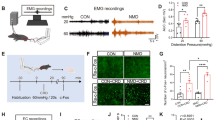
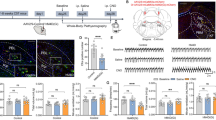
Abstract
A subset of hippocampal GABAergic neurons, which are cholecystokinin-positive, highly express cannabinoid type 1 (CB1) receptors. Activation of these receptors inhibits GABA release and thereby limits inhibitory control. While genetic deletion of CB1 receptors from GABAergic neurons led to behavioural alterations and neuroinflammatory reactions, it remained unclear whether these changes in the knockout animals were a direct consequence of the enhanced transmitter release or reflected developmental deficits. The hippocampus is vital for the generation of spatial, declarative and working memory. Here, we addressed the question how CB1 receptors in GABAergic neurons influence hippocampal function. Patch clamp and field potential recordings in mice devoid of CB1 receptors in GABAergic neurons revealed an enhanced frequency and faster kinetics of spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic currents in CA1 pyramidal neurons while tonic inhibition, paired-pulse facilitation and long-term potentiation in the hippocampus were not affected. Evaluation of cognitive functions demonstrated impaired acquisition of spatial memory and deficits in novel object recognition and partner recognition in the knockout mice, while working memory and spatial memory remained intact. The density of GABAergic neurons was also similar in knockout mice and their littermates, which argues against global deficits in hippocampal development. Together, these results suggest that CB1 receptors in GABAergic neurons influence specific aspects of neuronal excitability and hippocampal learning.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albayram O, Alferink J, Pitsch J, Piyanova A, Neitzert K, Poppensieker K, Mauer D, Michel K, Legler A, Becker A, Monory K, Lutz B, Zimmer A, Bilkei-Gorzo A (2011) Role of CB1 cannabinoid receptors on GABAergic neurons in brain aging. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:11256–11261
Baddeley A, Jarrold C, Vargha-Khadem F (2011) Working memory and the hippocampus. J Cogn Neurosci 23:3855–3861
Balderas I, Rodriguez-Ortiz CJ, Bermudez-Rattoni F (2015) Consolidation and reconsolidation of object recognition memory. Behav Brain Res 285:213–222
Bellocchio L, Lafenetre P, Cannich A, Cota D, Puente N, Grandes P, Chaouloff F, Piazza PV, Marsicano G (2010) Bimodal control of stimulated food intake by the endocannabinoid system. Nat Neurosci 13:281–283
Berghuis P, Rajnicek AM, Morozov YM, Ross RA, Mulder J, Urban GM, Monory K, Marsicano G, Matteoli M, Canty A, Irving AJ, Katona I, Yanagawa Y, Rakic P, Lutz B, Mackie K, Harkany T (2007) Hardwiring the brain: endocannabinoids shape neuronal connectivity. Science 316:1212–1216
Bernard C, Milh M, Morozov YM, Ben-Ari Y, Freund TF, Gozlan H (2005) Altering cannabinoid signaling during development disrupts neuronal activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:9388–9393
Bilkei-Gorzo A, Mauer D, Michel K, Zimmer A (2014) Dynorphins regulate the strength of social memory. Neuropharmacology 77:406–413
Bird CM, Burgess N (2008) The hippocampus and memory: insights from spatial processing. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:182–194
Bohme GA, Laville M, Ledent C, Parmentier M, Imperato A (2000) Enhanced long-term potentiation in mice lacking cannabinoid CB1 receptors. Neuroscience 95:5–7
Brown MW, Warburton EC, Aggleton JP (2010) Recognition memory: material, processes, and substrates. Hippocampus 20:1228–1244
Cass DK, Flores-Barrera E, Thomases DR, Vital WF, Caballero A, Tseng KY (2014) CB1 cannabinoid receptor stimulation during adolescence impairs the maturation of GABA function in the adult rat prefrontal cortex. Mol Psychiatry 19:536–543
Castillo PE, Younts TJ, Chavez AE, Hashimotodani Y (2012) Endocannabinoid signaling and synaptic function. Neuron 76:70–81
Compagnucci C, Di SS, Bustamante MB, Di GD, Di TM, Maccarrone M, Grimaldi P, Sette C (2013) Type-1 (CB1) cannabinoid receptor promotes neuronal differentiation and maturation of neural stem cells. PLoS ONE 8, e54271
D’Hooge R, De Deyn PP (2001) Applications of the Morris water maze in the study of learning and memory. Brain Res Rev 36:60–90
Deng W, Aimone JB, Gage FH (2010) New neurons and new memories: how does adult hippocampal neurogenesis affect learning and memory? Nat Rev Neurosci 11:339–350
Diaz-Alonso J, Guzman M, Galve-Roperh I (2012) Endocannabinoids via CB(1) receptors act as neurogenic niche cues during cortical development. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 367:3229–3241
Fitzgerald ML, Lupica CR, Pickel VM (2011) Decreased parvalbumin immunoreactivity in the cortex and striatum of mice lacking the CB1 receptor. Synapse 65:827–831
Floresco SB, Seamans JK, Phillips AG (1997) Selective roles for hippocampal, prefrontal cortical, and ventral striatal circuits in radial-arm maze tasks with or without a delay. J Neurosci 17:1880–1890
Freund TF, Katona I, Piomelli D (2003) Role of endogenous cannabinoids in synaptic signaling. Physiol Rev 83:1017–1066
Gaffuri AL, Ladarre D, Lenkei Z (2012) Type-1 cannabinoid receptor signaling in neuronal development. Pharmacology 90:19–39
Galve-Roperh I, Chiurchiu V, az-Alonso J, Bari M, Guzman M, Maccarrone M (2013) Cannabinoid receptor signaling in progenitor/stem cell proliferation and differentiation. Prog Lipid Res 52:633–650
Gomez-Gonzalo M, Navarrete M, Perea G, Covelo A, Martin-Fernandez M, Shigemoto R, Lujan R, Araque A (2014) Endocannabinoids induce lateral long-term potentiation of transmitter release by stimulation of gliotransmission. Cereb Cortex 25:3699–3712
Guggenmos M, Rothkirch M, Obermayer K, Haynes JD, Sterzer P (2015) A hippocampal signature of perceptual learning in object recognition. J Cogn Neurosci 27:787–797
Hajos N, Katona I, Naiem SS, Mackie K, Ledent C, Mody I, Freund TF (2000) Cannabinoids inhibit hippocampal GABAergic transmission and network oscillations. Eur J Neurosci 12:3239–3249
Haller J, Bakos N (2002) Stress-induced social avoidance: a new model of stress-induced anxiety? Physiol Behav 77:327–332
Henke K (2010) A model for memory systems based on processing modes rather than consciousness. Nat Rev Neurosci 11:523–532
Hoffman AF, Lupica CR (2000) Mechanisms of cannabinoid inhibition of GABA(A) synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. J Neurosci 20:2470–2479
Katona I, Sperlagh B, Magloczky Z, Santha E, Kofalvi A, Czirjak S, Mackie K, Vizi ES, Freund TF (2000) GABAergic interneurons are the targets of cannabinoid actions in the human hippocampus. Neuroscience 100:797–804
Lee SH, Foldy C, Soltesz I (2010) Distinct endocannabinoid control of GABA release at perisomatic and dendritic synapses in the hippocampus. J Neurosci 30:7993–8000
Losonczy A, Biro AA, Nusser Z (2004) Persistently active cannabinoid receptors mute a subpopulation of hippocampal interneurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:1362–1367
Lynch MA (2004) Long-term potentiation and memory. Physiol Rev 84:87–136
Marsicano G, Lutz B (1999) Expression of the cannabinoid receptor CB1 in distinct neuronal subpopulations in the adult mouse forebrain. Eur J Neurosci 11:4213–4225
Monory K, Massa F, Egertova M, Eder M, Blaudzun H, Westenbroek R, Kelsch W, Jacob W, Marsch R, Ekker M, Long J, Rubenstein JL, Goebbels S, Nave KA, During M, Klugmann M, Wolfel B, Dodt HU, Zieglgansberger W, Wotjak CT, Mackie K, Elphick MR, Marsicano G, Lutz B (2006) The endocannabinoid system controls key epileptogenic circuits in the hippocampus. Neuron 51:455–466
Monory K, Polack M, Remus A, Lutz B, Korte M (2015) Cannabinoid CB1 receptor calibrates excitatory synaptic balance in the mouse hippocampus. J Neurosci 35:3842–3850
Navarrete M, Diez A, Araque A (2014) Astrocytes in endocannabinoid signalling. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 369:20130599
Neu A, Foldy C, Soltesz I (2007) Postsynaptic origin of CB1-dependent tonic inhibition of GABA release at cholecystokinin-positive basket cell to pyramidal cell synapses in the CA1 region of the rat hippocampus. J Physiol 578:233–247
Nissen W, Szabo A, Somogyi J, Somogyi P, Lamsa KP (2010) Cell type-specific long-term plasticity at glutamatergic synapses onto hippocampal interneurons expressing either parvalbumin or CB1 cannabinoid receptor. J Neurosci 30:1337–1347
Passlick S, Grauer M, Schafer C, Jabs R, Seifert G, Steinhauser C (2013) Expression of the gamma2-subunit distinguishes synaptic and extrasynaptic GABA(A) receptors in NG2 cells of the hippocampus. J Neurosci 33:12030–12040
Passlick S, Trotter J, Seifert G, Steinhauser C, Jabs R (2016) The NG2 protein is not required for glutamatergic neuron-NG2 cell synaptic signaling. Cereb Cortex 26:51–57
Preston AR, Eichenbaum H (2013) Interplay of hippocampus and prefrontal cortex in memory. Curr Biol 23:R764–R773
Ryals AJ, Wang JX, Polnaszek KL, Voss JL (2015) Hippocampal contribution to implicit configuration memory expressed via eye movements during scene exploration. Hippocampus 25:1028–1041
Saez TM, Aronne MP, Caltana L, Brusco AH (2014) Prenatal exposure to the CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptor agonist WIN 55,212-2 alters migration of early-born glutamatergic neurons and GABAergic interneurons in the rat cerebral cortex. J Neurochem 129:637–648
Slanina KA, Roberto M, Schweitzer P (2005) Endocannabinoids restrict hippocampal long-term potentiation via CB1. Neuropharmacology 49:660–668
Stanley DP, Shetty AK (2004) Aging in the rat hippocampus is associated with widespread reductions in the number of glutamate decarboxylase-67 positive interneurons but not interneuron degeneration. J Neurochem 89:204–216
Steiner MA, Marsicano G, Wotjak CT, Lutz B (2008) Conditional cannabinoid receptor type 1 mutants reveal neuron subpopulation-specific effects on behavioral and neuroendocrine stress responses. Psychoneuroendocrinology 33:1165–1170
Sweatt JD (2004) Hippocampal function in cognition. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 174:99–110
Szabo GG, Lenkey N, Holderith N, Andrasi T, Nusser Z, Hajos N (2014) Presynaptic calcium channel inhibition underlies CB(1) cannabinoid receptor-mediated suppression of GABA release. J Neurosci 34:7958–7963
Szabo GG, Papp OI, Mate Z, Szabo G, Hajos N (2014) Anatomically heterogeneous populations of CB1 cannabinoid receptor-expressing interneurons in the CA3 region of the hippocampus show homogeneous input–output characteristics. Hippocampus 24:1506–1523
Tamano H, Minamino T, Fujii H, Takada S, Nakamura M, Ando M, Takeda A (2015) Blockade of intracellular Zn signaling in the dentate gyrus erases recognition memory via impairment of maintained LTP. Hippocampus 25:952–962
Terzian AL, Micale V, Wotjak CT (2014) Cannabinoid receptor type 1 receptors on GABAergic vs. glutamatergic neurons differentially gate sex-dependent social interest in mice. Eur J Neurosci 40:2293–2298
Tsou K, Mackie K, Sanudo-Pena MC, Walker JM (1999) Cannabinoid CB1 receptors are localized primarily on cholecystokinin-containing GABAergic interneurons in the rat hippocampal formation. Neuroscience 93:969–975
Wang GW, Cai JX (2006) Disconnection of the hippocampal-prefrontal cortical circuits impairs spatial working memory performance in rats. Behav Brain Res 175:329–336
Wilson RI, Nicoll RA (2002) Endocannabinoid signaling in the brain. Science 296:678–682
Wu CS, Zhu J, Wager-Miller J, Wang S, O’Leary D, Monory K, Lutz B, Mackie K, Lu HC (2010) Requirement of cannabinoid CB(1) receptors in cortical pyramidal neurons for appropriate development of corticothalamic and thalamocortical projections. Eur J Neurosci 32:693–706
Yang L, Zou B, Xiong X, Pascual C, Xie J, Malik A, Xie J, Sakurai T, Xie XS (2013) Hypocretin/orexin neurons contribute to hippocampus-dependent social memory and synaptic plasticity in mice. J Neurosci 33:5275–5284
Yonelinas AP (2013) The hippocampus supports high-resolution binding in the service of perception, working memory and long-term memory. Behav Brain Res 254:34–44
Yonelinas AP, Aly M, Wang WC, Koen JD (2010) Recollection and familiarity: examining controversial assumptions and new directions. Hippocampus 20:1178–1194
Zalcman G, Federman N, de lF V, Romano A (2015) Nuclear factor kappa B-dependent Zif268 expression in hippocampus is required for recognition memory in mice. Neurobiol Learn Mem 119:10–17
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. C. Henneberger and S. Künzel for comments on the manuscript and technical support. Grant Sponsors: Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft; STE552/3 (to CS), FOR926 SP2, BI-1227/5-1 (to ABG) and FOR926 CP2 (to AZ). European Union; ESF EuroEPINOMICS (to CS). A.Z. is a member of the DFG Cluster of Excellence ImmunoSensation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Önder Albayram and Stefan Passlick contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM Fig. 1
Representative microphotographs of GAD67 immunostaining (green) in the CA1 and CA3 regions of the hippocampus of GABA/CB1+/+ and GABA/CB1-/- mice. White arrows indicate the location of GAD67+ cell bodies. Scale bar represents 100 μm (JPG 200 kb)
ESM Fig. 2
Representative microphotographs of PV immunostaining (green) and Hoechst fluorescence (blue) in the CA1 and CA3 regions of the hippocampus of GABA/CB1+/+ and GABA/CB1-/- mice. White arrows indicate the location of PV+ interneurons. Scale bar represents 100 μm (JPG 235 kb)
ESM Fig. 3
Representative microphotographs of CCK immunostaining (green) and Hoechst fluorescence (blue) in the CA1 and CA3 regions of the hippocampus of GABA/CB1+/+ and GABA/CB1-/- mice. White arrows indicate the location of CCK+ interneurons. Scale bar represents 100 μm (JPG 135 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Albayram, Ö., Passlick, S., Bilkei-Gorzo, A. et al. Physiological impact of CB1 receptor expression by hippocampal GABAergic interneurons. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 468, 727–737 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-015-1782-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-015-1782-5