Abstract
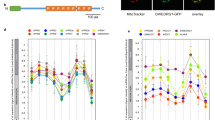
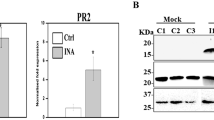
Ribosome-inactivating proteins (RIPs) are N-glycosidases that remove a specific adenine from the sarcin/ricin (S/R) loop of the large rRNA, thus arresting protein synthesis at the translocation step. In the present study, ME1, a type-1 RIP, was cloned and sequenced from storage roots of Mirabilis expansa (Ruiz & Pavon). The full-length cDNA sequence of ME1 has 1,129 nucleotides with an open reading frame of 951 nucleotides representing 317 amino acids. Nucleotide analysis revealed that the N-terminal region of ME1 was cleaved, and the mature protein started at amino acid 34. ME1 showed very close similarities to MAP and MAP-4 from Mirabilis jalapa. Southern blot analysis revealed the presence of two homologous genes for ME1 cDNA in M. expansa. Northern blot analysis showed high levels of ME1 transcripts in primary and storage roots. Interestingly, jasmonic acid induced ME1 transcript expression in cell suspension cultures of M. expansa; however, the production of ME1 protein was not enhanced as observed by Western blot analysis. Our data suggest that ME1 has the ability to depurinate its own mRNA, thus inhibiting its translation. These observations suggest a possible mechanism by which ME1 protein levels are post-transcriptionally regulated.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- JA:
-
jasmonic acid
- MAP:
-
Mirabilis antiviral protein
- PAP:
-
pokeweed antiviral protein
- RACE:
-
rapid amplification of cDNA ends
- RIP:
-
ribosome-inactivating protein
References
Aron GM, Irvin JD (1980) Inhibition of herpes simplex virus multiplication by the pokeweed antiviral protein. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 17:1302–1303
Barbieri L, Aron GM, Irvin JD, Stirpe F (1982) Purification and partial characterization of another form of the antiviral protein from the seeds of Phytolacca americana L. (pokeweed). Biochem J 203:55–56
Barbieri L, Gorini P, Valbonesi P, Castiglioni P, Stirpe F (1994) Unexpected activity of saporins. Nature 372:624
Barbieri L, Valbonesi P, Bonora E, Gorini P, Bolognesi A, Stirpe F (1997) Polynucleotide:adenosine glycosidase activity of ribosome-inactivating proteins: effect on DNA, RNA and poly (A). Nucleic Acids Res 25:518–522
Becker W, Apel K (1993) Differences in gene expression between natural and artificially induced leaf senescence. Planta 189:74–79
Bolognesi A, Polito L, Lubelli C, Barbieri L, Parente A, Stirpe F (2002) Ribosome-inactivating and adenine polynucleotide glycosylase activities in Mirabilis jalapa L. tissues. J Biol Chem 277:13709–13716
Carmona MJ, Hernandez-Lucas C, San Martin C, Gonzalez P, Garcia-Olmedo F (1997) Subcellular localization of type I thionins in the endosperms of wheat and barley. Protoplasma 173:1–7
Chaudhry B, Műller-Uri F, Cameron-Mills V, Gough S, Simpson D, Skriver K, Mundy J (1994) The barley 60 kDa jasmonate-induced protein (JIP60) is a novel ribosome-inactivating protein. Plant J 6:815–824
Den Hartog MT, Lubelli C, Boon L, Heerkens S, Ortiz Buijsse AP, de Boer M, Stirpe F (2002) Cloning and expression of cDNA coding for bouganin. Eur J Biochem 269:1772–1779
Di Maro A, Ferranti P, Mastronicola M, Polito L, Bolognesi A, Stirpe F, Malorni A, Parente A (2001) Reliable sequence determination of ribosome-inactivating proteins by combining electrospray mass spectrometry and Edman degradation. J Mass Spectrom 36:38–46
Emanuelsson O, von Heijne G (2001) Prediction of organellar targeting signals. Biochim Biophys Acta 1541:114–119
Emanuelsson O, Nielsen H, Brunak S, von Heijne G (2000) Predicting subcellular localization of proteins based on their N-terminal amino acid sequence. J Mol Biol 300:1005–1016
Endo Y, Tsurugi K (1988) RNA N-glycosidase activity of ricin A-chain: mechanism of action of the toxic lectin ricin on eukaryotic ribosomes. J Biol Chem 263:8735–8739
Endo Y, Mitsui K, Motizuki M, Tsurugi K (1987) The mechanism of action of ricin and related toxic lectins on eukaryotic ribosomes: the site and the characteristics of the modification in 28S ribosomal RNA caused by the toxins. J Biol Chem 262:5908–5912
Habuka N, Murakami Y, Noma M, Kudo T, Horikoshi K (1989) Amino acid sequence of Mirabilis antiviral protein, total synthesis of its gene and expression in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 264:6629–6637
Hudak KA, Wang P, Tumer NE (2000) A novel mechanism for inhibition of translation by pokeweed antiviral protein: depurination of the capped RNA template. RNA 6:369–380
Humphreys WJ (1978) Critical point drying of cryo-fractured specimens. In: Hayat MA (ed) Principles and techniques of scanning electron microscopy. Van Nostraud Reinhold, New York, pp 136–169
Irvin JD (1975) Purification and partial characterization of the antiviral protein from Phytolacca americana which inhibits eukaryotic protein synthesis. Arch Biochem Biophys 169:522–528
Irvin JD (1983) Pokeweed antiviral protein. Pharmacol Ther 21:371–87
Irvin JD, Uckun FM (1992) Pokeweed antiviral protein: ribosome inactivation and therapeutic applications. Pharmacol Ther 55:279–302
Irvin JD, Kelly T, Robertus JD (1980) Purification and properties of a second antiviral protein from Phytolacca americana which inactivates eukaryotic ribosomes. Arch Biochem Biophys 200:418–425
Kataoka J, Habuka N, Furuno M, Miyano M, Takanami Y, Koiwai A (1991) DNA sequence of Mirabilis antiviral protein (MAP), a ribosome-inactivating protein with an antiviral property, from Mirabilis jalapa L. and its expression in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 266:8426–8430
Kubo S, Ikeda T, Imaizumi S, Takanami Y, Mikami Y (1990) A potent plant virus inhibitor found in Mirabilis jalapa L. Ann Phytopath Soc Jpn 56:481–487
Lin Q, Chen ZC, Antoniw JF, White RF (1991) Isolation and characterization of a cDNA clone encoding the anti-viral protein from Phytolacca americana. Plant Mol Biol 17:609–14
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Nielsen K, Boston RS (2001) Ribosome-inactivating proteins: a plant perspective. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 52:785–816
Parikh BA, Coetzer C, Tumer NE (2002) Pokeweed antiviral protein regulates the stability of its own mRNA by a mechanism that requires depurination, but can be separated from depurination of the alpha-sarcin/ricin loop of rRNA. J Biol Chem 277:41428–41437
Ready MP, Brown DT, Robertus JD (1986) Extracellular localization of pokeweed protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:5053-5056
Reinbothe S, Reinbothe C, Parthier B (1993) Methyl jasmonate represses translation initiation of a specific set of mRNAs in barley. Plant J 4:459–467
Reinbothe S, Reinbothe C, Lehman J, Becker W, Parthier B (1994) JIP60, a methyl jasmonate-induced ribosome-inactivating protein involved in plant stress reactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:7012–7016
Reinbothe C, Parthier B, Reinbothe S (1997) Temporal pattern of jasmonate-induced alterations in gene expression of barley leaves. Planta 201:281–287
Sambrook J, Fritsch E F, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Sembdner G, Parthier B (1993) The biochemistry and the physiological and molecular actions of jasmonates. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 44:569–589
Song S-K, Choi Y, Moon YH, Kim S-G, Choi YD, Lee JS (2000) Systemic induction of a Phytolacca insularis antiviral protein gene by mechanical wounding, jasmonic acid, and abscisic acid. Plant Mol Biol 43:439–450
Stirpe F, Barbieri L, Batelli MG, Soria M, Lappi DA (1992) Ribosome-inactivating proteins from plants: present status and future prospects. Bio/Technology 10:405–412
Tully RE, Beevers H (1976) Protein bodies of the castor bean endosperm. Plant Physiol 58:710–716
Tumer NE, Hwang D-J, Bonness M (1997) C-terminal deletion mutant of pokeweed antiviral protein inhibits viral infection but does not depurinate ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:3866–3871
Ussery MA, Irvin JD, Hardesty B (1977) Inhibition of poliovirus replication by a plant antiviral peptide. Ann NY Acad Sci 284:431–440
Vivanco JM, Flores HE (2000) Biosynthesis of ribosome-inactivating proteins from callus and cell suspension cultures of Mirabilis expansa (Ruiz & Pavon). Plant Cell Rep 19:1033–1039
Vivanco JM, Savary BJ, Flores HE (1999) Characterization of two novel type I ribosome-inactivating proteins from the storage roots of the Andean crop Mirabilis expansa. Plant Physiol 119:1447–1456
Woodhead M, Davies HV, Brennan RM, Taylor MA (1998) The isolation of genomic DNA from blackcurrant (Ribes nigrum L.). Mol Biotechnol 9:243–6
Wright L, Rine B (1989) Transmission electron microscopy and immunocytochemical studies of yeast: analysis of HMG-GoA reductase overproduction by electron microscopy. Mol Cell Biol 31:473–512
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vepachedu, R., Bais, H.P. & Vivanco, J.M. Molecular characterization and post-transcriptional regulation of ME1, a type-I ribosome-inactivating protein from Mirabilis expansa . Planta 217, 498–506 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-003-1014-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-003-1014-7