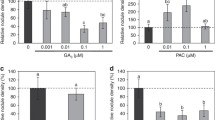
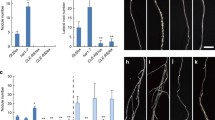
Abstract
Legumes can acquire nitrogen through a symbiotic interaction with rhizobial bacteria. The initiation of this process is determined by a molecular dialogue between the two partners. Legume roots exude flavonoids that induce the expression of the bacterial nodulation genes, which encode proteins involved in the synthesis and secretion of signals called Nod factors (NFs). NFs signal back to the plant root and trigger several responses, leading to bacterial invasion and nodule formation. Here, we describe the molecular and cellular characterization of a Phaseolus vulgaris non-nodulating mutant (NN-mutant). Root hair cells of the NN-mutant plant respond with swelling and branching when inoculated with Rhizobium etli, albeit without curling induction. Furthermore, neither initiation of cell division in the outer cortex, nor entrapment of bacteria nor infection thread formation was observed. Both the bean wild-type and the NN-mutant responded with elevated intracellular calcium changes in the root hairs. Although the NN-mutant is deficient in early nodulin gene expression when inoculated with R. etli, it can be effectively colonized by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (Glomus intraradices). Our data indicate that the P. vulgaris NN-mutant is not blocked at the NFs early perception stage, but at later downstream stages between Ca2+ signaling and early nodulin induction. This supports the idea that both microsymbionts are perceived and trigger different downstream pathways in the host plant.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CaM:
-
Calmodulin
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- CCD:
-
Charge-coupled device
References
Bécard G, Fortin J (1998) Early events of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza formation on Ri T-DNA transformed roots. New Phytologist 108:211–218
Ben Amor B, Shaw SL, Oldroyd GE, Maillet F, Penmetsa RV, Cook D, Long SR, Denarie J, Gough C (2003) The NFP locus of Medicago truncatula controls an early step of Nod factor signal transduction upstream of a rapid calcium flux and root hair deformation. Plant J 34:495–506
Bonfante P, Genre A, Faccio A, Martini I, Schauser L, Stougaard J, Webb J, Parniske M (2000) The Lotus japonicus LjSym4 gene is required for the successful symbiotic infection of root epidermal cells. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 13:1109–1120
Bonilla I, Mergold-Villasenor C, Campos ME, Sanchez N, Perez H, Lopez L, Castrejon L, Sanchez F, Cassab GI (1997) The aberrant cell walls of boron-deficient bean root nodules have no covalently bound hydroxyproline-/proline-rich proteins. Plant Physiol 115:1329–1340
Cárdenas L, Domínguez J, Quinto C, Lopez-Lara I, Lugtenberg B, Spaink H, Rademarker GH, Haverkamp J, Thomas-Oates JE (1995) Isolation, chemical structure and biological activity of the lipo-chitin oligosaccharide nodulation signal from Rhizobium etli. Plant Mol Biol 29:453–464
Cárdenas L, Feijó JA, Kunkel JG, Sánchez F, Holdaway-Clarke T, Hepler PK, Quinto C (1999) Rhizobium Nod factors induce increases in intracellular free calcium and extracellular calcium influxes in bean root hairs. Plant J 19:347–352
Cárdenas L, Holdaway-Clarke TL, Sánchez F, Quinto C, Feijó JA, Kunkel JG, Hepler PK (2000) Ion changes in legume root hairs responding to nod factors. Plant Physiol 123:443–452
Cárdenas L, Vidali L, Domínguez J, Pérez H, Sánchez F, Hepler PK, Quinto C (1998) Rearrangement of actin microfilaments in plant root hairs responding to Rhizobium etli nodulation signals. Plant Physiol 116:871–877
Catoira R, Galera C, de Billy F, Penmetsa RV, Journet EP, Maillet F, Rosenberg C, Cook D, Gough C, Denarie J (2000) Four genes of Medicago truncatula controlling components of a Nod factor transduction pathway. Plant Cell 12:1647–1666
Charon C, Johansson C, Kondorosi E, Kondorosi A, Crespi M (1997) enod40 induces dedifferentiation and division of root cortical cells in legumes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:8901–8906
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 162:156–159
Crespi MD, Jurkevitch E, Poiret M, d’Aubenton-Carafa Y, Petrovics G, Kondorosi E, Kondorosi A (1994) enod40, a gene expressed during nodule organogenesis, codes for a non-translatable RNA involved in plant growth. Embo J 13:5099–5112
Davis J, Guiller K, Kipe-Nolt J, Awah M (1988) Non-nodulating mutants in common bean. Crop Sci 28:859–860
Dickstein R, Bisseling T, Reinhold VN, Ausubel FM, (1988) Expression of nodule-specific genes in alfalfa root nodules blocked at an early stage of development. Genes Dev 2:677–687
Du L, Poovaiah BW (2004) A novel family of Ca(2+)/calmodulin-binding proteins involved in transcriptional regulation: interaction with fsh/ring3 class transcription activators. Plant Mol Biol 54:549–569
Ehrhardt DW, Wais R, Long SR (1996) Calcium spiking in plant root hairs responding to Rhizobium nodulation signals. Cell 85:673–681
Endre G, Kereszt A, Kevei Z, Mihacea S, Kalo P, Kiss GB (2002) A receptor kinase gene regulating symbiotic nodule development. Nature 417:962–966
Geurts R, Bisseling T (2002) Rhizobium nod factor perception and signaling. Plant Cell 14(Suppl):S239–S249
Heidstra R, Nilsen G, Martinez-Abarca F, van Kammen A, Bisseling T (1997) Nod factor-induced expression of leghemoglobin to study the mechanism of NH4NO3 inhibition on root hair deformation. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 10:215–220
Henikoff S, Till BJ, Comai L (2004) TILLING. Traditional mutagenesis meets functional genomics. Plant Physiol 135:630–636
Hoeflich KP, Ikura M (2002) Calmodulin in action: diversity in target recognition and activation mechanisms. Cell 108:739–742
Kalo P, Gleason C, Edwards A, Marsh J, Mitra RM, Hirsch S, Jakab J, Sims S, Long SR, Rogers J, Kiss GB, Downie JA, Oldroyd GE (2005) Nodulation signaling in legumes requires NSP2, a member of the GRAS family of transcriptional regulators. Science 308:1786–1789
Levy J, Bres C, Geurts R, Chalhoub B, Kulikova O, Duc G, Journet EP, Ane JM, Lauber E, Bisseling T, Denarie J, Rosenberg C, Debelle F (2004) A putative Ca2+ and calmodulin-dependent protein kinase required for bacterial and fungal symbioses. Science 303:1361–1364
Mitra RM, Gleason CA, Edwards A, Hadfield J, Downie JA, Oldroyd GE, Long SR (2004) A Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase required for symbiotic nodule development: gene identification by transcript-based cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:4701–4705
Oldroyd GE, Downie JA (2004) Calcium, kinases and nodulation signalling in legumes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:566–576
Oldroyd GE, Long SR (2003) Identification and characterization of nodulation-signaling pathway 2, a gene of Medicago truncatula involved in Nod actor signaling. Plant Physiol 131:1027–1032
Papadopoulou K, Roussis A, Katinakis P (1996) Phaseolus ENOD40 is involved in symbiotic and non-symbiotic organogenetic processes: expression during nodule and lateral root development. Plant Mol Biol 30:403–417
Park S, Buttery B (1989) Inheritance of nitrate-tolerant super nodulation in EMS-induced mutants of common bean. J Hered 80:486–488
Park S, Buttery B (1992) Ethyl-methane sulphonate (EMS) induced nodulation mutants of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) lacking effective nodules. Plant Soil 139:295–298
Park S, Buttery B (1994) Inheritance of non-nodulation and ineffective nodulation mutants in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). J Hered 85:1–3
Parniske M (2004) Molecular genetics of the arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:414–421
Pedalino M, Giller K, Kipe-Nolt J (1992) Genetic and physiological characterization of the non-nodulating mutant of Phaseolus vulgaris L.-NOD125. J Exp Bot 48:843–849
Powell R, Gannon F (1988) The leghaemoglobins. Bioessays 9:117–121
Radutoiu S, Madsen LH, Madsen EB, Felle HH, Umehara Y, Gronlund M, Sato S, Nakamura Y, Tabata S, Sandal N, Stougaard J (2003) Plant recognition of symbiotic bacteria requires two LysM receptor-like kinases. Nature 425:585–592
Schauser L, Handberg K, Sandal N, Stiller J, Thykjaer T, Pajuelo E, Nielsen A, Stougaard J (1998) Symbiotic mutants deficient in nodule establishment identified after T-DNA transformation of Lotus japonicus. Mol Gen Genet 259:414–423
Shaw SL, Long SR (2003) Nod factor elicits two separable calcium responses in Medicago truncatula root hair cells. Plant Physiol 131:976–984
Shirtliffe SJ, Vessey JK (1996) A nodulation (Nod+/Fix−) mutant of Phaseolus vulgaris L. has nodule-like structures lacking peripheral vascular bundles (Pvb−) and is resistant to mycorrhizal infection (Myc−). Plant Sci 118:209–220
Smit P, Raedts J, Portyanko V, Debelle F, Gough C, Bisseling T, Geurts R (2005) NSP1 of the GRAS protein family is essential for rhizobial Nod factor-induced transcription. Science 308:1789–1791
Stracke S, Kistner C, Yoshida S, Mulder L, Sato S, Kaneko T, Tabata S, Sandal N, Stougaard J, Szczyglowski K, Parniske M (2002) A plant receptor-like kinase required for both bacterial and fungal symbiosis. Nature 417:959–962
Szczyglowski K, Kapranov P, Hamburger D, de Bruijn FJ (1998) The Lotus japonicus LjNOD70 nodulin gene encodes a protein with similarities to transporters. Plant Mol Biol 37:651–661
Till BJ, Colbert T, Tompa R, Enns LC, Codomo CA, Johnson JE, Reynolds SH, Henikoff JG, Greene EA, Steine MN, Comai L, Henikoff S (2003) High-throughput TILLING for functional genomics. Methods Mol Biol 236:205–220
Till BJ, Reynolds SH, Weil C, Springer N, Burtner C, Young K, Bowers E, Codomo CA, Enns LC, Odden AR, Greene EA, Comai L, Henikoff S (2004) Discovery of induced point mutations in maize genes by TILLING. BMC Plant Biol 4:12
van de Wiel C, Scheres B, Franssen H, van Lierop MJ, van Lammeren A, van Kammen A, Bisseling T (1990) The early nodulin transcript ENOD2 is located in the nodule parenchyma (inner cortex) of pea and soybean root nodules. Embo J 9:1–7
van Rhijn P, Fang Y, Galili S, Shaul O, Atzmon N, Wininger S, Eshed Y, Lum M, Li Y, To VV, Fujishige N, Kapulnik Y, Hirsch AM (1997) Expression of early nodulin genes in alfalfa mycorrhizae indicates that signal transduction pathways used in forming arbuscular mycorrhizae and Rhizobium-induced nodules may be conserved. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:5467–5472
Wais RJ, Galera C, Oldroyd G, Catoira R, Penmetsa RV, Cook D, Gough C, Denarie J, Long SR (2000) Genetic analysis of calcium spiking responses in nodulation mutants of Medicago truncatula. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:13407–13412
Wais RJ, Wells DH, Long SR (2002) Analysis of differences between Sinorhizobium meliloti 1021 and 2011 strains using the host calcium spiking response. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 15:1245–1252
Walker SA, Viprey V, Downie JA (2000) Dissection of nodulation signaling using pea mutants defective for calcium spiking induced by nod factors and chitin oligomers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:13413–13418
Yang T, Chaudhuri S, Yang L, Chen Y, Poovaiah BW (2004) Calcium/calmodulin up-regulates a cytoplasmic receptor-like kinase in plants. J Biol Chem 279:42552–42559
Yang T, Poovaiah BW (2003) Calcium/calmodulin-mediated signal network in plants. Trends Plant Sci 8:505–512
Acknowledgment
We thank DGAPA (grant IN209202, IN228903 and IN209804) and CONACYT (grant 42560-Q) for the financial support. We also thank Dr. Beatriz Xoconostle for providing us with the G. intraradices strain and Alberto Camas for his helpful technical advices. We thank Dr. Marco Villanueva, Otto Geiger and Chris Wood for their critical reading of the manuscript. We are grateful to the UC-MEXUS CN98-0706 grant for partial support. E. Alemán was supported by a CONACYT scholarship No. 176451.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cárdenas, L., Alemán, E., Nava, N. et al. Early responses to Nod factors and mycorrhizal colonization in a non-nodulating Phaseolus vulgaris mutant. Planta 223, 746–754 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-005-0132-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-005-0132-9