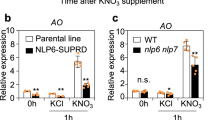
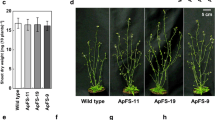
Abstract
The PII signal transducing protein is involved in carbon/nitrogen (C/N) sensing in bacteria and cyanobacteria. In higher plants the function of the PII homolog GLB1 is not known. GLB1 transcripts were found in all plant organs tested, while in Arabidopsis leaves GLB1 expression and PII protein levels were not significantly affected by either the day/night cycle or N-nutrition. Its putative regulatory role in plants has been studied by analysing Arabidopsis thaliana T-DNA insertion lines in the GLB1 gene. These PII mutants showed an 80% (PIIV1 mutant) and 100% (PIIS2 mutant) reduced AtGLB1 transcript level and no detectable PII protein. They did not display an altered growth or developmental phenotype when grown under non-limiting conditions suggesting that the PII protein does not play a crucial role in plants. However, in vitro grown PII mutants did show a higher sensitivity to nitrite (NO −2 ) compared to the wild-type plants. This observation is reminiscent of the role of PII in the regulation of NO −2 metabolism in cyanobacteria. Furthermore, when grown hydroponically, the PII mutants displayed a slight increase in carbohydrate (starch and sugars) levels in response to N starvation and a slight decrease in the levels of ammonium (NH +4 ) and amino acids (mainly Gln) in response to NH +4 resupply. Although the phenotypic changes are rather small in the mutant lines, these data support the hypothesis of a subtle involvement of the PII protein in the regulation of some steps of primary C and N metabolism.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- WS:
-
Wassilewskija ecotype
- Col:
-
Colombia ecotype
- FW:
-
Fresh weight
- DW:
-
Dry weight
- EF1α:
-
Elongation factor one alpha
- α-KG:
-
α-ketoglutarate
- NR:
-
Nitrate reductase
- NiR:
-
Nitrite reductase
- GS:
-
Glutamine synthetase
- GOGAT:
-
Glutamate synthase
References
Atkinson MR, Ninfa AJ (1998) Role of the GlnK signal transduction protein in the regulation of nitrogen assimilation in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 29:431–47
Aldehni MF, Sauer J, Spielhaupter Schmid R, Forchhammer K (2003) Signal transduction protein PII is required for NtcA-regulated gene expression during nitrogen deprivation in cyanobacterium Synechococcus elongatus strain PCC 7942. J Bact 185:2582–2591
Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, Christopher J, Huaming Chen K, Shinn P, Stevenson DK, Zimmerman J, Barajas P, Cheuk R, Gadrinab C, Heller C, Jeske A, Koesema E, Meyers CC, Parker H, Prednis L, Ansari Y, Choy N, Deen H, Geralt M, Hazari N, Hom E, Karnes M, Mulholland C, Ndubaku R, Schmidt I, Guzman P, Aguilar-Henonin L, Schmid Weigel D, Carter DE, Marchand T, Risseeuw E, Brogden D, Zeko A, Crosby WL, Berry CC, Ecker JR (2003) Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301:653–657
Bouchez D, Camilleri C, Caboche M (1993) A binary vector based on Basta resistance in planta transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. C R Acad Sci Ser III Sci Vie 316:1188–1193
Burillo S, Luque I, Fuentes I, Contreras A (2004) Interactions between the nitrogen signal transduction protein PII and N-Acetyl Glutamate kinase in organisms that perform oxygenic photosynthesis. J Bact 186:3346–3354
Brunswick P, Cresswell CF (1988) Nitrite uptake into intact pea chloroplasts. II. Influence of electron transport regulators, uncouplers, ATPase and anion uptake inhibitors and protein binding reagents. Plant Physiol 86:384–389
Coïc Y, Lesaint C (1975) La nutrition minérale et en eau des plantes en horticulture avancée. Doc Tech Soc Commer Potasses Azot 23:1–22
Coutts G, Thomas G, Blakey D, Merrick M (2002) Membrane sequestration of the signal transduction protein GlnK by the ammonium transporter AmtB. EMBO J 21:536–545
Estelle MA, Somerville CR (1987) Auxin-resistant mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana with an altered morphology. Mol Gen Genet 206:200–206
Ferrario-Méry S, Thibaud M-C, Betsche T, Valadier M-H, Foyer CH (1997) Modulation of carbon and nitrogen metabolism, and of nitrate reductase, in untransformed and transformed Nicotiana plumbaginifolia during CO2 enrichment of plants grown in pots and in hydroponic cultures. Planta 202:510–520
Ferrario-Mery S, Hodges M, Hirel B, Foyer CH (2002) Photorespiration-dependent increases in phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, isocitrate dehydrogenase and glutamate dehydrogenase in transformed tobacco plants deficient in ferredoxin-dependent glutamine-α-ketoglutarate aminotransferase. Planta 214:877–886
Filleur S, Dorbe M-F, Cerezo M, Orsel M, Granier F, Gojon A, Daniel-Vedele F (2001) An Arabidopsis T-DNA mutant affected in Nrt2 genes is impaired in nitrate uptake. FEBS Lett 489:3220–3224
Forchhammer K, Tandeau de Marsac N (1994) The PII protein in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain PCC7942 is modified by serine phosphorylation and signals the cellular N-status. J Bact 176:84–91
Forchhammer K, Tandeau de Marsac N (1995) Functional analysis of the phosphoprotein PII (glnB gene product) in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942. J Bact 177:2033–40
Garcia-Dominguez M, Florencio FJ (1997) Nitrogen availability and electron transport control the expression of glnB gene (encoding PII protein) in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Plant Mol Biol 35:723–734
Heinrich A, Maheswaran M, Ruppertand U, Forchhammer K (2004) The Synechococcus elongates PII signal transduction protein controls arginine synthesis by complex formation with N-acetyl-L-glutamate kinase. Mol Microbiol 52:1303–1314
Hisberges M, Jeanjean R, Joset F, Tandeau de Marsac N, Bédu S (1999) Protein PII regulates both inorganic and nitrate uptake and is modified by a redox signal in Synechocystis PCC 6803. FEBS Lett 463:216–220
Hsieh MH, Lam HM, van de Loo FJ, Coruzzi G (1998) A PII-like protein in Arabidopsis: putative role in nitrogen sensing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:13965–13970
Joy KM, Hageman RH (1966) The purification and properties of nitrite reductase from higher plants and its dependence on ferredoxin. Biochem J 100:263–273
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lee HM, Flores E, Forchhammer K, Herrero A, Tandeau de Marsac N (2000) Phosphorylation of the signal transducer PII protein and an additional effector are required for the PII-mediated regulation of nitrate and nitrite uptake in the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. PCC 7942. Eur J Biochem 267:591–600
Lee HM, Flores E, Herrero A, Houmard J, Tandeau de Marsac N (1998) A role for the signal transduction protein PII in the control of nitrate/nitrite uptake in a cyanobacterium. FEBS Lett 427:291–295
Liboz T, Bardet C, Le Van Thai A, Axelos M, Lescure B (1990) The four members of the gene family encoding the Arabidopsis thaliana translation elongation factor EF-1 alpha are actively transcribed. Plant Mol Biol 14:107–110
Lillo C, Meyer C, Lea US, Provan F, Oltedal S (2004) Mechanism and importance of post-translational regulation of nitrate reductase. J Exp Bot 55:1275–1282
Moorhead BGG, Smith CS (2003) Interpreting the plastid carbon, nitrogen, and energy status. A role for PII? Plant Physiol 133:492–498
Nielsen TH, Krapp A, Röper-Schwarz U, Stitt M (1998) The sugar-mediated regulation of genes encoding the small subunit of Rubisco and the regulator subunit of ADP glucose pyrophosphorylase is modified by the phosphate and nitrogen. Plant Cell Environ 21:443–454
Ninfa AJ, Atkinson MR (2000) PII signal transduction protein. Trends Microbiol 8:172–179
O’Neal D, Joy KW (1973) Localization of glutamate synthetase in chloroplasts. Nat New Biol 246:61–62
Orsel M, Krapp A, Daniel-Vedele F (2002) Analysis of the NRT2 nitrate transporter family in Arabidopsis. Structure and gene expression. Plant Physiol 129:886–896
Rexach J, Fernández E, Galván A (2000) The Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Nar1 gene encodes a chloroplast membrane protein involved in nitrite transport. Plant Cell 12:1441–1453
Rochat C, Boutin JP (1989) Carbohydrates and nitrogenous compounds changes in the hull and in the seed during the pod development of pea. Arch Biochem Biophys 27:881–887
Shingles R, Roh MH, McCarty RE (1996) Nitrite transport in chloroplast inner envelope vesicles. I. Direct measurement of proton-linked transport. Plant Physiol 112:1375–1381
Smith CS, Zaplachinski ST, Muench D, Moorhead GBG (2002) Expression and purification of the chloroplast putative nitrogen sensor, PII, of Arabidopsis thaliana. Protein Expr Purif 25:2–7
Smith CS, Weljie AM, Moorhead GBG (2003) Molecular properties of the putative nitrogen sensor PII from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 33:353–360
Smith CS, Morrice NA, Moorhead GBG (2004) Lack of evidence for phosphorylation of Arabidopsis thaliana PII: implication for plastid carbon and nitrogen signalling. Biochim Biophys Acta 1699:145–154
van Heeswijk WC, Hoving S, Molenaar D, Stegeman B, Kahn D, Westerhoff HV (1996) An alternative PII protein in the regulation of glutamine synthetase in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 21:133–146
Stitt M, Krapp A (1999) The interaction between elevated carbon dioxide and nitrogen nutrition: the physiological and molecular background. Plant Cell Environ 22:583–621
Sugiyama K, Hayakawa T, Kudo T, Ito T, Yamaya T (2004) Interaction of N-acetylglutamate kinase with a PII-like protein in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 45:1768–1778
Vaucheret H, Kronenberger J, Lepingle A, Vilaine F, Boutin J-P, Caboche M (1992) Inhibition of tobacco nitrite reductase activity by expression of antisense RNA. Plant J 2:559–569
Walch-Liu P, Neumann G, Bangerth F, Engels C (2000) Rapid effects of nitrogen form on leaf morphogenesis in tobacco. J Exp Bot 51:227–237
Acknowledgements
We thank Fabienne Granier (Unité de Biologie Cellulaire, INRA Versailles, France) and Adeline Kamara (Unité de la Nutrition Azotée des Plantes, INRA Versailles, France) for their technical help and Joël Talbotec and François Gosse (Unité de la Nutrition Azotée des Plantes, INRA Versailles, France) for their great help in taking care of the plants. This work was partly supported by the Gabi-Génoplante joint project AF2001-092 and by the EU contract BIO4CT97-2231.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferrario-Méry, S., Bouvet, M., Leleu, O. et al. Physiological characterisation of Arabidopsis mutants affected in the expression of the putative regulatory protein PII. Planta 223, 28–39 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-005-0063-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-005-0063-5