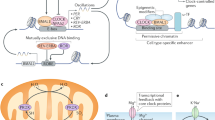
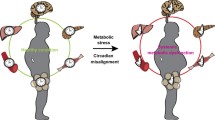
Abstract
Circadian rhythms are generated by the circadian clock, a self-sustained internal timing system that exhibits 24-h rhythms in the body. In mammals, circadian rhythms are driven by a central clock located in suprachiasmatic nucleus and various peripheral clocks located in different tissues and organs of the body. Many cellular, behavioral, and physiological processes are regulated by the circadian clock in coordination with environmental cues. The process of metabolism is also under circadian regulation. Loss of synchronization between the internal clock and environmental zeitgebers results in disruption of the circadian rhythms that seriously impacts metabolic homeostasis leading to changed eating behavior, altered glucose and lipid metabolism, and weight gain. This in turn augments the risk of having various cardio-metabolic disorders such as obesity, diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular disease. This review sheds light on circadian rhythms and their role in metabolism with the identification of gaps in the current knowledge that remain to be explored in these fields. In this review, the molecular mechanisms underlying circadian rhythms have been elaborated first. Then, the focus has been kept on explaining the physiological significance of circadian rhythms in regulating metabolism. Finally, the implications for metabolism when these rhythms are disrupted due to genetic mutations or social and occupational needs enforced by modern lifestyle have been discussed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison KC, Ahima RS, O’Reardon JP, Dinges DF, Sharma V, Cummings DE, Heo M, Martino NS, Stunkard AJ (2005) Neuroendocrine profiles associated with energy intake, sleep, and stress in the night eating syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 90:6214–6217. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2005-1018
Anea CB, Zhang M, Stepp DW, Simkins GB, Reed G, Fulton DJ, Rudic RD (2009) Vascular disease in mice with a dysfunctional circadian clock. Circulation 119:1510–1517. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.827477
Antunes LC, Levandovski R, Dantas G, Caumo W, Hidalgo MP (2010) Obesity and shift work: chronobiological aspects. Nutr Res Rev 23:155–168. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954422410000016
Ashby T, Louis M (2019) Circadian misalignment and cardiovascular risk. Cardiovasc Innov Appl 3:435–440. https://doi.org/10.15212/CVIA.2017.0070
Asher G, Sassone-Corsi P (2015) Time for food: the intimate interplay between nutrition, metabolism, and the circadian clock. Cell 161:84–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.03.015
Astiz M, Heyde I, Oster H (2019) Mechanisms of communication in the mammalian circadian timing system. Int J Mol Sci 20:343. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020343
Bäckhed F, Manchester JK, Semenkovich CF, Gordon JI (2007) Mechanisms underlying the resistance to diet-induced obesity in germ-free mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:979–984. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0605374104
Balieiro LCT, Rossato LT, Waterhouse J, Paim SL, Mota MC, Crispim CA (2014) Nutritional status and eating habits of bus drivers during the day and night. Chronobiol Int 31:1123–1129. https://doi.org/10.3109/07420528.2014.957299
Balsalobre A (2002) Clock genes in mammalian peripheral tissues. Cell Tissue Res 309:193–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-002-0585-0
Barclay JL, Husse J, Bode B, Naujokat N, Meyer-Kovac J, Schmid SM, Lehnert H, Oster H (2012) Circadian desynchrony promotes metabolic disruption in a mouse model of shiftwork. PLoS One 7:e37150. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0037150
Barclay JL, Shostak A, Leliavski A, Tsang AH, Jöhren O, Müller-Fielitz H, Landgraf D, Naujokat N, van der Horst GT, Oster H (2013) High-fat diet-induced hyperinsulinemia and tissue-specific insulin resistance in cry-deficient mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 304:E1053–E1063. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00512.2012
Bo S, Ciccone G, Durazzo M, Ghinamo L, Villois P, Canil S, Gambino R, Cassader M, Gentile L, Cavallo-Perin P (2011) Contributors to the obesity and hyperglycemia epidemics. A prospective study in a population-based cohort. Int J Obes 35:1442–1449. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2011.5
Bonham MP, Bonnell EK, Huggins CE (2016) Energy intake of shift workers compared to fixed day workers: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Chronobiol Int 33:1086–1100. https://doi.org/10.1080/07420528.2016.1192188
Buchvold HV, Pallesen S, Waage S, Bjorvatn BJ (2018) Shift work schedule and night work load: effects on body mass index – a four-year longitudinal study. Scand J Work Environ Health 44:251–257. https://doi.org/10.5271/sjweh.3702
Bugge A, Feng D, Everett LJ, Briggs ER, Mullican SE, Wang F, Jager J, Lazar MA (2012) Rev-erbα and Rev-erbβ coordinately protect the circadian clock and normal metabolic function. Genes Dev 26:657–667. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.186858.112
Burch JB, Yost MG, Johnson W, Allen E (2005) Melatonin, sleep, and shift work adaptation. J Occup Environ Med 47:893–901. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.jom.0000177336.21147.9f
Cailotto C, Lei J, van der Vliet J, van Heijningen C, van Eden CG, Kalsbeek A, Pévet P, Buijs RM (2009) Effects of nocturnal light on (clock) gene expression in peripheral organs: a role for the autonomic innervation of the liver. PLoS One 4:e5650. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0005650
Canaple L, Rambaud J, Dkhissi-Benyahya O, Ba R, Tan NS, Michalik L, Delaunay F, Wahli W, Laudet V (2006) Reciprocal regulation of brain and muscle Arnt-like protein 1 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α defines a novel positive feedback loop in the rodent liver circadian clock. Mol Endocrinol 20:1715–1727. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2006-0052
Castro C, Briggs W, Paschos GK, FitzGerald GA, Griffin JL (2015) A metabolomic study of adipose tissue in mice with a disruption of the circadian system. Mol BioSyst 11:1897–1906. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5mb00032g
Chaix A, Zarrinpar A, Miu P, Panda S (2014) Time-restricted feeding is a preventative and therapeutic intervention against diverse nutritional challenges. Cell Metab 20:991–1005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2014.11.001
Chaix A, Lin T, Le HD, Chang MW, Panda S (2019) Time-restricted feeding prevents obesity and metabolic syndrome in mice lacking a circadian clock. Cell Metab 29:303–319.e304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2018.08.004
Chaudhari A, Gupta R, Makwana K, Kondratov R (2017) Circadian clocks, diets and aging. Nutr Healthy Aging 4:101–112. https://doi.org/10.3233/NHA-160006
Chen X, Devaraj S (2018) Gut microbiome in obesity, metabolic syndrome, and diabetes. Curr Diab Rep 18:129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-018-1104-3
Chen L, Yang G (2014) PPARs integrate the mammalian clock and energy metabolism. PPAR Res 2014:6–6. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/653017
Chen L, Yang G (2015) Recent advances in circadian rhythms in cardiovascular system. Front Pharmacol 6:71–71. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2015.00071
Chung S, Son GH, Kim K (2011) Circadian rhythm of adrenal glucocorticoid: its regulation and clinical implications. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) - Mol Basis Dis 1812:581–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.02.003
Chung H, Chou W, Sears DD, Patterson RE, Webster NJG, Ellies LG (2016) Time-restricted feeding improves insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis in a mouse model of postmenopausal obesity. Metabolism 65:1743–1754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2016.09.006
Cipolla-Neto J, Amaral FG, Afeche SC, Tan DX, Reiter RJ (2014) Melatonin, energy metabolism, and obesity: a review. J Pineal Res 56:371–381. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpi.12137
Coomans CP, van den Berg SA, Houben T, van Klinken JB, van den Berg R, Pronk AC, Havekes LM, Romijn JA, van Dijk KW, Biermasz NR, Meijer JH (2013) Detrimental effects of constant light exposure and high-fat diet on circadian energy metabolism and insulin sensitivity. FASEB J 27:1721–1732. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.12-210898
Crnko S, Du Pré BC, Sluijter JPG, Van Laake LW (2019) Circadian rhythms and the molecular clock in cardiovascular biology and disease. Nat Rev Cardiol 16:437–447. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41569-019-0167-4
Curtis AM, Cheng Y, Kapoor S, Reilly D, Price TS, Fitzgerald GA (2007) Circadian variation of blood pressure and the vascular response to asynchronous stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:3450–3455. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0611680104
Dallmann R, Weaver DR (2010) Altered body mass regulation in male mPeriod mutant mice on high-fat diet. Chronobiol Int 27:1317–1328. https://doi.org/10.3109/07420528.2010.489166
Damiola F, Le Minh N, Preitner N, Kornmann B, Fleury-Olela F, Schibler U (2000) Restricted feeding uncouples circadian oscillators in peripheral tissues from the central pacemaker in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Genes Dev 14:2950–2961. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.183500
Di Lorenzo L, De Pergola G, Zocchetti C, L'Abbate N, Basso A, Pannacciulli N, Cignarelli M, Giorgino R, Soleo L (2003) Effect of shift work on body mass index: results of a study performed in 319 glucose-tolerant men working in a southern Italian industry. Int J Obes 27:1353–1358. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802419
Dubrovsky YV, Samsa WE, Kondratov RV (2010) Deficiency of circadian protein CLOCK reduces lifespan and increases age-related cataract development in mice. Aging 2:936–944. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.100241
Duez H, Staels B (2008) The nuclear receptors rev-erbs and RORs integrate circadian rhythms and metabolism. Diab Vasc Dis Res 5:82–88. https://doi.org/10.3132/dvdr.2008.0014
Duez H, Staels B (2009) Rev-erb-alpha: an integrator of circadian rhythms and metabolism. J Appl Physiol (1985) 107:1972–1980. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00570.2009
Eckel-Mahan K, Sassone-Corsi P (2013) Metabolism and the circadian clock converge. Physiol Rev 93:107–135. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00016.2012
Einarson TR, Acs A, Ludwig C, Panton UH (2018) Prevalence of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes: a systematic literature review of scientific evidence from across the world in 2007-2017. Cardiovasc Diabetol 17:83–83. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-018-0728-6
El Aidy S, Merrifield CA, Derrien M, van Baarlen P, Hooiveld G, Levenez F, Doré J, Dekker J, Holmes E, Claus SP, Reijngoud D-J, Kleerebezem M (2013) The gut microbiota elicits a profound metabolic reorientation in the mouse jejunal mucosa during conventionalisation. Gut 62:1306–1314. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2011-301955
Farhud D, Aryan Z (2018) Circadian rhythm, lifestyle and health: a narrative review. Iran J Public Health 47:1068–1076
Federation IDJBIDF (2006) Diabetes atlas. Available via DIALOG. https://www.idf.org/e-library/epidemiology-research/diabetes-atlas/22-atlas-3rd-edition.html
Fisk AS, Tam SKE, Brown LA, Vyazovskiy VV, Bannerman DM, Peirson SN (2018) Light and cognition: roles for circadian rhythms, sleep, and arousal. Front Neurol 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2018.00056
Fonken LK, Nelson RJ (2014) The effects of light at night on circadian clocks and metabolism. Endocr Rev 35:648–670. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2013-1051
Fonken LK, Workman JL, Walton JC, Weil ZM, Morris JS, Haim A, Nelson RJ (2010) Light at night increases body mass by shifting the time of food intake. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:18664–18669. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1008734107
Fonken LK, Lieberman RA, Weil ZM, Nelson RJ (2013) Dim light at night exaggerates weight gain and inflammation associated with a high-fat diet in male mice. Endocrinology 154:3817–3825. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2013-1121
Fonken LK, Weil ZM, Nelson RJ (2013) Dark nights reverse metabolic disruption caused by dim light at night. Obesity (Silver Spring) 21:1159–1164. https://doi.org/10.1002/oby.20108
Garaulet M, Gomez-Abellan P (2014) Timing of food intake and obesity: a novel association. Physiol Behav 134:44–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2014.01.001
Gómez-Abellán P, Hernández-Morante JJ, Luján JA, Madrid JA, Garaulet M (2007) Clock genes are implicated in the human metabolic syndrome. Int J Obes 32:121–128. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803689
Gooley JJ, Chamberlain K, Smith KA, Khalsa SBS, Rajaratnam SMW, Van Reen E, Zeitzer JM, Czeisler CA, Lockley SW (2011) Exposure to room light before bedtime suppresses melatonin onset and shortens melatonin duration in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:E463–E472. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2010-2098
Grimaldi B, Bellet MM, Katada S, Astarita G, Hirayama J, Amin RH, Granneman JG, Piomelli D, Leff T, Sassone-Corsi P (2010) PER2 controls lipid metabolism by direct regulation of PPARγ. Cell Metab 12:509–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2010.10.005
Guerrero-Vargas NN, Espitia-Bautista E, Buijs RM, Escobar C (2018) Shift-work: is time of eating determining metabolic health? Evidence from animal models. Proc Nutr Soc 77:199–215. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0029665117004128
Guillaumond F, Dardente H, Giguère V, Cermakian N (2005) Differential control of Bmal1 circadian transcription by REV-ERB and ROR nuclear receptors. J Biol Rhythm 20:391–403. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748730405277232
Ha M, Park J (2005) Shiftwork and metabolic risk factors of cardiovascular disease. J Occup Health 47:89–95. https://doi.org/10.1539/joh.47.89
Haraguchi A, Fukuzawa M, Iwami S, Nishimura Y, Motohashi H, Tahara Y, Shibata S (2018) Night eating model shows time-specific depression-like behavior in the forced swimming test. Sci Rep 8:1081. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-19433-8
Harfmann BD, Schroder EA, Kachman MT, Hodge BA, Zhang X, Esser KA (2016) Muscle-specific loss of Bmal1 leads to disrupted tissue glucose metabolism and systemic glucose homeostasis. Skelet Muscle 6:12–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13395-016-0082-x
Hatanaka F, Matsubara C, Myung J, Yoritaka T, Kamimura N, Tsutsumi S, Kanai A, Suzuki Y, Sassone-Corsi P, Aburatani H, Sugano S, Takumi T (2010) Genome-wide profiling of the core clock protein BMAL1 targets reveals a strict relationship with metabolism. Mol Cell Biol 30:5636–5648. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00781-10
Hirayama J, Alifu Y, Hamabe R, Yamaguchi S, Tomita J, Maruyama Y, Asaoka Y, K-i N, Tamaru T, Takamatsu K, Takamatsu N, Hattori A, Nishina S, Azuma N, Kawahara A, Kume K, Nishina H (2019) The clock components Period2, Cryptochrome1a, and Cryptochrome2a function in establishing light-dependent behavioral rhythms and/or total activity levels in zebrafish. Sci Rep 9:196. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-37879-8
Ho JM, Barf RP, Opp MR (2016) Effects of sleep disruption and high fat intake on glucose metabolism in mice. Psychoneuroendocrinology 68:47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2016.02.024
Hu D, Mao Y, Xu G, Liao W, Ren J, Yang H, Yang J, Sun L, Chen H, Wang W, Wang Y, Sang X, Lu X, Zhang H, Zhong S (2019) Time-restricted feeding causes irreversible metabolic disorders and gut microbiota shift in pediatric mice. Pediatr Res 85:518–526. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-018-0156-z
Huang PL (2009) A comprehensive definition for metabolic syndrome. Dis Model Mech 2:231–237. https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.001180
Huang R-C (2018) The discoveries of molecular mechanisms for the circadian rhythm: the 2017 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Biom J 41:5–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bj.2018.02.003
Husse J, Eichele G, Oster H (2015) Synchronization of the mammalian circadian timing system: light can control peripheral clocks independently of the SCN clock. BioEssays 37:1119–1128. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.201500026
Ikeda R, Tsuchiya Y, Koike N, Umemura Y, Inokawa H, Ono R, Inoue M, Sasawaki Y, Grieten T, Okubo N, Ikoma K, Fujiwara H, Kubo T, Yagita K (2019) REV-ERBα and REV-ERBβ function as key factors regulating mammalian circadian output. Sci Rep 9:10171. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-46656-0
Itani O, Kaneita Y, Murata A, Yokoyama E, Ohida T (2011) Association of onset of obesity with sleep duration and shift work among Japanese adults. Sleep Med 12:341–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2010.09.007
Jagannath A, Taylor L, Wakaf Z, Vasudevan SR, Foster RG (2017) The genetics of circadian rhythms, sleep and health. Hum Mol Genet 26:R128–R138. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddx240
Jing E, Emanuelli B, Hirschey MD, Boucher J, Lee KY, Lombard D, Verdin EM, Kahn CR (2011) Sirtuin-3 (Sirt3) regulates skeletal muscle metabolism and insulin signaling via altered mitochondrial oxidation and reactive oxygen species production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:14608–14613. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1111308108
Jones SE, Lane JM, Wood AR, van Hees VT, Tyrrell J, Beaumont RN, Jeffries AR, Dashti HS, Hillsdon M, Ruth KS, Tuke MA, Yaghootkar H, Sharp SA, Jie Y, Thompson WD, Harrison JW, Dawes A, Byrne EM, Tiemeier H, Allebrandt KV, Bowden J, Ray DW, Freathy RM, Murray A, Mazzotti DR, Gehrman PR, Lawlor DA, Frayling TM, Rutter MK, Hinds DA, Saxena R, Weedon MN (2019) Genome-wide association analyses of chronotype in 697,828 individuals provides insights into circadian rhythms. Nat Commun 10:343. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-08259-7
Kalsbeek A, Fliers E, Romijn JA, la Fleur SE, Wortel J, Bakker O, Endert E, Buijs RM (2001) The suprachiasmatic nucleus generates the diurnal changes in plasma leptin levels. Endocrinology 142:2677–2685. https://doi.org/10.1210/endo.142.6.8197
Karatsoreos IN, Bhagat S, Bloss EB, Morrison JH, McEwen BS (2011) Disruption of circadian clocks has ramifications for metabolism, brain, and behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sc U S A 108:1657–1662. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1018375108
Karlsson B, Knutsson A, Lindahl B (2001) Is there an association between shift work and having a metabolic syndrome? Results from a population based study of 27 485 people. Occup Environ Med 58:747–752. https://doi.org/10.1136/oem.58.11.747
Kim M-J, Son K-H, Park H-Y, Choi D-J, Yoon C-H, Lee H-Y, Cho E-Y, Cho M-C (2013) Association between shift work and obesity among female nurses: Korean nurses’ survey. BMC Public Health 13:1204. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-13-1204
Kojetin DJ, Burris TP (2014) REV-ERB and ROR nuclear receptors as drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov 13:197–216. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd4100
Lamia KA, Evans RM (2010) Metabolism Tick, tock, a β-cell clock. Nature 466(7306):571–572. https://doi.org/10.1038/466571a
Lamia KA, Storch K-F, Weitz CJ (2008) Physiological significance of a peripheral tissue circadian clock. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:15172–15177. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0806717105
Larsson E, Tremaroli V, Lee YS, Koren O, Nookaew I, Fricker A, Nielsen J, Ley RE, Bäckhed F (2012) Analysis of gut microbial regulation of host gene expression along the length of the gut and regulation of gut microbial ecology through MyD88. Gut 61:1124–1131. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2011-301104
Lebeche D, Davidoff AJ, Hajjar RJ (2008) Interplay between impaired calcium regulation and insulin signaling abnormalities in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med 5:715–724. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncpcardio1347
Leone TC, Weinheimer CJ, Kelly DP (1999) A critical role for the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) in the cellular fasting response: the PPARα-null mouse as a model of fatty acid oxidation disorders. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:7473–7478. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.13.7473
Leone V, Gibbons Sean M, Martinez K, Hutchison Alan L, Huang Edmond Y, Cham Candace M, Pierre Joseph F, Heneghan Aaron F, Nadimpalli A, Hubert N, Zale E, Wang Y, Huang Y, Theriault B, Dinner Aaron R, Musch Mark W, Kudsk Kenneth A, Prendergast Brian J, Gilbert Jack A, Chang Eugene B (2015) Effects of diurnal variation of gut microbes and high-fat feeding on host circadian clock function and metabolism. Cell Host Microbe 17:681–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2015.03.006
Li X (2013) SIRT1 and energy metabolism. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin Shanghai 45:51–60. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gms108
Liang X, Bushman FD, FitzGerald GA (2015) Rhythmicity of the intestinal microbiota is regulated by gender and the host circadian clock. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:10479–10484. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1501305112
Liu S, Downes M, Evans RM (2015) Metabolic regulation by nuclear receptors. Innovative medicine. Springer, Japan, p 25-37
Liu Q, Shi J, Duan P, Liu B, Li T, Wang C, Li H, Yang T, Gan Y, Wang X, Cao S, Lu Z (2018) Is shift work associated with a higher risk of overweight or obesity? A systematic review of observational studies with meta-analysis. Int J Epidemiol 47:1956–1971. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyy079
Manoogian ENC, Panda S (2017) Circadian rhythms, time-restricted feeding, and healthy aging. Ageing Res Rev 39:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2016.12.006
Marcheva B, Ramsey KM, Buhr ED, Kobayashi Y, Su H, Ko CH, Ivanova G, Omura C, Mo S, Vitaterna MH, Lopez JP, Philipson LH, Bradfield CA, Crosby SD, JeBailey L, Wang X, Takahashi JS, Bass J (2010) Disruption of the clock components CLOCK and BMAL1 leads to hypoinsulinaemia and diabetes. Nature 466:627–631. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature09253
Marcheva B, Ramsey KM, Peek CB, Affinati A, Maury E, Bass J (2013) Circadian clocks and metabolism. Handb Exp Pharmacol 217:127–155. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-25950-0_6
Martinez-Guryn K, Hubert N, Frazier K, Urlass S, Musch MW, Ojeda P, Pierre JF, Miyoshi J, Sontag TJ, Cham CM, Reardon CA, Leone V, Chang EB (2018) Small intestine microbiota regulate host digestive and absorptive adaptive responses to dietary lipids. Cell Host Microbe 23:458–469.e455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2018.03.011
Masri S (2015) Sirtuin-dependent clock control: new advances in metabolism, aging and cancer. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 18:521–527. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCO.0000000000000219
Masuki S, Todo T, Nakano Y, Okamura H, Nose H (2005) Reduced alpha-adrenoceptor responsiveness and enhanced baroreflex sensitivity in cry-deficient mice lacking a biological clock. J Physiol 566:213–224. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2005.086728
Maury E (2019) Off the clock: from circadian disruption to metabolic disease. Int J Mol Sci 20:1597. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071597
Maury E, Ramsey KM, Bass J (2010) Circadian rhythms and metabolic syndrome: from experimental genetics to human disease. Circ Res 106(3):447–462. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.109.208355
McHill AW, Wright KP Jr (2017) Role of sleep and circadian disruption on energy expenditure and in metabolic predisposition to human obesity and metabolic disease. Obes Rev 18:15–24. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.12503
McHill AW, Melanson EL, Higgins J, Connick E, Moehlman TM, Stothard ER, Wright KP (2014) Impact of circadian misalignment on energy metabolism during simulated nightshift work. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:17302–17307. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1412021111
Milano W, De Rosa M, Milano L, Capasso A (2012) Night eating syndrome: an overview. J Pharm Pharmacol 64:2–10. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2042-7158.2011.01353.x
Morris CJ, Purvis TE, Mistretta J, Scheer FAJL (2016) Effects of the internal circadian system and circadian misalignment on glucose tolerance in chronic shift workers. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 101:1066–1074. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2015-3924
Mure LS, Le HD, Benegiamo G, Chang MW, Rios L, Jillani N, Ngotho M, Kariuki T, Dkhissi-Benyahya O, Cooper HM, Panda S (2018) Diurnal transcriptome atlas of a primate across major neural and peripheral tissues. Science 359:eaao0318. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aao0318
Oishi K, Miyazaki K, Kadota K, Kikuno R, Nagase T, G-i A, Ohkura N, Azama T, Mesaki M, Yukimasa S, Kobayashi H, Iitaka C, Umehara T, Horikoshi M, Kudo T, Shimizu Y, Yano M, Monden M, Machida K, Matsuda J, Horie S, Todo T, Ishida N (2003) Genome-wide expression analysis of mouse liver reveals CLOCK-regulated circadian output genes. J Biol Chem 278:41519–41527. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M304564200
Oishi K, Shirai H, Ishida N (2005) CLOCK is involved in the circadian transactivation of peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) in mice. Biochem J 386:575–581. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20041150
Okano S, Akashi M, Hayasaka K, Nakajima O (2009) Unusual circadian locomotor activity and pathophysiology in mutant CRY1 transgenic mice. Neurosci Lett 451:246–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2009.01.014
Opperhuizen A-L, van Kerkhof LWM, Proper KI, Rodenburg W, Kalsbeek A (2015) Rodent models to study the metabolic effects of shiftwork in humans. Front Pharmacol 6:50–50. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2015.00050
Parkar SG, Kalsbeek A, Cheeseman JF (2019) Potential role for the gut microbiota in modulating host circadian rhythms and metabolic health. Microorganisms 7:41. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7020041
Parkes KR (2002) Shift work and age as interactive predictors of body mass index among offshore workers. Scand J Work Environ Health 28:64–71. https://doi.org/10.5271/sjweh.648
Paschos GK, FitzGerald GA (2017) Circadian clocks and metabolism: implications for microbiome and aging. Trends Genet 33:760–769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2017.07.010
Paschos GK, Ibrahim S, Song W-L, Kunieda T, Grant G, Reyes TM, Bradfield CA, Vaughan CH, Eiden M, Masoodi M, Griffin JL, Wang F, Lawson JA, FitzGerald GA (2012) Obesity in mice with adipocyte-specific deletion of clock component Arntl. Nat Med 18:1768–1777. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2979
Potter GDM, Skene DJ, Arendt J, Cade JE, Grant PJ, Hardie LJ (2016) Circadian rhythm and sleep disruption: causes, metabolic consequences, and countermeasures. Endocr Rev 37:584–608. https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2016-1083
Preitner N, Damiola F, Luis Lopez M, Zakany J, Duboule D, Albrecht U, Schibler U (2002) The orphan nuclear receptor REV-ERBα controls circadian transcription within the positive limb of the mammalian circadian oscillator. Cell 110:251–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00825-5
Rana S, Mahmood S (2010) Circadian rhythm and its role in malignancy. J Circadian Rhythms 8:3–3. https://doi.org/10.1186/1740-3391-8-3
Reppert SM, Weaver DR (2002) Coordination of circadian timing in mammals. Nature 418:935–941. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature00965
Rothschild J, Hoddy KK, Jambazian P, Varady KA (2014) Time-restricted feeding and risk of metabolic disease: a review of human and animal studies. Nutr Rev 72:308–318. https://doi.org/10.1111/nure.12104
Ruiter M, La Fleur SE, van Heijningen C, van der Vliet J, Kalsbeek A, Buijs RM (2003) The daily rhythm in plasma glucagon concentrations in the rat is modulated by the biological clock and by feeding behavior. Diabetes 52:1709–1715. https://doi.org/10.2337/diabetes.52.7.1709
Sadacca LA, Lamia KA, deLemos AS, Blum B, Weitz CJ (2011) An intrinsic circadian clock 54:120-124. Of the pancreas is required for normal insulin release and glucose homeostasis in mice. Diabetologica. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-010-1920-8
Sakamoto K, Nagase T, Fukui H, Horikawa K, Okada T, Tanaka H, Sato K, Miyake Y, Ohara O, Kako K, Ishida N (1998) Multitissue circadian expression of rat periodHomolog (rPer2) mRNA is governed by the mammalian circadian clock, the suprachiasmatic nucleus in the brain. J Biol Chem 273:27039–27042. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.42.27039
Salgado-Delgado RC, Saderi N, Basualdo MC, Guerrero-Vargas NN, Escobar C, Buijs RM (2013) Shift work or food intake during the rest phase promotes metabolic disruption and desynchrony of liver genes in male rats. PLoS One 8:e60052. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0060052
Scheer FAJL, Hilton MF, Mantzoros CS, Shea SA (2009) Adverse metabolic and cardiovascular consequences of circadian misalignment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:4453–4458. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0808180106
Scott EM, Carter AM, Grant PJ (2007) Association between polymorphisms in the clock gene, obesity and the metabolic syndrome in man. Int J Obes 32:658–662. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0803778
Serin Y, Acar Tek N (2019) Effect of circadian rhythm on metabolic processes and the regulation of energy balance. Ann Nutr Metab 74:322–330. https://doi.org/10.1159/000500071
Serón-Ferré M, Forcelledo ML, Torres-Farfan C, Valenzuela FJ, Rojas A, Vergara M, Rojas-Garcia PP, Recabarren MP, Valenzuela GJ (2013) Impact of chronodisruption during primate pregnancy on the maternal and newborn temperature rhythms. PLoS One 8:e57710. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0057710
Shimba S, Ogawa T, Hitosugi S, Ichihashi Y, Nakadaira Y, Kobayashi M, Tezuka M, Kosuge Y, Ishige K, Ito Y, Komiyama K, Okamatsu-Ogura Y, Kimura K, Saito M (2011) Deficient of a clock gene, brain and muscle Arnt-like protein-1 (BMAL1), induces dyslipidemia and ectopic fat formation. PLoS One 6:e25231. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0025231
Skene DJ, Skornyakov E, Chowdhury NR, Gajula RP, Middleton B, Satterfield BC, Porter KI, Van Dongen HPA, Gaddameedhi S (2018) Separation of circadian- and behavior-driven metabolite rhythms in humans provides a window on peripheral oscillators and metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115:7825–7830. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1801183115
Shi S-q, Ansari TS, McGuinness Owen P, Wasserman David H, Johnson Carl H (2013) Circadian disruption leads to insulin resistance and obesity. Curr Biol 23:372–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2013.01.048
Stenvers DJ, Scheer FAJL, Schrauwen P, la Fleur SE, Kalsbeek A (2019) Circadian clocks and insulin resistance. Nat Rev Endocrinol 15:75–89. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-018-0122-1
Sun L, Wang Y, Song Y, Cheng X-R, Xia S, Rahman MRT, Shi Y, Le G (2015) Resveratrol restores the circadian rhythmic disorder of lipid metabolism induced by high-fat diet in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 458:86–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.01.072
Sun M, Feng W, Wang F, Li P, Li Z, Li M, Tse G, Vlaanderen J, Vermeulen R, Tse LA (2018) Meta-analysis on shift work and risks of specific obesity types. Obes Rev 19:28–40. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.12621
Sutton EF, Beyl R, Early KS, Cefalu WT, Ravussin E, Peterson CM (2018) Early time-restricted feeding improves insulin sensitivity, blood pressure, and oxidative stress even without weight loss in men with prediabetes. Cell Metab 27:1212–1221.e1213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2018.04.010
Sweeney E, Yu ZM, Dummer TJB, Cui Y, DeClercq V, Forbes C, Grandy SA, Keats M, Parker L, Adisesh A (2019) The relationship between anthropometric measures and cardiometabolic health in shift work: findings from the Atlantic PATH cohort study. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 93(1):67–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-019-01459-8
Takahashi JS, Hong H-K, Ko CH, McDearmon EL (2008) The genetics of mammalian circadian order and disorder: implications for physiology and disease. Nat Rev Genet 9:764–775. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2430
Tamai TK, Vardhanabhuti V, Foulkes NS, Whitmore D (2004) Early embryonic light detection improves survival. Curr Biol 14:R104–R105
Tamai TK, Carr AJ, Whitmore D (2005) Zebrafish circadian clocks: cells that see light. Biochem Soc Trans 33:962–966. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST0330962
Thaiss Christoph A, Zeevi D, Levy M, Zilberman-Schapira G, Suez J, Tengeler Anouk C, Abramson L, Katz Meirav N, Korem T, Zmora N, Kuperman Y, Biton I, Gilad S, Harmelin A, Shapiro H, Halpern Z, Segal E, Elinav E (2014) Transkingdom control of microbiota diurnal oscillations promotes metabolic homeostasis. Cell 159:514–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.048
Thosar SS, Butler MP, Shea SA (2018) Role of the circadian system in cardiovascular disease. J Clin Investig 128:2157–2167. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI80590
Turek FW, Joshu C, Kohsaka A, Lin E, Ivanova G, McDearmon E, Laposky A, Losee-Olson S, Easton A, Jensen DR, Eckel RH, Takahashi JS, Bass J (2005) Obesity and metabolic syndrome in circadian clock mutant mice. Science 308:1043–1045. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1108750
Valenzuela FJ, Torres-Farfan C, Richter HG, Mendez N, Campino C, Torrealba F, Valenzuela GJ, Serón-Ferré M (2008) Clock gene expression in adult primate suprachiasmatic nuclei and adrenal: is the adrenal a peripheral clock responsive to melatonin? Endocrinology 149:1454–1461. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2007-1518
Valenzuela FJ, Vera J, Venegas C, Muñoz S, Oyarce S, Muñoz K, Lagunas C (2016) Evidences of polymorphism associated with circadian system and risk of pathologies: a review of the literature. Int J Endocrinol 2016:12–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2746909
Villanueva JE, Livelo C, Trujillo AS, Chandran S, Woodworth B, Andrade L, Le HD, Manor U, Panda S, Melkani GC (2019) Time-restricted feeding restores muscle function in Drosophila models of obesity and circadian-rhythm disruption. Nat Commun 10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10563-9
Voigt RM, Forsyth CB, Green SJ, Engen PA, Keshavarzian A (2016) Circadian rhythm and the gut microbiome. Int Rev Neurobiol 131:193–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.irn.2016.07.002
Voigt RM, Summa KC, Forsyth CB, Green SJ, Engen P, Naqib A, Vitaterna MH, Turek FW, Keshavarzian A (2016) The circadian clock mutation promotes intestinal Dysbiosis. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 40:335–347. https://doi.org/10.1111/acer.12943
Westermeier F, Sáez PJ, Villalobos-Labra R, Sobrevia L, Farías-Jofré M (2014) Programming of fetal insulin resistance in pregnancies with maternal obesity by ER stress and inflammation. Biomed Res Int 2014:13–13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/917672
Wyse CA, Celis Morales CA, Graham N, Fan Y, Ward J, Curtis AM, Mackay D, Smith DJ, Bailey MES, Biello S, Gill JMR, Pell JP (2017) Adverse metabolic and mental health outcomes associated with shiftwork in a population-based study of 277,168 workers in UK biobank. Ann Med 49:411–420. https://doi.org/10.1080/07853890.2017.1292045
Xie Z, Su W, Liu S, Zhao G, Esser K, Schroder EA, Lefta M, Stauss HM, Guo Z, Gong MC (2015) Smooth-muscle BMAL1 participates in blood pressure circadian rhythm regulation. J Clin Investig 125:324–336. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI76881
Yang X, Downes M, Yu RT, Bookout AL, He W, Straume M, Mangelsdorf DJ, Evans RM (2006) Nuclear receptor expression links the circadian clock to metabolism. Cell 126:801–810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.06.050
Yang S, Liu A, Weidenhammer A, Cooksey RC, McClain D, Kim MK, Aguilera G, Abel ED, Chung JH (2009) The role of mPer2 clock gene in glucocorticoid and feeding rhythms. Endocrinology 150:2153–2160. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2008-0705
Yang G, Jia Z, Aoyagi T, McClain D, Mortensen RM, Yang T (2012) Systemic PPARγ deletion impairs circadian rhythms of behavior and metabolism. PLoS One 7:e38117. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0038117
Yoshida J, Eguchi E, Nagaoka K, Ito T, Ogino K (2018) Association of night eating habits with metabolic syndrome and its components: a longitudinal study. BMC Public Health 18:1366. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-018-6262-3
Yu JH, Yun C-H, Ahn JH, Suh S, Cho HJ, Lee SK, Yoo HJ, Seo JA, Kim SG, Choi KM, Baik SH, Choi DS, Shin C, Kim NH (2015) Evening chronotype is associated with metabolic disorders and body composition in middle-aged adults. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100:1494–1502. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2014-3754
Zhang R, Lahens NF, Ballance HI, Hughes ME, Hogenesch JB (2014) A circadian gene expression atlas in mammals: implications for biology and medicine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:16219–16224. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1408886111
Zhao Y, Zhang Y, Zhou M, Wang S, Hua Z, Zhang J (2012) Loss of mPer2 increases plasma insulin levels by enhanced glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and impaired insulin clearance in mice. FEBS Lett 586:1306–1311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2012.03.034
Zhou S, Tang X, Chen H-Z (2018) Sirtuins and insulin resistance. Front Endocrinol 9:748. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2018.00748
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fatima, N., Rana, S. Metabolic implications of circadian disruption. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 472, 513–526 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-020-02381-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-020-02381-6