Abstract.
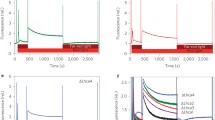
Mature chromoplasts from daffodil (Narcissus pseudonarcissus) flowers, although devoid of thylakoid structures, contain immunologically detectable α-subunits of ATP-synthase (H+-transporting ATP phosphohydrolase; EC 3.6.3.14). To show the presence of the entire functional protein complex, chromoplast membrane proteins were solubilized and reconstituted in phosphatidylcholine liposomes. The membranes were energized by an acid-base transition in the presence of a K+/valinomycin diffusion potential, and the initial rate of ATP synthesis was measured with a luciferin/luciferase assay. In addition, by demonstrating NADPH-dependent ATP synthesis, we show that an NAD(P)H-dependent respiratory redox pathway in chromoplasts, previously identified as an important constituent of the carotene desaturation system, proceeds concomitant with membrane energization.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morstadt, L., Gräber, P., de Pascalis, L. et al. Chemiosmotic ATP synthesis in photosynthetically inactive chromoplasts from Narcissus pseudonarcissus L. linked to a redox pathway potentially also involved in carotene desaturation. Planta 215, 134–140 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-001-0724-y
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-001-0724-y