Abstract.
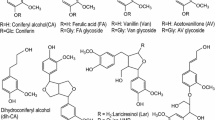
Cell-suspension cultures were produced from transgenic tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L. ) plants harboring a constitutively expressed alfalfa cinnamate 4-hydroxylase (C4H) transgene. Increased levels of C4H enzyme activity in the transgenic cultures were observed only following exposure of the cells to yeast elicitor, although alfalfa C4H transcripts were expressed at a high level from the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter in the absence of elicitation. Increased expression of C4H in elicited cell-suspension cultures had no appreciable effect on the HPLC profiles of soluble phenolic compounds. However, levels of one compound, subsequently identified as 3,5-dimethoxy-4-hydroxy acetophenone (acetosyringone), were strongly elevated in the wall-bound phenolic fraction. The results are discussed in relation to the correlation between C4H activity and the synthesis of 3,5-dimethylated hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives in tobacco.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blount, J.W., Masoud, S., Sumner, L.W. et al. Over-expression of cinnamate 4-hydroxylase leads to increased accumulation of acetosyringone in elicited tobacco cell-suspension cultures. Planta 214, 902–910 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-001-0701-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-001-0701-5