Abstract
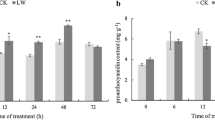
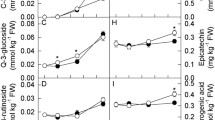
Persimmon fruits accumulate a large amount of proanthocyanidin (PA). Fruits of the mutant non-astringent (NA) type lose their ability to accumulate PA at an early stage of fruit development, whereas fruits of the normal astringent (A) type sustain PA accumulation until ripening. This allelotype is determined by the genotype of a single ASTRINGENCY (AST) locus. It is possible that the reduction in PA accumulation in NA-type fruits is due to phenological down-regulation of DkMyb4 (a PA regulator) and the resultant down-regulation of structural genes in the PA pathway. In this study, attempts were made to identify the regulatory mechanisms of phenological PA accumulation in A- and NA-type fruits, focusing particularly on the effects of ambient temperature. Continuous cool temperature conditions caused sustained expression of DkMyb4 in NA-type fruits, as well as in A-type fruits, resulting in increased expression of PA pathway genes and PA accumulation. However, the expression of some A/NA phenotypic marker genes was not significantly affected by the cool temperature conditions. In addition, PA composition in NA-type fruits exposed to cool temperatures differed from that in A-type fruits. These results indicate that a cool ambient temperature may have induced DkMyb4 expression and resultant PA accumulation, but did not directly affect the expression of the AST gene.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANR:
-
Anthocyanidin reductase
- A-type:
-
Astringent type
- CA:
-
Catechin
- CHS:
-
Chalcone synthase
- EC:
-
Epicatechin
- EC-G:
-
Epicatechin-gallate
- EGC:
-
Epigallocatechin
- EGC-G:
-
Epigallocatechin-gallate
- F3′H:
-
Flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase
- F3′5′H:
-
Flavonoid 3′5′-hydroxylase
- GC:
-
Gallocatechin
- LAR:
-
Leucoanthocyanidin reductase
- NA-type:
-
Non-astringent type
- PA:
-
Proanthocyanidin
- TF:
-
Transcription factor
References
Abe H, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Urao T, Iwasaki T, Hosokawa D, Shinozaki K (1997) Role of Arabidopsis MYC and MYB homologs in drought-and abscisic acid-regulated gene expression. Plant Cell 9:1859–1868
Akagi T, Ikegami A, Suzuki Y, Yoshida J, Yamada M, Sato A, Yonemori K (2009a) Expression balances of structural genes in shikimate and flavonoid biosynthesis cause a difference in proanthocyanidin accumulation in persimmon (Diospyros kaki Thunb.) fruit. Planta 230:899–915
Akagi T, Ikegami A, Tsujimoto T, Kobayashi S, Sato A, Kono A, Yonemori K (2009b) DkMyb4 is a Myb transcription factor involved in proanthocyanidin biosynthesis in persimmon fruit. Plant Physiol 151:2028–2045
Akagi T, Kanzaki S, Gao M, Tao R, Parfitt DE, Yonemori K (2009c) Quantitative real-time PCR to determine allele number for the astringency locus by analysis of a linked marker in Diosypros kaki Thunb. Tree Genet Genomes 5:483–492
Akagi T, Ikegami A, Yonemori K (2010a) DkMyb2 wound-induced transcription factor of persimmon (Diospyros kaki Thunb.), contributes to proanthocyanidin regulation. Planta. doi: 10.1007/s00425-010-1241-7
Akagi T, Suzuki Y, Ikegami A, Kamitakahara H, Takano T, Nakatsubo F, Yonemori K (2010b) Condensed tannin composition analysis in persimmon (Diospyros kaki Thunb.) fruit by acid catalysis in the presence of excess phloroglucinol. J Jap Soc Hort Sci 79:275–281
Aron PM, Kennedy JA (2008) Flavan-3-ols: nature, occurrence and biological activity. Mol Nutr Food Res 52:79–104
Bagchi D, Bagchi M, Stohs SJ, Das DK, Ray SD, Kuszynski CA, Joshi SS, Pruess HG (2000) Free radicals and grape seed proanthocyanidin extract: importance in human health and disease prevention. Toxicology 148:187–197
Bogs J, Jaffé FW, Takos AM, Walker AR, Robinson SP (2007) The grapevine transcription factor VvMYBPA1 regulates proanthocyanidin synthesis during fruit development. Plant Physiol 143:1347–1361
Deluc L, Bogs J, Walker AR, Ferrier T, Decendit A, Merillon JM, Robinson SP, Barrieu F (2008) The transcription factor VvMYB5b contributes to the regulation of anthocyanin and proanthocyanidin biosynthesis in developing grape berries. Plant Physiol 147:2041–2053
Dixon RA, Xie D-Y, Sharma SB (2005) Proanthocyanidins—a final frontier in flavonoid research? New Phytol 165:9–28
Downey MO, Harvey JS, Robinson SP (2003) Analysis of tannins in seeds and skins of Shiraz grapes throughout berry development. Aust J Grape Wine Res 9:15–27
Gagné S, Lacampagnea S, Claissea O, Gény L (2009) Leucoanthocyanidin reductase and anthocyanidin reductase gene expression and activity in flowers, young berries and skins of Vitis vinifera L. cv. Cabernet-Sauvignon during development. Plant Physiol Biochem 47:282–290
Harborne JB, Grayer RJ (1993) Flavonoids and insects. In: Harborne JB (ed) The flavonoids: advances in research since 1986. Chapman & Hall, London, pp 589–618
Hattori T, Vasil V, Rosenkrans L, Hannah LC, McCarty DR, Vasil K (1992) The Viviparous-1 gene and abscisic acid activate the C1 regulatory gene for anthocyanin biosynthesis during seed maturation in maize. Genes Dev 6:609–618
Hoballah ME, Gübitz T, Stuurman J, Broger L, Barone M, Mandel T, Dell’Olivo A, Arnold M, Kuhlemeier C (2007) Single gene-mediated shift in pollinator attraction in Petunia. Plant Cell 19:779–790
Ikegami A, Kitajima A, Yonemori K (2005) Inhibition of flavonoid biosynthetic gene expression coincides with loss of astringency in pollination-constant, non-astringent (PCNA)-type persimmon fruit. J Hort Sci Biotech 80:225–228
Ikegami A, Eguchi S, Kitajima A, Inoue K, Yonemori K (2007) Identification of genes involved in proanthocyanidin biosynthesis of persimmon (Diospyros kaki) fruit. Plant Sci 172:1037–1047
Ikegami A, Akagi T, Potter D, Yamada M, Sato A, Yonemori K, Kitajima A, Inoue K (2009) Molecular identification of 1-cys peroxiredoxin and anthocyanidin/flavonol 3-O-galactosyltransferase from proanthocyanidin-rich young fruits of persimmon (Diospyros kaki Thunb.). Planta 230:841–855
Kennedy JA, Jones GP (2001) Analysis of proanthocyanidin cleavage products following acid-catalysis in the presence of excess phloroglucinol. J Agric Food Chem 49:1740–1746
Kobayashi S (2009) Regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in grape. J Jap Soc Hort Sci 78:387–393
Kojima K, Shiozaki K, Koshita Y, Ishida M (1999) Changes of endogenous levels of ABA, IAA and GA-like substances in fruitlets of parthenocarpic persimmon [Diospyros kaki]. J Jap Soc Hort Sci 68:242–247
Koyama K, Goto-Yamamoto N (2008) Bunch shading during different developmental stages affects the phenolic biosynthesis in berry skins of ‘Cabernet Sauvignon’ grapes. J Am Soc Hort Sci 133:743–753
Lacampagne S, Gagné S, Gény L (2010) Involvement of abscisic acid in controlling the proanthocyanidin biosynthesis pathway in grape skin: new elements regarding the regulation of tannin composition and leucoanthocyanidin reductase (LAR) and anthocyanidin reductase (ANR) activities and expression. J Plant Growth Regul 29:81–90
Lavola A (1998) Accumulation of flavonoids and related compounds in birch induced by UV-B irradiance. Tree Physiol 18:53–58
Lees GL (1992) Condensed tannins in some forage legumes: their role in the prevention of ruminant pasture bloat. Basic Life Sci 59:915–934
Lepiniec L, Debeaujon I, Routaboul JM, Baudry A, Pourcel L, Nesi N, Caboche M (2006) Genetics and biochemistry of seed flavonids. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:405–430
Li YG, Tanner G, Larkin P (1996) The DMACA-HCl protocol and the threshold proanthocyanidin content for bloat safety in forage legumes. J Sci Food Agric 70:89–101
Lin-Wang K, Bolitho K, Grafton K, Kortstee A, Karunairetnam S, McGhie TK, Espley RV, Hellens RP, Allan AC (2010) An R2R3 MYB transcription factor associated with regulation of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway in Rosaceae. BMC Plant Biol 10:50
Matsuo T, Ito S (1978) The chemical structure of kaki-tannin from immature fruit of the persimmon (Diospyros kaki L.). Agric Biol Chem 42:1637–1643
Matus JT, Loyola R, Vega A, Peña-Neira A, Bordeu E, Arce-Johnson P, Alcalde JA (2009) Post-veraison sunlight exposure induces MYB-mediated transcriptional regulation of anthocyanin and flavonol synthesis in berry skins of Vitis vinifera. J Exp Bot 60:853–867
Mellway RD, Tran LT, Prouse MB, Campbell MM, Constabel CP (2009) The wound-, pathogen-, and UV-B -responsive MYB134 gene encodes an R2R3 MYB transcription factor that regulates proanthocyanidin synthesis in poplar. Plant Physiol 150:924–941
Miranda M, Ralph SG, Mellway R, White R, Heath MC, Bohlmann J, Constabel CP (2007) The transcriptional response of hybrid poplar (Populus trichocarpa × P deltoides) to infection by Melampsora medusae leaf rust involves induction of flavonoid pathway genes leading to the accumulation of proanthocyanidins. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 20:816–831
Mori K, Goto-Yamamoto N, Kitayama M, Hashizume K (2007) Loss of anthocyanins in red-wine grape under high temperature. J Exp Bot 58:1935–1945
Nesi N, Jond C, Debeaujon I, Caboche M, Lepiniec L (2001) The Arabidopsis TT2 gene encodes an R2R3 MYB domain protein that acts as a key determinant for proanthocyanidin accumulation in developing seed. Plant Cell 13:2099–2114
Pang Y, Peel GJ, Wright E, Wang Z, Dixon RA (2007) Early steps in proanthocyanidin biosynthesis in the model legume Medicago truncatula. Plant Physiol 145:601–615
Peters DJ, Constabel CP (2002) Molecular analysis of herbivore-induced condensed tannin synthesis: cloning and expression of dihydroflavonol reductase from trembling aspen (Populus tremuloides). Plant J 32:701–712
Spayd SE, Tarara JM, Mee DL, Ferguson JC (2002) Separation of sunlight and temperature effects on the composition of Vitis vinifera cv. Merlot Berries. Am J Enol Vitic 53:171–182
Taira S (1996) Astringency in persimmon. In: Linskens HF, Jackson JF (eds) Fruit analysis. Springer, Berlin, pp 97–110
Taira S, Matsumoto N, Ono M (1998) Accumulation of soluble and insoluble tannins during fruit development in nonastringent and astringent persimmon. J Jap Soc Hort Sci 67:572–576
Takos AM, Jaffe FW, Jacob SR, Bogs J, Robinson SP, Walker AR (2006) Light-induced expression of a MYB gene regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis in red apples. Plant Physiol 142:1216–1232
Tanner GJ, Francki KT, Abrahams S, Watson JM, Larkin PJ, Ashton AR (2003) Proanthocyanidin biosynthesis in plants. Purification of legume leucoanthocyanidin reductase and molecular cloning of its cDNA. J Biol Chem 278:31647–31656
Terrier T, Torregrosa L, Ageorges A, Vialet S, Verries C, Cheynier V, Romieu C (2009) Ectopic expression of VvMybPA2 promotes proanthocyanidin biosynthesis in grapevine and suggests additional targets in the pathway. Plant Physiol 149:1028–1041
Urao T, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Urao S, Shinozaki K (1993) An Arabidopsis myb homolog is induced by dehydration stress and its gene product binds to the conserved MYB recognition sequence. Plant Cell 5:1529–1539
Wan CY, Wilkins TA (1994) A modified hot borate method significantly enhances the yield of high-quality RNA from cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Anal Biochem 223:7–12
Winkel-Shirley B (2001) Flavonoid biosynthesis. A colorful model for genetics, biochemistry, cell biology, and biotechnology. Plant Physiol 126:485–493
Xie D-Y, Sharma SB, Paiva NL, Ferreira D, Dixon RA (2003) Role of anthocyanidin reductase, encoded by BANYULS in plant flavonid biosynthesis. Science 299:396–399
Yamada M, Sato A (2002) Segregation for fruit astringency type in progenies derived from crosses of ‘Nishimura-wase’ × pollination constant non-astringent genotypes in oriental persimmon (Diospyros kaki Thunb). Sci Hort 92:107–111
Yamane H, Jeong ST, Goto-Yamamoto N, Koshita Y, Kobayashi S (2006) Effects of temperature on anthocyanin biosynthesis in grape berry skins. Am J Enol Vitic 57:49–54
Yonemori K, Sugiura A, Yamada M (2000) Persimmon genetics and breeding. In: Janick J (ed) Plant breeding reviews 19. Wiley, New York, pp 191–225
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akagi, T., Tsujimoto, T., Ikegami, A. et al. Effects of seasonal temperature changes on DkMyb4 expression involved in proanthocyanidin regulation in two genotypes of persimmon (Diospyros kaki Thunb.) fruit. Planta 233, 883–894 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-010-1346-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-010-1346-z