Abstract
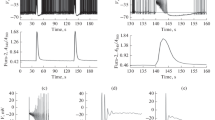
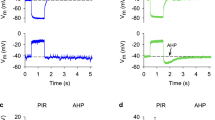
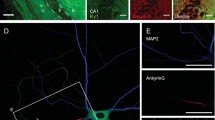
Neuronal cell firing is crucial to nerve-nerve communication. The ability to produce consecutive action potentials is related to the activation of inward currents after each upstroke. If fast Na current is indeed responsible for the overshoot, it is still unclear which current drives membrane voltage to the Na threshold. In this study we present evidence that in adult rat sensory neurones a dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca channel exists in addition to the well characterized L-type, or high-threshold Ca channel. During stimulated action potential trains, L-type Ca channels open during the excitation wave, whereas activity of the other dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca channel was observed primarily between action potentials. This second Ca pathway shows remarkably long openings at negative potentials after a series of positive prepulses. The nerve action potential and the repetitive firing work as a physiological Ca channel facilitation mechanism. Therefore, we suggest that this novel Ca conductance provides inward current, between two consecutive action potentials, able to modulate the frequency of neuronal bursts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References[954-963]
Artalejo CR, Mogul DJ, Perlman R, Fox AP (1991) Three types of bovine chromaffin cell Ca channels: facilitation increase the opening probability of a 27 pS channel. J Physiol (Lond) 444: 231–240
Carbone E, Lux HD (1984) A low voltage-activated, fully inactivating Ca channel in vertebrate sensory neurones. Nature 310: 501–502
Catteral WA (1991) Functional subunit structure of voltage-gated calcium channels. Science 253:1499–1500
Catteral WA (1991) Structure and function of voltage-gated sodium and calcium channels. Curr Opin Neurobiol 1:5–13
Ferroni A, Mancinelli E, Camagni S, Wanke E (1989) Two high voltage-activated calcium currents are present in isolation in adult rat spinal neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 159:379–384
Forti L, Pietrobon D (1993) Functional diversity of L-type calcium channels in rat cerebellar neurons. Neuron 10:437–450
Fox AP, Nowycky MC, Tsien RW(1987) Single channel recordings of three types of calcium channels in chick sensory neurons. J Physiol (Lond) 394:173–200
Galli A, Ferroni A, Bertollini L, Mazzanti M (1994) Inactivation of single Ca2+ channels in rat sensory neurons by extracellular Ca2+ J Physiol (Lond) 477:15–26
Hess P, Lansman JB, Tsien RW (1984) Different modes of Ca channel gating behavior favoured by dihydropyridine Ca agonists and antagonists. Nature 311:538–544
Imredy JP, Yue DT (1992) Submicroscopic Ca2+ diffusion mediates inhibitory coupling between individual Ca2+ channels. Neuron 9:197–207
Imredy JP, Yue DT (1994) Mechanism of Ca-sensitive inactivation of L-type Ca Channels. Neuron 12:1301–1318
Johnson BD, Byerly L (1993) cytoskeletal mechanism for Ca2+ channel metabolic dependence and inactivation by intra-cellular Ca2+ Neuron 10:797–804
Kavalali Ege T, Plummer MR (1994) Selective potentiation of a novel calcium channel in rat hippocampal neurones. J Physiol (Lond) 480:475–484
Kramer RH, Zucker R (1985) Calcium dependent inward current in Aplysia bursting pace-maker neurones. J Physiol (Lond) 362:107–130
Llinas R (1988) The intrinsic electrophysiological properties of mammalian neurons: insights into central nervous system function. Science 242:1654–1664
Llinas R, Sugimory M, Cherksey B (1989) Voltage-dependent calcium conductance in mammalian neurons. Ann NY Acad Sci 560:103–111
Maccaferri G, Mangoni M, Lazzari L, DiFrancesco D (1993) Properties of the hyperpolarization-activated current in rat hyppocampal CA1 pyramidal cells. J Neurophysiol 69:2129–2136
Mazzanti M, DeFelice LJ (1987) Na channel kinetics during the spontaneous beat in heart cells. Biophys J 52:95–100
Mazzanti M, DeFelice LJ (1990) Ca channel gating during cardiac action potentials. Biophys J 58:1059–1065
Mazzanti M, DeFelice LJ, Liu YM (1991) Gating of L-type Ca channels in embryonic chick ventricle cell: dependence on voltage, current, and channel density. J Physiol (Lond) 443: 307–334
Mazzanti M, Galli A, Ferroni A (1992) Effect of firing rate on calcium permeability in adult neurons during spontaneous action potential. Biophys J 63:926–934
McCleskey EW (1994) Calcium channels: cellular roles and molecular mechanisms. Curr Opin Neurobiol 4:304–312
Mintz JM, Adams ME, Bean BB (1992) P-type calcium channels in rat central and peripheral neurons. Neuron 9:85–98
Mogul DJ, Fox A (1991) Evidence for multiple types of Ca2+ channels in acutely isolated hippocampal Ca3 neurones of the guinea-pig. J Physiol (Lond) 433:259–281
Nowycky MC, Fox AP, Tsien RW (1985) Three types of neuronal calcium channel with different calcium agonist sensitivity. Nature 316:440–443
Pietrobon D, Hess P (1990) Novel mechanism of voltage dependent gating in L-type Ca channels. Nature 346:651–655
Sather WA, Yang J, Tsien R (1994) Structural basis of ion channel permeation and selectivity. Curr Opin Neurobiol 4:313–323
Swandulla D, Carbone E, Lux HD (1991) Calcium channel classification account for neuronal calcium channel diversity Trends Neurosci 14:46–51
Thibault O, Porter NM, Landfield PW (1993) Low Ba2+ and Ca2+ induce a sustained high probability of repolarization openings of L-type Ca2+ channels in hippocampal neurons: physiological implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 90: 11792–11796
Wanke E, Ferroni A, Malgaroli A, Ambrosini A, Pozzan T, Meldolesi J (1987) Activation of a muscarinic receptor selectively inhibits a rapidly inactivated Ca2+ current in rat sympathetic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 84:4313–4317
Wanke E, Becchetti A, Biella G, DelBo R, Ferroni A (1992) A quantitative description of low- and high-threshold Ca2+ spikes in rat sensory neurons: a perforated-patch study. Eur J Neurosci 4:723–732
Wellis DP, DeFelice LJ, Mazzanti M (1990) Outward sodium current in beating heart cells. Biophys J 57:41–48
Yang J, Ellinor PT, Sather WA, Fang Zhang JI, Tsien RW (1993) Molecular determinants of Ca2+ selectivity and ion permeation in L-type Ca2+ channels. Nature 366:158–161
Yue DT, Marban E (1990) Permeation in the dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca channel: multi ion occupancy but no mole-fraction effect between Ba and Ca. J Gen Physiol 95:911–939
Yue DT, Backx PH, Imredy JP (1991) Ca-sensitive inactivation in the gating of single Ca channels. Science 250:1735–1738
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferroni, A., Galli, A. & Mazzanti, M. Functional role of low-voltage-activated dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca channels during the action potential in adult rat sensory neurones. Pflügers Arch. 431, 954–963 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240050091
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240050091