Abstract
Main conclusion
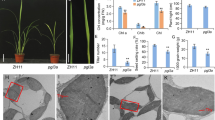
The Ycf46 mutant of Synechocystis showed growth inhibition under low dissolved CO 2 conditions, suggesting a role for the Ycf46 protein in the process of photosynthetic CO 2 uptake and utilization.
Abstract
Hypothetical chloroplast open reading frame Ycf46 proteins are highly conserved in all cyanobacterial lineages and most algal chloroplast genomes, but their exact function is still unknown. In the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803, the Ycf46 encoding gene slr0374 is part of an operon (with slr0373 and slr0376) and responds to many environmental stresses. Transcript levels of the slr0373, slr0374 and slr0376 genes were increased under a low concentration of dissolved inorganic carbon (Ci). Compared with the wild type, the mutant lacking slr0374 showed growth arrest under Ci-deficient conditions but not under iron-deficient or low-light conditions. In addition, the mutant grew more slowly than the wild type under pH 6.0 conditions in which CO2 was the dominant Ci source, indicating the mutant cells had weak CO2 uptake and/or utilization ability. Supplying a high concentration of CO2 (5 %, v/v) to the mutant restored its phenotype to the wild type level. The photosynthetic activity of the mutant was inhibited to a lesser extent by a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor than that of the wild type, which specifically blocked CO2 uptake. Inactivation of slr0374 decreased expression of the ecaB gene and reduced carbonic anhydrase activity. A subcellular localization assay indicated that the Ycf46 protein was soluble. By co-immunoprecipitation assay using Slr0374 as a bait-protein, potential interacting proteins in the size range of 30 kDa were identified. These results suggest that the Ycf46 protein plays a role in the regulation of photosynthesis in cyanobacteria, especially in CO2 uptake and utilization.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AAA:
-
ATPases associated with diverse cellular activities
- CA:
-
Carbonic anhydrase
- CCM:
-
CO2-concentrating mechanism
- Ci :
-
Dissolved inorganic carbon
- Co-IP:
-
Co-immunoprecipitation
- EZ:
-
Ethoxyzolamide
- LC–MS/MS:
-
Liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry
- ncRNA:
-
Non-coding RNA
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative reverse transcription PCR
- Ycf:
-
Hypothetical chloroplast open reading frame
References
Anthony KC, So M, John M, Espie GS (2002) Characterization of a mutant lacking carboxysomal carbonic anhydrase from the cyanobacterium Synechocystis PCC 6803. Planta 214:456–467
Badger MR, Price GD (2003) CO2 concentrating mechanisms in cyanobacteria: molecular components, their diversity and evolution. J Exp Bot 383:609–622
Bussemer J, Chigri F, Vothknecht UC (2009) Arabidopsis ATPase family gene 1-like protein is a calmodulin-binding AAA+-ATPase with a dual localization in chloroplasts and mitochondria. FEBS J 276:3870–3880
Eisenhut M, Wobeser EAV, Jonas L, Schubert H, Ibelings BW, Bauwe H, Matthijs HCP, Hagemann M (2007) Long-term response toward inorganic carbon limitation in wild type and glycolate turnover mutants of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803. Plant Physiol 44:1946–1959
El Bakkouri M, Gutsche I, Kanjee U, Zhao B, Yu M, Goret G, Schoehn G, Burmeister WP, Houry WA (2010) Structure of RavA MoxR AAA+ protein reveals the design principles of a molecular cage modulating the inducible lysine decarboxylase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:22499–22504
Gao H, Xu XD (2009) Depletion of Vipp1 in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 affects photosynthetic activity before the loss of thylakoid membranes. FEMS Microbiol Lett 292:63–70
Golterman HL, Clymo RS, Ohnstad MAM (1978) Methods for chemical analysis of freshwater. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, p 213
Jiang HB, Kong RQ, Xu XD (2010) The N-acetylmuramic acid 6-phosphate etherase gene promotes growth and cell differentiation of cyanobacteria under light-limiting conditions. J Bacteriol 192:2239–2245
Jiang HB, Lou WJ, Du HY, Price NM, Qiu BS (2012) Sll1263, a unique cation diffusion facilitator protein that promotes iron uptake in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803. Plant Cell Physiol 53:1404–1417
Jiang HB, Cheng HM, Gao KS, Qiu BS (2013) Inactivation of Ca2+/H+ exchanger in Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 promotes cyanobacterial calcification by upregulating CO2-concentrating mechanisms. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:4048–4055
Kobayashi M, Ishizuka T, Katayama M, Kanehisa M, Pakrasi MB, Pakrasi HB, Ikeuchi M (2004) Response to oxidative stress involves a novel peroxiredoxin gene in the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Plant Cell Physiol 45:290–299
Kupriyanova EV, Villarejo A, Markelova AG, Gerasimenko L, Zavarzin G, Samuelsson G, Los DA, Pronina NA (2007) Extracellular carbonic anhydrases of the stromatolite-forming cyanobacterium Microcoleus chthonoplastes. Microbiology 153:1149–1156
Kupriyanova EV, Sinetova MA, Markelova AG, Allakhverdiev SI, Los DA, Pronina NA (2011) Extracellular β-class carbonic anhydrase of the alkaliphilic cyanobacterium Microcoleus chthonoplastes. J Photochem Photobiol, B 103:78–86
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Mäenpää P, Gonzalez EB, Chen L, Khan MS, Gray JC, Aro EM (2000) The ycf9 (orf 62) gene in the plant chloroplast genome encodes a hydrophobic protein of stromal thylakoid membranes. J Exp Bot 51:375–382
Martin W, Stoebe B, Goremykin V, Hapsmann S, Hasegawa M, Kowallik KV (1998) Gene transfer to the nucleus and the evolution of chloroplasts. Nature 393:162–165
Omata T, Price GD, Badger MR, Okamura M, Gohta S, Ogawa T (1999) Identification of an ATP-binding cassette transporter involved in bicarbonate uptake in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:13571–13576
Omata T, Gohta S, Takahashi Y, Harano Y, Maeda S (2001) Involvement of a CbbR homolog in low CO2-induced activation of the bicarbonate transporter operon in cyanobacteria. J Bacteriol 183:1891–1898
Pandy A, Mann M (2000) Proteomics to study genes and genomes. Nature 405:837–846
Price GD, Badger MR (1989) Ethoxyzolamide Inhibition of CO2 uptake in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus PCC7942 without apparent inhibition of internal carbonic anhydrase activity. Plant Physiol 89:37–43
Price GD, Woodger FJ, Badger MR, Howitt SM, Tucker L (2004) Identification of a SulP-type bicarbonate transporter in marine cyanobacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:18228–18233
Price GD, Badger MR, Woodger FJ, Long BM (2008) Advances in understanding the cyanobacterial CO2-concentrating-mechanism (CCM): functional components, Ci transporters, diversity, genetic regulation and prospects for engineering into plants. J Exp Bot 59:1441–1461
Shibata M, Ohkawa H, Kaneko T, Fukuzawa H, Tabata S, Kaplan A, Ogawa T (2001) Distinct constitutive and low-CO2-induced CO2 uptake systems in cyanobacteria: genes involved and their phylogenetic relationship with homologous genes in other organisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:11789–11794
Shibata M, Katoh H, Sonoda M, Ohkawa H, Shimoyama M, Fukuzawa H, Kaplan A, Ogawa T (2002) Genes essential to sodium-dependent bicarbonate transport in cyanobacteria. J Biol Chem 277:18658–18664
Singh AK, Sherman LA (2000) Identification of iron-responsive, differential gene expression in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 with a customized amplification library. J Bacteriol 182:3536–3543
Singh AK, Sherman LA (2002) Characterization of a stress-responsive operon in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803. Gene 297:11–19
Singh AK, McIntyre LM, Sherman LA (2003) Microarray analysis of the genome-wide response to iron deficiency and iron reconstitution in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Plant Physiol 132:1825–1839
Snider JD, Houry WA (2006) MoxR AAA+ ATPases: a novel family of molecular chaperones? J Struct Biol 156:200–209
So AKC, Van Spall HGC, Coleman JR, Espie GS (1998) Catalytic exchange of 18O from 13C 18O-labelled CO2 by wild-type cells and ecaA, ecaB, and ccaA mutants of the cyanobacteria Synechococcus PCC7942 and Synechocystis PCC6803. Can J Bot 76:1153–1160
Voß B, Georg J, Schön V, Ude S, Hess W (2009) Biocomputational prediction of non-coding RNAs in model cyanobacteria. BMC Genom 10:123
Wang HL, Bradley LP, Robert LB (2004) Alterations in global patterns of gene expression in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 in response to inorganic carbon limitation and the inactivation of ndhR, a LysR family regulator. J Biol Chem 279:5739–5751
Williams JGK (1988) Construction of specific mutations in photosystem II photosynthetic reaction center by genetic engineering methods in Synechocystis 6803. Methods Enzymol 167:766–778
Xu P, Peng JM (2006) Dissecting the ubiquitin pathway by mass spectrometry. Biochim Biophys Acta 1764:1940–1947
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Professor Xudong Xu (Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences) for kindly providing the anti-CP47 antiserum. This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31100184 and No. 31170309).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, HB., Song, WY., Cheng, HM. et al. The hypothetical protein Ycf46 is involved in regulation of CO2 utilization in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Planta 241, 145–155 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-014-2169-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-014-2169-0