Abstract.
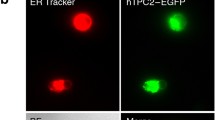
Nuclear envelope (NE) cisternal Ca2+ and cytosolic ATP are required for nuclear-pore-complex- (NPC-) mediated transport of DNAs, RNAs, transcription factors and other large molecules. Isolated cardiomyocyte nuclei, capable of macromolecular transport (MMT), have intrinsic NPC ion channel behavior. The large ion conductance (γ) activity of the NPC channel (NPCC) is blocked by the NPC monoclonal antibody mAb414, known to block MMT, and is also silenced during periods of MMT. In cardiomyocytes, neither cytosolic Ca2+ nor ATP alone directly affects NPCC gating. To test the role of Ca2+ and ATP in NPCC activity, we carried out the present patch-clamp study with the pipette attached to the outer NE membrane of nuclei isolated from cultured Dunning G prostate cancer cells. Our investigations demonstrate that in these isolated nuclei neither cytosolic Ca2+ nor ATP alone directly affects NPCC gating. However, when simultaneously applied to the bath and pipette, they transiently silence NPCC activity through stimulation of MMT by raising the Ca2+ concentration in the NE cisterna ([Ca2+]NE). Our fluorescence microscopy observations with nuclear-targeted macromolecular fluorochromes (B-phycoerythrin and plasmid for the enhanced green fluorescence protein EGFP, pEGFP-C1) and with FITC-labeled RNA support the view that channel silence accompanies MMT. Repeated Ca2+ loading of the NE with Ca2+ and ATP, after unloading with 1–5 µM inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3), thapsigargin (TSG) or 5 mM BAPTA or EGTA, failed to affect channel gating. This result indicates that other factors are involved in this phenomenon and that they are exhausted during the first cycle of NE Ca2+ loading/unloading – in agreement with current theories of NPC-mediated MMT. The results explain how Ca2+ and IP3 waves may convert the NE into an effective Ca2+ barrier and, consequently, affect the regulation of gene activity and expression through their feedback on MMT and NPCC gating. Thus, [Ca2+]NE regulation by intracellular messengers is an effective mechanism for synchronizing gene activity and expression to the cellular rhythm.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received after revision: 4 October 1999
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bustamante, J., Michelette, E., Geibel, J. et al. Calcium, ATP and nuclear pore channel gating. Pflügers Arch – Eur J Physiol 439, 433–444 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004249900189
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004249900189