Abstract
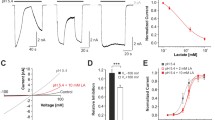
TRPA1 is a nonselective cation channel activated by a wide variety of noxious chemicals. Intriguingly, several TRPA1 modulators induce a bimodal effect, activating the channel at micromolar concentrations and inhibiting it at higher concentrations. Here we report the bimodal action of cinnamaldehyde (CA) and camphor, which are thus far reported as agonist and antagonist of TRPA1, respectively. Whole-cell patch-clamp experiments in TRPA1-expressing CHO cells revealed that, as previously reported, extracellular application of 100 μM CA strongly stimulates TRPA1 currents. However, subsequent application of 3 mM CA induced fast and reversible current inhibition. Application of 3 mM CA in basal conditions induced a rather small current increase, followed by current inhibition and a dramatic rebound of current amplitude upon washout. These observations are reminiscent of the effects of TRPA1 modulators having bimodal effects, e.g., menthol and nicotine. In line with previous reports, extracellular application of 1 mM camphor induced a decrease of basal TRPA1 currents. However, the current amplitude showed a significant overshoot upon washout. On the other hand, application of 100 μM camphor induced a 3-fold increase of the basal current amplitude measured at −75 mV. The bimodal effects of CA and camphor on TRPA1 were also observed in microfluorimetric measurements of intracellular Ca2+ in intact TRPA1-expressing CHO cells and in primary cultures of mouse dorsal root ganglion neurons. These findings are essential for the understanding of the complex sensory properties of these compounds, as well as their utility when used to study the pathophysiological relevance of TRPA1.






Similar content being viewed by others

References
Albin KC, Carstens MI, Carstens E (2008) Modulation of oral heat and cold pain by irritant chemicals. Chem Senses 33:3–15
Andersson DA, Gentry C, Moss S, Bevan S (2008) Transient receptor potential A1 is a sensory receptor for multiple products of oxidative stress. J Neurosci 28:2485–2494
Andrade EL, Luiz AP, Ferreira J, Calixto JB (2008) Pronociceptive response elicited by TRPA1 receptor activation in mice. Neuroscience 152:511–520
Andre E, Campi B, Materazzi S, Trevisani M, Amadesi S, Massi D, Creminon C, Vaksman N, Nassini R, Civelli M, Baraldi PG, Poole DP, Bunnett NW, Geppetti P, Patacchini R (2008) Cigarette smoke-induced neurogenic inflammation is mediated by alpha, beta-unsaturated aldehydes and the TRPA1 receptor in rodents. J Clin Invest 118:2574–2582
Andre E, Gatti R, Trevisani M, Preti D, Baraldi PG, Patacchini R, Geppetti P (2009) Transient receptor potential ankyrin receptor 1 is a novel target for pro-tussive agents. Br J Pharmacol 158:1621–1628
Bandell M, Story GM, Hwang SW, Viswanath V, Eid SR, Petrus MJ, Earley TJ, Patapoutian A (2004) Noxious cold ion channel TRPA1 is activated by pungent compounds and bradykinin. Neuron 41:849–857
Bang S, Kim KY, Yoo S, Kim YG, Hwang SW (2007) Transient receptor potential A1 mediates acetaldehyde-evoked pain sensation. Eur J Neurosci 26:2516–2523
Banner KH, Igney F, Poll C (2011) TRP channels: emerging targets for respiratory disease. Pharmacol Ther 130:371–384
Bautista DM, Jordt SE, Nikai T, Tsuruda PR, Read AJ, Poblete J, Yamoah EN, Basbaum AI, Julius D (2006) TRPA1 mediates the inflammatory actions of environmental irritants and proalgesic agents. Cell 124:1269–1282
Descoeur J, Pereira V, Pizzoccaro A, Francois A, Ling B, Maffre V, Couette B, Busserolles J, Courteix C, Noel J, Lazdunski M, Eschalier A, Authier N, Bourinet E (2011) Oxaliplatin-induced cold hypersensitivity is due to remodelling of ion channel expression in nociceptors. EMBO Mol Med 3:266–278
Doerner JF, Gisselmann G, Hatt H, Wetzel CH (2007) Transient receptor potential channel A1 is directly gated by calcium ions. J Biol Chem 282:13180–13189
Everaerts W, Gees M, Alpizar YA, Farre R, Leten C, Apetrei A, Dewachter I, van Leuven F, Vennekens R, De Ridder D, Nilius B, Voets T, Talavera K (2011) The capsaicin receptor TRPV1 is a crucial mediator of the noxious effects of mustard oil. Curr Biol 21:316–321
Fajardo O, Meseguer V, Belmonte C, Viana F (2008) TRPA1 channels mediate cold temperature sensing in mammalian vagal sensory neurons: pharmacological and genetic evidence. J Neurosci 28:7863–7875
Green BG (1990) Sensory characteristics of camphor. J Invest Dermatol 94:662–666
Gu Q, Lin RL (2010) Heavy metals zinc, cadmium, and copper stimulate pulmonary sensory neurons via direct activation of TRPA1. J Appl Physiol 108:891–897
Holzer P (2011) Transient receptor potential (TRP) channels as drug targets for diseases of the digestive system. Pharmacol Ther 131:142–170
Hu H, Bandell M, Petrus MJ, Zhu MX, Patapoutian A (2009) Zinc activates damage-sensing TRPA1 ion channels. Nat Chem Biol 5:183–190
Jordt SE, Bautista DM, Chuang HH, McKemy DD, Zygmunt PM, Hogestatt ED, Meng ID, Julius D (2004) Mustard oils and cannabinoids excite sensory nerve fibres through the TRP channel ANKTM1. Nature 427:260–265
Karashima Y, Damann N, Prenen J, Talavera K, Segal A, Voets T, Nilius B (2007) Bimodal action of menthol on the transient receptor potential channel TRPA1. J Neurosci 27:9874–9884
Karashima Y, Talavera K, Everaerts W, Janssens A, Kwan KY, Vennekens R, Nilius B, Voets T (2009) TRPA1 acts as a cold sensor in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:1273–1278
Macpherson LJ, Dubin AE, Evans MJ, Marr F, Schultz PG, Cravatt BF, Patapoutian A (2007) Noxious compounds activate TRPA1 ion channels through covalent modification of cysteines. Nature 445:541–545
Macpherson LJ, Hwang SW, Miyamoto T, Dubin AE, Patapoutian A, Story GM (2006) More than cool: promiscuous relationships of menthol and other sensory compounds. Mol Cell Neurosci 32:335–343
Matta JA, Cornett PM, Miyares RL, Abe K, Sahibzada N, Ahern GP (2008) General anesthetics activate a nociceptive ion channel to enhance pain and inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:8784–8789
Meseguer VM, Denlinger BL, Talavera K (2011) Methodological considerations to understand the sensory function of TRP channels. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 12:3–11
Miyamoto T, Dubin AE, Petrus MJ, Patapoutian A (2009) TRPV1 and TRPA1 mediate peripheral nitric oxide-induced nociception in mice. PLoS One 4:e7596
Moqrich A, Hwang SW, Earley TJ, Petrus MJ, Murray AN, Spencer KS, Andahazy M, Story GM, Patapoutian A (2005) Impaired thermosensation in mice lacking TRPV3, a heat and camphor sensor in the skin. Science 307:1468–1472
Moran MM, McAlexander MA, Biro T, Szallasi A (2011) Transient receptor potential channels as therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10:601–620
Nagata K, Duggan A, Kumar G, Garcia-Anoveros J (2005) Nociceptor and hair cell transducer properties of TRPA1, a channel for pain and hearing. J Neurosci 25:4052–4061
Namer B, Seifert F, Handwerker HO, Maihofner C (2005) TRPA1 and TRPM8 activation in humans: effects of cinnamaldehyde and menthol. Neuroreport 16:955–959
Nassenstein C, Kwong K, Taylor-Clark T, Kollarik M, Macglashan DM, Braun A, Undem BJ (2008) Expression and function of the ion channel TRPA1 in vagal afferent nerves innervating mouse lungs. J Physiol 586:1595–1604
Nassini R, Materazzi S, De Siena G, De Cesaris F, Geppetti P (2010) Transient receptor potential channels as novel drug targets in respiratory diseases. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 11:535–542
Nilius B, Appendino G, Owsianik G (2012) The transient receptor potential channel TRPA1: from gene to pathophysiology. Pflügers Arch 464:425–458
Nilius B, Prenen J, Owsianik G (2011) Irritating channels: the case of TRPA1. J Physiol 589:1543–1549
Sawada Y, Hosokawa H, Hori A, Matsumura K, Kobayashi S (2007) Cold sensitivity of recombinant TRPA1 channels. Brain Res 1160:39–46
Schwartz ES, Christianson JA, Chen X, La JH, Davis BM, Albers KM, Gebhart GF (2011) Synergistic role of TRPV1 and TRPA1 in pancreatic pain and inflammation. Gastroenterology 140(1283–1291):e1–e2
Story GM, Peier AM, Reeve AJ, Eid SR, Mosbacher J, Hricik TR, Earley TJ, Hergarden AC, Andersson DA, Hwang SW, McIntyre P, Jegla T, Bevan S, Patapoutian A (2003) ANKTM1, a TRP-like channel expressed in nociceptive neurons, is activated by cold temperatures. Cell 112:819–829
Stotz SC, Vriens J, Martyn D, Clardy J, Clapham DE (2008) Citral sensing by transient receptor potential channels in dorsal root ganglion neurons. PLoS One 3:e2082
Takahashi N, Kuwaki T, Kiyonaka S, Numata T, Kozai D, Mizuno Y, Yamamoto S, Naito S, Knevels E, Carmeliet P, Oga T, Kaneko S, Suga S, Nokami T, Yoshida J, Mori Y (2012) TRPA1 underlies a sensing mechanism for O2. Nat Chem Biol 7:701–711
Takahashi N, Mori Y (2011) TRP channels as sensors and signal integrators of redox status changes. Front Pharmacol 2:58
Talavera K, Gees M, Karashima Y, Meseguer VM, Vanoirbeek JA, Damann N, Everaerts W, Benoit M, Janssens A, Vennekens R, Viana F, Nemery B, Nilius B, Voets T (2009) Nicotine activates the chemosensory cation channel TRPA1. Nat Neurosci 12:1293–1299
Talavera K, Janssens A, Klugbauer N, Droogmans G, Nilius B (2003) Extracellular Ca2+ modulates the effects of protons on gating and conduction properties of the T-type Ca2+ channel α1G (CaV3.1). J Gen Physiol 121:511–528
Talavera K, Nilius B (2011) Electrophysiological methods for the study of TRP channels. In: Zhu MX (ed) Series methods in signal transduction. CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton, pp 237–254
Trevisani M, Siemens J, Materazzi S, Bautista DM, Nassini R, Campi B, Imamachi N, Andre E, Patacchini R, Cottrell GS, Gatti R, Basbaum AI, Bunnett NW, Julius D, Geppetti P (2007) 4-Hydroxynonenal, an endogenous aldehyde, causes pain and neurogenic inflammation through activation of the irritant receptor TRPA1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:13519–13524
Voets T, Talavera K, Nilius B (2012) Transient receptor potential channel promiscuity frustrates constellation pharmacology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:E3338
Wang YY, Chang RB, Waters HN, McKemy DD, Liman ER (2008) The nociceptor ion channel TRPA1 is potentiated and inactivated by permeating calcium ions. J Biol Chem 283:32691–32703
Xu H, Blair NT, Clapham DE (2005) Camphor activates and strongly desensitizes the transient receptor potential vanilloid subtype 1 channel in a vanilloid-independent mechanism. J Neurosci 25:8924–8937
Zanotto KL, Merrill AW, Carstens MI, Carstens E (2007) Neurons in superficial trigeminal subnucleus caudalis responsive to oral cooling, menthol, and other irritant stimuli. J Neurophysiol 97:966–978
Zhang XF, Chen J, Faltynek CR, Moreland RB, Neelands TR (2008) Transient receptor potential A1 mediates an osmotically activated ion channel. Eur J Neurosci 27:605–611
Zhong J, Minassi A, Prenen J, Taglialatela-Scafati O, Appendino G, Nilius B (2011) Umbellulone modulates TRP channels. Pflügers Arch 462:861–870
Zhong J, Pollastro F, Prenen J, Zhu Z, Appendino G, Nilius B (2011) Ligustilide: a novel TRPA1 modulator. Pflügers Arch 462:841–849
Zurborg S, Yurgionas B, Jira JA, Caspani O, Heppenstall PA (2007) Direct activation of the ion channel TRPA1 by Ca2+. Nat Neurosci 10:277–279
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alpizar, Y.A., Gees, M., Sanchez, A. et al. Bimodal effects of cinnamaldehyde and camphor on mouse TRPA1. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 465, 853–864 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-012-1204-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-012-1204-x