Abstract
Main conclusion
Moringa oleifera TPSs were genome-wide identified for the first time, and a phylogenetic analysis was performed to investigate evolutionary divergence. The qRT-PCR data show that MoTPS genes response to different stress treatments.
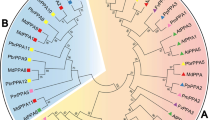
The trehalose-6-phosphate synthase (TPS) family is involved in a wide range of stress-resistance processes in plants. Its direct product, trehalose-6-phosphate, acts as a specific signal of sucrose status and a regulator to modulate carbon metabolism within the plant. In this study, eight TPS genes were identified and cloned based on the M. oleifera genome; only MoTPS1 exhibited TPS activity among Group I proteins. The characteristics of the MoTPS gene family were determined by analyzing phylogenetic relationships, gene structures, conserved motifs, selective forces, and expression patterns. The Group II MoTPS genes were under relaxed purifying selection or positive selection. The glycosyltransferase family 20 domains generally had lower Ka/Ks ratios and nonsynonymous (Ka) changes compared with those of trehalose-phosphatase domains, which is consistent with stronger purifying selection due to functional constraints in performing TPS enzyme activity. Phylogenetic analyses of TPS proteins from M. oleifera and 17 other plant species indicated that TPS were present before the monocot–dicot split, whereas Group II TPSs were duplicated after the separation of dicots and monocots. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis showed that the expression patterns of TPSs displayed group specificities in M. oleifera. Particularly, Group I MoTPS genes closely relate to reproductive development and Group II MoTPS genes closely relate to high temperature resistance in leaves, stem, stem tip and roots. This work provides a scientific classification of plant TPSs, dissects the internal relationships between their evolution and expressions, and promotes functional researches.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TPS:
-
Trehalose-6-phosphate synthase
- TPP:
-
Trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase
- Tre6P:
-
Trehalose-6-phosphate
- Ka:
-
Number of non-synonymous substitutions per non-synonymous site
- Ks:
-
Number of synonymous substitutions per synonymous site
- MRCA:
-
Most recent common ancestor
References
Anisimova M, Bielawski JP, Yang Z (2001) The accuracy and power of likelihood ratio tests to detect positive selection at amino acid sites. Mol Biol Evol 18(8):1585–1592. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a003945
Anisimova M, Bielawski JP, Yang Z (2002) Accuracy and power of Bayes prediction of amino acid sites under positive selection. Mol Biol Evol 19(6):950–958. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a004152
Anisimova M, Bielawski JP, Yang Z (2003) Effect of recombination on the accuracy of the likelihood method for detecting positive selection at amino acid sites. Genetics 164(3):1229–1236
Avonce N, Mendoza VA, Morett E (2006) Insights on the evolution of trehalose biosynthesis. BMC Evol Biol 6(1):109. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-6-109
Avonce N, Wuyts J, Verschooten K, Vandesteene L, Van Dijck P (2010) The Cytophaga hutchinsonii ChTPSP: first characterized bifunctional TPS–TPP protein as putative ancestor of all eukaryotic trehalose biosynthesis proteins. Mol Biol Evol 27(2):359–369. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msp241
Bailey TL, Bodén M, Buske FA, Frith M, Grant CE, Clementi L et al (2009) MEME SUITE: tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res 37:W202–W208. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkp335
Batool A, Wahid A, Farooq M (2016) Evaluation of aqueous extracts of Moringa leaf and flower applied through medium supplementation for reducing heat stress induced oxidative damage in maize. Int J Agric Biol 18(4):757–764. https://doi.org/10.17957/IJAB/15.0163
Chaw S, Chang C, Chen H, Li W (2004) Dating the monocot–dicot divergence and the origin of core eudicots using whole chloroplast genomes. J Mol Evol 58(4):424–441. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-003-2564-9
Chen F, Chen C, Li W, Chuang T (2010) Gene family size conservation is a good indicator of evolutionary rates. Mol Biol Evol 27(8):1750–1758. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msq055
Cominelli E, Tonelli C (2010) Transgenic crops coping with water scarcity. New Biotechnol 27(5):473–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbt.2010.08.005
Da Costa Morato Nery D, da Silva CG, Mariani D, Fernandes PN, Pereira MD et al (2008) The role of trehalose and its transporter in protection against reactive oxygen species. BBA Gen Subj 780(12):1408–1411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2008.05.011
Delorge I, Figueroa CM, Feil R, Lunn JE, Van Dijck P (2015) Trehalose-6-phosphate synthase 1 is not the only active TPS in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochem J 466(2):283–290. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20141322
Deng LT, Wu YL, Li JC, Ouyang KX, Ding MM et al (2016) Screening reliable reference genes for RT-qPCR analysis of gene expression in Moringa oleifera. PLoS One 11(8):20159458. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0159458
Du L, Qi S, Ma J, Xing L et al (2017) Identification of TPS family members in apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.) and the effect of sucrose sprays on TPS expression and floral induction. Plant Physiol Biochem 120:10–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2017.09.015
Elbein AD, Pan YT, Pastuszak I, Carrpll D (2003) New insights on trehalose: a multifunctional molecule. Glycobiology 13(4):17R–27R. https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/cwg047
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39(4):783–791. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.1985.tb00420.x
Fernandez O, Bethencourt L, Quero A, Sangwan RS, Clement C (2010) Trehalose and plant stress responses: friend or foe. Trends Plant Sci 15(7):409–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2010.04.004
Fichtner F, Barbier FF, Feil R, Watanabe M, Annunziata MG et al (2017) Trehalose 6-phosphate is involved in triggering axillary bud outgrowth in garden pea (Pisum sativum L.). Plant J 92(4):611–623. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.13705
Finn RD, Coggill P, Eberhardt RY, Eddy SR, Jaina M et al (2016) The Pfam protein families database: towards a more sustainable future. Nucleic Acids Res 44(D1):D279–D285. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1344
Garg AK, Kim JK, Owens TG, Ranwala AP et al (2002) Trehalose accumulation in rice plants confers high tolerance levels to different abiotic stresses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(25):15898–15903. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.252637799
Haak DC, Fukao T, Grene R (2017) Multilevel regulation of abiotic stress responses in plants. Front Plant Sci 8:1564. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2017.01564
Harthill JE, Meek SE, Morrice N, Peggie MW, Borch J et al (2006) Phosphorylation and 14-3-3 binding of Arabidopsis trehalose-phosphate synthase 5 in response to 2-deoxyglucose. Plant J 47(2):211–223. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02780.x
Hu B, Jin JP, Guo AY, Zhang H, Luo JC, Gao G (2015) GSDS 2.0: an upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 31(8):1296–1297. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu817
Iturriaga G, Suárez R, Nova-Franco B (2009) Trehalose metabolism: from osmoprotection to signaling. Int J Mol Sci 10(9):3793–3810. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms10093793
Jang IC, Oh SJ, Seo JS, Choi WB, Sang IS et al (2003) Expression of a bifunctional fusion of the Escherichia coli genes for trehalose-6-phosphate synthase and trehalose-6-phosphate phosphatase in transgenic rice plants increases trehalose accumulation and abiotic stress tolerance without stunting growth. Plant Physiol 131(2):516–524. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.007237
Jin Q, Hu X, Li X, Wang B, Wang Y et al (2016) Genome-wide identification and evolution analysis of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase gene family in Nelumbo nucifera. Front Plant Sci 7:1445. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.01445
Koch MA, Haubold B, Mitchell-Olds T (2000) Comparative evolutionary analysis of chalcone synthase and alcohol dehydrogenase loci in Arabidopsis, Arabis, and related genera (Brassicaceae). Mol Biol Evol 17(10):1483–1498. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026248
Kuznetsova E, Proudfoot M, Gonzales CF, Brown G, Omelchenko MV et al (2006) Genome-wide analysis of substrate specificities of the Escherichia coli haloacid dehalogenase-like phosphatase family. J Biol Chem 281(47):36149–36161. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M605449200
Leyman B, Van Dijck P, Thevelein JM (2001) An unexpected plethora of trehalose biosynthesis genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Trends Plant Sci 6(11):510–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1360-1385(01)02125-2
Li HW, Zang BS, Deng XW, Wang XP (2011) Overexpression of the trehalose-6-phosphate synthase gene OsTPS1 enhances abiotic stress tolerance in rice. Planta 234(5):1007–1018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-011-1458-0
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25(4):402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Lunn JE (2007) Gene families and evolution of trehalose metabolism in plants. Funct Plant Biol 34(6):550–563. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP06315
Lunn JE, Delorge I, Figueroa CM, Van Dijck P, Stitt M (2014) Trehalose metabolism in plants. Plant J 79(4):544–567. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12509
Miranda JA, Avonce N, Suárez R et al (2007) A bifunctional TPS-TPP enzyme from yeast confers tolerance to multiple and extreme abiotic-stress conditions in transgenic Arabidopsis. Planta 226(6):1411–1421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-007-0579-y
Mittler R (2006) Abiotic stress, the field environment and stress combination. Trends Plant Sci 11(1):15–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2005.11.002
Nunes C, Primavesi LF, Patel MK, Martinez-Barajas E, Powers SJ et al (2013) Inhibition of Sn RK1 by metabolites: tissue-dependent effects and cooperative inhibition by glucose 1-phosphate in combination with trehalose 6-phosphate. Plant Physiol Biochem 63(4):89–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2012.11.011
Pandey GK, Pandey A, Prasad M, Böhmer M (2016) Editorial: abiotic stress signaling in plants: functional genomic intervention. Front Plant Sci 7:681. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00681
Poueymiro M, Cazalé AC, François JM et al (2014) A Ralstonia solanacearum type III effector directs the production of the plant signal metabolite trehalose-6-phosphate. mBio 5(6):e02065-14. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.02065-14
Redillas Mark CFR, Park SH, Lee JW, Kim YS, Jeong JS, Jung H et al (2012) Accumulation of trehalose increases soluble sugar contents in rice plants conferring tolerance to drought and salt stress. Plant Biotechnol Rep 6(1):89–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-011-0210-3
Schluepmann H (2004) Arabidopsis trehalose-6-phosphate synthase 1 is essential for normal vegetative growth and transition to flowering. Plant Physiol 135(2):969–977. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.039743
Schluepmann H, Dijken AV, Aghdasi M, Wobbes B, Paul M, Smeekens S (2004) Trehalose mediated growth inhibition of Arabidopsis seedlings is due to trehalose-6-phosphate accumulation. Plant Physiol 135(2):879–890. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.039503
Shiu SH, Karlowski WM, Pan R, Tzeng YH, Mayer KFX, Li WH (2004) Comparative analysis of the receptor-like kinase family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Cell 16(5):1220–1234. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.020834
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30(12):2725–2729. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst197
Tian Y, Zeng Y, Zhang J, Yang CG, Yan L, Wang XJ et al (2015) High quality reference genome of drumstick tree (Moringa oleifera Lam.), a potential perennial crop. Sci China Life Sci 58(7):627–638. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-015-4872-x
Van den Ende W, Valluru R (2009) Sucrose, sucrosyl oligosaccharides, and oxidative stress: scavenging and salvaging. J Exp Bot 60(1):9–18. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ern297
Van Dijck P, Mascorro-Gallardo JO, De Bus M, Royackers K, Iturriaga G et al (2002) Truncation of Arabidopsis thaliana and Selaginella lepidophylla trehalose-6-phosphate synthase unlocks high catalytic activity and supports high trehalose levels on expression in yeast. Biochem J 366(1):63–71. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20020517
Vandesteene L, Lopez-Galvis L, Vanneste K, Feil R, Maere S, Lammens W, Rolland F et al (2012) Expansive evolution of the TREHALOSE-6-PHOSPHATE PHOSPHATASE gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 160(2):884–896. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.112.201400
Vogel G, Fiehn O, Jean-Richard-Dit-Bressel L et al (2001) Trehalose metabolism in Arabidopsis: occurrence of trehalose and molecular cloning and characterization of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase homologues. J Exp Bot 52(362):1817–1826. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/52.362.1817
Wahl V, Ponnu J, Schlereth A, Arrivault S, Langenecker T et al (2013) Regulation of flowering by trehalose-6-phosphate signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 339:704–707. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1230406
Wikstrom N, Savolainen V, Chase MW (2001) Evolution of the angiosperms: calibrating the family tree. Proc Biol Sci 268(1482):2211–2220. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2001.1782
Yadav UP, Ivakov A, Feil R, Duan GY, Walther D, Giavalisco P, Piques M et al (2014) The sucrose–trehalose 6-phosphate (Tre6P) nexus: specificity and mechanisms of sucrose signalling by Tre6P. J Exp Bot 65(4):1051–1068. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ert457
Yang ZH (1995) Evaluation of several methods for estimating phylogenetic trees when substitution rates differ over nucleotide sites. J Mol Evol 40(6):689–697. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00160518
Yang ZH, Nielsen R (2000) Estimating synonymous and nonsynonymous substitution rates under realistic evolutionary models. Mol Biol Evol 17(1):32–43. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026236
Yang ZH, Nielsen R (2002) Codon-substitution models for detecting molecular adaptation at individual sites along specific lineages. Mol Biol Evol 19(6):908–917. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a004148
Yang HL, Liu YJ, Wang CL, Zeng QY (2012) Molecular evolution of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase (TPS) gene family in Populus, Arabidopsis and rice. PLoS One 7(8):e42438. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0042438
Yang X, Liu YB, Qin LJ et al (2015) Trehalose-6-phosphate synthase gene TPS1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae improve root growth in transgenic maize under drought stress. Plant Physiol J 51(3):363–369. https://doi.org/10.13592/j.cnki.ppj.2014.0453
Zhang JJ, Yang YS, Lin MF, Li SQ, Tang Y, Chen HB, Chen XY (2017) An efficient micropropagation protocol for direct organogenesis from leaf explants of an economically valuable plant, drumstick (Moringa oleifera Lam.). Ind Crop Prod 103:59–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.03.028
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Professor P. Van Dijck and Xinsheng Hu for their help and guidance.
Funding
This study was funded by Forestry Technology Innovation Program, the Department of Forestry of Guangdong Province (2015KJCX009); Guangzhou Science Technology and Innovation Commission (201707010462); Graduate Student Overseas Study Program (2018LHPY014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, M., Jia, R., Li, J. et al. Evolution and expression patterns of the trehalose-6-phosphate synthase gene family in drumstick tree (Moringa oleifera Lam.). Planta 248, 999–1015 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-018-2945-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-018-2945-3