.049
Fletcher JC, Brand U, Running MP, Simon R, Meyerowitz EM (1999) Signaling of cell fate decisions by CLAVATA3 in Arabidopsis shoot meristems. Science 283(5409):1911–1914. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.283.5409.1911
Friml J, Benkova E, Blilou I, Wisniewska J, Hamann T, Ljung K, Woody S, Sandberg G, Scheres B, Jurgens G, Palme K (2002) AtPIN4 mediates sink-driven auxin gradients and root patterning in Arabidopsis. Cell 108(5):661–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00656-6
Friml J, Vieten A, Sauer M, Weijers D, Schwarz H, Hamann T, Offringa R, Jurgens G (2003) Efflux-dependent auxin gradients establish the apical-basal axis of Arabidopsis. Nature 426(6963):147–153. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02085
Geldner N, Friml J, Stierhof YD, Jurgens G, Palme K (2001) Auxin transport inhibitors block PIN1 cycling and vesicle trafficking. Nature 413(6854):425–428. https://doi.org/10.1038/35096571
Goda H, Sasaki E, Akiyama K, Maruyama-Nakashita A, Nakabayashi K, Li W, Ogawa M, Yamauchi Y, Preston J, Aoki K, Kiba T, Takatsuto S, Fujioka S, Asami T, Nakano T, Kato H, Mizuno T, Sakakibara H, Yamaguchi S, Nambara E, Kamiya Y, Takahashi H, Hirai MY, Sakurai T, Shinozaki K, Saito K, Yoshida S, Shimada Y (2008) The atgenexpress hormone and chemical treatment data set: experimental design, data evaluation, model data analysis and data access. Plant J 55(3):526–542. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0960-7412.2008.03510.x
Grieneisen VA, Xu J, Maree AF, Hogeweg P, Scheres B (2007) Auxin transport is sufficient to generate a maximum and gradient guiding root growth. Nature 449(7165):1008–1013. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature06215
Grunewald W, Friml J (2010) The march of the PINs: developmental plasticity by dynamic polar targeting in plant cells. EMBO J 29(16):2700–2714. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2010.181
Hirakawa Y, Shinohara H, Kondo Y, Inoue A, Nakanomyo I, Ogawa M, Sawa S, Ohashi-Ito K, Matsubayashi Y, Fukuda H (2008) Non-cell-autonomous control of vascular stem cell fate by a CLE peptide/receptor system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(39):15208–15213. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0808444105
Hu YF, Zhou G, Na XF, Yang L, Nan WB, Liu X, Zhang YQ, Li JL, Bi YR (2013) Cadmium interferes with maintenance of auxin homeostasis in Arabidopsis seedlings. J Plant Physiol 170(11):965–975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2013.02.008
Ito Y, Nakanomyo I, Motose H, Iwamoto K, Sawa S, Dohmae N, Fukuda H (2006) Dodeca-CLE peptides as suppressors of plant stem cell differentiation. Science 313(5788):842–845. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1128436
Kondo T, Sawa S, Kinoshita A, Mizuno S, Kakimoto T, Fukuda H, Sakagami Y (2006) A plant peptide encoded by CLV3 identified by in situ MALDI-TOF MS analysis. Science 313(5788):845–848. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1128439
Laskowski M, Grieneisen VA, Hofhuis H, Hove CA, Hogeweg P, Maree AF, Scheres B (2008) Root system architecture from coupling cell shape to auxin transport. PLoS Biol 6(12):e307. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0060307
Li X, Yang H, Wang C, Yang S, Wang J (2018) Distinct transgenic effects of poplar TDIF genes on vascular development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep 37(5):799–808. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-018-2268-7
Liu Y, Yang S, Song Y, Men S, Wang J (2016) Gain-of-function analysis of poplar CLE genes in Arabidopsis by exogenous application and over-expression assays. J Exp Bot 67(8):2309–2324. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erw045
Marhavy P, Vanstraelen M, De Rybel B, Ding ZJ, Bennett MJ, Beeckman T, Benkova E (2013) Auxin reflux between the endodermis and pericycle promotes lateral root initiation. EMBO J 32(1):149–158. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2012.303
Mashiguchi K, Tanaka K, Sakai T, Sugawara S, Kawaide H, Natsume M, Hanada A, Yaeno T, Shirasu K, Yao H, McSteen P, Zhao Y, Hayashi K, Kamiya Y, Kasahara H (2011) The main auxin biosynthesis pathway in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(45):18512–18517. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1108434108
Mayer KF, Schoof H, Haecker A, Lenhard M, Jurgens G, Laux T (1998) Role of WUSCHEL in regulating stem cell fate in the Arabidopsis shoot meristem. Cell 95(6):805–815. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81703-1
Michniewicz M, Ho CH, Enders TA, Floro E, Damodaran S, Gunther LK, Powers SK, Frick EM, Topp CN, Frommer WB, Strader LC (2019) TRANSPORTER OF IBA1 links auxin and cytokinin to influence root architecture. Dev Cell 50(5):599–609 e594. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2019.06.010
Muller R, Bleckmann A, Simon R (2008) The receptor kinase CORYNE of Arabidopsis transmits the stem cell-limiting signal CLAVATA3 independently of CLAVATA1. Plant Cell 20(4):934–946. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.107.057547
Nisar N, Cuttriss AJ, Pogson BJ, Cazzonelli CI (2014) The promoter of the Arabidopsis PIN6 auxin transporter enabled strong expression in the vasculature of roots, leaves, floral stems and reproductive organs. Plant Signal Behav 9(1):e27898. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.27898
Ogawa M, Shinohara H, Sakagami Y, Matsubayashi Y (2008) Arabidopsis CLV3 peptide directly binds CLV1 ectodomain. Science 319(5861):294. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1150083
Petrasek J, Friml J (2009) Auxin transport routes in plant development. Development 136(16):2675–2688. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.030353
Sawchuk MG, Edgar A, Scarpella E (2013) Patterning of leaf vein networks by convergent auxin transport pathways. PLoS Genet 9(2):e1003294. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003294
Schaller GE, Bishopp A, Kieber JJ (2015) The yin-yang of hormones: cytokinin and auxin interactions in plant development. Plant Cell 27(1):44–63. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.114.133595
Schoof H, Lenhard M, Haecker A, Mayer KF, Jurgens G, Laux T (2000) The stem cell population of Arabidopsis shoot meristems in maintained by a regulatory loop between the CLAVATA and WUSCHEL genes. Cell 100(6):635–644. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80700-x
Shin H, Shin HS, Guo Z, Blancaflor EB, Masson PH, Chen R (2005) Complex regulation of Arabidopsis AGR1/PIN2-mediated root gravitropic response and basipetal auxin transport by cantharidin-sensitive protein phosphatases. Plant J 42(2):188–200. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02369.x
Simon S, Skupa P, Viaene T, Zwiewka M, Tejos R, Klima P, Carna M, Rolcik J, De Rycke R, Moreno I, Dobrev PI, Orellana A, Zazimalova E, Friml J (2016) PIN6 auxin transporter at endoplasmic reticulum and plasma membrane mediates auxin homeostasis and organogenesis in Arabidopsis. New Phytol 211(1):65–74. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14019
Stahl Y, Wink RH, Ingram GC, Simon R (2009) A signaling module controlling the stem cell niche in Arabidopsis root meristems. Curr Biol 19(11):909–914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2009.03.060
Stepanova AN, Robertson-Hoyt J, Yun J, Benavente LM, Xie DY, Dolezal K, Schlereth A, Jurgens G, Alonso JM (2008) TAA1-mediated auxin biosynthesis is essential for hormone crosstalk and plant development. Cell 133(1):177–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.01.047
Sun P, Tian QY, Chen J, Zhang WH (2010) Aluminium-induced inhibition of root elongation in Arabidopsis is mediated by ethylene and auxin. J Exp Bot 61(2):347–356. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erp306
Ulmasov T, Murfett J, Hagen G, Guilfoyle TJ (1997) Aux/IAA proteins repress expression of reporter genes containing natural and highly active synthetic auxin response elements. Plant Cell 9(11):1963–1971. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.9.11.1963
Vanneste S, Friml J (2009) Auxin: a trigger for change in plant development. Cell 136(6):1005–1016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.03.001
Whitford R, Fernandez A, De Groodt R, Ortega E, Hilson P (2008) Plant CLE peptides from two distinct functional classes synergistically induce division of vascular cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(47):18625–18630. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0809395105
Won C, Shen X, Mashiguchi K, Zheng Z, Dai X, Cheng Y, Kasahara H, Kamiya Y, Chory J, Zhao Y (2011) Conversion of tryptophan to indole-3-acetic acid by tryptophan aminotransferases of Arabidopsis and YUCCAs in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(45):18518–18523. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1108436108
Xu W, Jia L, Baluska F, Ding G, Shi W, Ye N, Zhang J (2012) PIN2 is required for the adaptation of Arabidopsis roots to alkaline stress by modulating proton secretion. J Exp Bot 63(17):6105–6114. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ers259
Xuan W, Audenaert D, Parizot B, Moller BK, Njo MF, De Rybel B, De Rop G, Van Isterdael G, Mahonen AP, Vanneste S, Beeckman T (2015) Root cap-derived auxin pre-patterns the longitudinal axis of the Arabidopsis root. Curr Biol 25(10):1381–1388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2015.03.046
Xuan W, Band LR, Kumpf RP, Van Damme D, Parizot B, De Rop G, Opdenacker D, Moller BK, Skorzinski N, Njo MF, De Rybel B, Audenaert D, Nowack MK, Vanneste S, Beeckman T (2016) Cyclic programmed cell death stimulates hormone signaling and root development in Arabidopsis. Science 351(6271):384–387. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aad2776
Zhao Y (2012) Auxin biosynthesis: a simple two-step pathway converts tryptophan to indole-3-acetic acid in plants. Mol Plant 5(2):334–338. https://doi.org/10.1093/mp/ssr104
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Key Research & Development Program (2016YFD0600103) and National Natural Science Foundation (31870572). We thank Prof. Deping Hua (Tianjin University, China) for PIN2:GUS seeds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Communicated by Anastasios Melis.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, S., Bai, J. & Wang, J. TDIF peptides regulate root growth by affecting auxin homeostasis and PINs expression in Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta 251, 109 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-020-03406-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-020-03406-1