Abstract
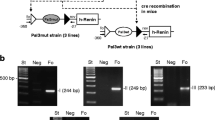
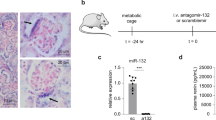
This study aimed to assess the role of cAMP target sequences enhancer cAMP response element (enhCRE) and cAMP and overlapping negative response element (CNRE) in the control of human renin gene (REN) in vivo. enhCRE and CNRE were silenced by mutations in a 12.2-kb human renin promoter fused to LacZ reporter gene. This construct was used to generate transgenic mice (RENMut-LacZ). The expression of the transgene was correctly targeted to the juxtaglomerular portions of renal afferent arterioles which express endogenous mouse renin. Therefore, enhCRE and CNRE do not seem to be relevant for the control of the cell-specific expression of the human renin gene. The β-adrenoreceptor agonist isoproterenol (10 mg/kg/day, for 2 days) stimulated the endogenous renin, but not the LacZ mRNA expression. Treatment of RENMut-LacZ mice with the angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor (enalapril 10 mg/kg/day, for 7 days) or their crossing to angiotensin receptor type 1a knockout mice led to increased renin and LacZ mRNA levels. Renin expression was upregulated by low-salt diet (0.03% NaCl, for 10 days) and downregulated by high-salt diet (4% NaCl, for 10 days). In contrast, low-salt diet did not influence, while high-salt diet inhibited the expression of LacZ. In summary, enhCRE and CNRE appear to be necessary for the transactivation of the human renin gene through β-adrenoreceptors and by low-salt diet. Our data also suggest that different intracellular mechanisms mediate the effect of low- and high-salt intake on renin expression in vivo.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borensztein P, Germain S, Fuchs S, Philippe J, Corvol P, Pinet F (1994) cis-regulatory elements and trans-acting factors directing basal and cAMP-stimulated human renin gene expression in chorionic cells. Circ Res 74:764–773
Castrop H, Hocherl K, Kurtz A, Schweda F, Todorov V, Wagner C (2010) Physiology of kidney renin. Physiol Rev 90:607–673
Castrop H, Oppermann M, Weiss Y, Huang Y, Mizel D, Lu H, Germain S, Schweda F, Theilig F, Bachmann S, Briggs J, Kurtz A, Schnermann J (2006) Reporter gene recombination in juxtaglomerular granular and collecting duct cells by human renin promoter-Cre recombinase transgene. Physiol Genomics 25:277–285
Chen L, Kim SM, Eisner C, Oppermann M, Huang Y, Mizel D, Li L, Chen M, Sequeira Lopez ML, Weinstein LS, Gomez RA, Schnermann J, Briggs JP (2010) Stimulation of renin secretion by angiotensin II blockade is Gsalpha-dependent. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:986–992
Desch M, Schreiber A, Schweda F, Madsen K, Friis UG, Weatherford ET, Sigmund CD, Sequeira Lopez ML, Gomez RA, Todorov VT (2010) Increased renin production in mice with deletion of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma in juxtaglomerular cells. Hypertension 55:660–666
Desch M, Schubert T, Schreiber A, Mayer S, Friedrich B, Artunc F, Todorov VT (2010) PPAR{gamma}-dependent regulation of adenylate cyclase 6 amplifies the stimulatory effect of cAMP on renin gene expression. Mol Endocrinol 24:2139–2151
DiBona GF, Kopp UC (1997) Neural control of renal function. Physiol Rev 77:75–197
Fuchs S, Germain S, Philippe J, Corvol P, Pinet F (2002) Expression of renin in large arteries outside the kidney revealed by human renin promoter/LacZ transgenic mouse. Am J Pathol 161:717–725
Germain S, Konoshita T, Philippe J, Corvol P, Pinet F (1996) Transcriptional induction of the human renin gene by cyclic AMP requires cyclic AMP response element-binding protein (CREB) and a factor binding a pituitary-specific trans-acting factor (Pit-1) motif. Biochem J 316(Pt 1):107–113
Germain S, Philippe J, Fuchs S, Lengronne A, Corvol P, Pinet F (1997) Regulation of human renin secretion and gene transcription in Calu-6 cells. FEBS Lett 407:177–183
Glenn ST, Jones CA, Pan L, Gross KW (2008) In vivo analysis of key elements within the renin regulatory region. Physiol Genomics 35:243–253
Gloerich M, Bos JL (2010) Epac: defining a new mechanism for cAMP action. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 50:355–375
Horiuchi M, Pratt RE, Nakamura N, Dzau VJ (1993) Distinct nuclear proteins competing for an overlapping sequence of cyclic adenosine monophosphate and negative regulatory elements regulate tissue-specific mouse renin gene expression. J Clin Invest 92:1805–1811
Ito M, Oliverio MI, Mannon PJ, Best CF, Maeda N, Smithies O, Coffman TM (1995) Regulation of blood pressure by the type 1A angiotensin II receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:3521–3525
Kim SM, Chen L, Faulhaber-Walter R, Oppermann M, Huang Y, Mizel D, Briggs JP, Schnermann J (2007) Regulation of renin secretion and expression in mice deficient in beta1- and beta2-adrenergic receptors. Hypertension 50:103–109
Klar J, Sandner P, Muller MW, Kurtz A (2002) Cyclic AMP stimulates renin gene transcription in juxtaglomerular cells. Pflugers Arch 444:335–344
Lang JA, Ying LH, Morris BJ, Sigmund CD (1996) Transcriptional and posttranscriptional mechanisms regulate human renin gene expression in Calu-6 cells. Am J Physiol 271:F94–F100
Mangrum AJ, Gomez RA, Norwood VF (2002) Effects of AT(1A) receptor deletion on blood pressure and sodium excretion during altered dietary salt intake. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 283:F447–F453
Markus MA, Goy C, Adams DJ, Lovicu FJ, Morris BJ (2007) Renin enhancer is crucial for full response in renin expression to an in vivo stimulus. Hypertension 50:933–938
Morello F, de Boer RA, Steffensen KR, Gnecchi M, Chisholm JW, Boomsma F, Anderson LM, Lawn RM, Gustafsson JA, Lopez-Ilasaca M, Pratt RE, Dzau VJ (2005) Liver X receptors alpha and beta regulate renin expression in vivo. J Clin Invest 115:1913–1922
Mrowka R, Steege A, Kaps C, Herzel H, Thiele BJ, Persson PB, Bluthgen N (2007) Dissecting the action of an evolutionary conserved non-coding region on renin promoter activity. Nucleic Acids Res 35:5120–5129
Pan L, Black TA, Shi Q, Jones CA, Petrovic N, Loudon J, Kane C, Sigmund CD, Gross KW (2001) Critical roles of a cyclic AMP responsive element and an E-box in regulation of mouse renin gene expression. J Biol Chem 276:45530–45538
Pan L, Xie Y, Black TA, Jones CA, Pruitt SC, Gross KW (2001) An Abd-B class HOX.PBX recognition sequence is required for expression from the mouse Ren-1c gene. J Biol Chem 276:32489–32494
Petrovic N, Black TA, Fabian JR, Kane C, Jones CA, Loudon JA, Abonia JP, Sigmund CD, Gross KW (1996) Role of proximal promoter elements in regulation of renin gene transcription. J Biol Chem 271:22499–22505
Sauter A, Machura K, Neubauer B, Kurtz A, Wagner C (2008) Development of renin expression in the mouse kidney. Kidney Int 73:43–51
Schweda F, Klar J, Narumiya S, Nusing RM, Kurtz A (2004) Stimulation of renin release by prostaglandin E2 is mediated by EP2 and EP4 receptors in mouse kidneys. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 287:F427–F433
Schweda F, Segerer F, Castrop H, Schnermann J, Kurtz A (2005) Blood pressure-dependent inhibition of Renin secretion requires A1 adenosine receptors. Hypertension 46:780–786
Sequeira Lopez ML, Gomez RA (2010) Novel mechanisms for the control of renin synthesis and release. Curr Hypertens Rep 12:26–32
Tamura K, Chen YE, Horiuchi M, Chen Q, Daviet L, Yang Z, Lopez-Ilasaca M, Mu H, Pratt RE, Dzau VJ (2000) LXRalpha functions as a cAMP-responsive transcriptional regulator of gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:8513–8518
Tamura K, Chen YE, Tanaka Y, Sakai M, Tsurumi Y, Koide Y, Kihara M, Pratt RE, Horiuchi M, Umemura S, Dzau VJ (2004) Nuclear receptor LXRalpha is involved in cAMP-mediated human renin gene expression. Mol Cell Endocrinol 224:11–20
Tamura K, Umemura S, Yamaguchi S, Iwamoto T, Kobayashi S, Fukamizu A, Murakami K, Ishii M (1994) Mechanism of cAMP regulation of renin gene transcription by proximal promoter. J Clin Invest 94:1959–1967
Tanimoto K, Sugiura A, Kanafusa S, Saito T, Masui N, Yanai K, Fukamizu A (2008) A single nucleotide mutation in the mouse renin promoter disrupts blood pressure regulation. J Clin Invest 118:1006–1016
Todorov VT, Desch M, Schmitt-Nilson N, Todorova A, Kurtz A (2007) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma is involved in the control of renin gene expression. Hypertension 50:939–944
Todorov VT, Desch M, Schubert T, Kurtz A (2008) The Pal3 promoter sequence is critical for the regulation of human renin gene transcription by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. Endocrinology 149:4647–4657
Todorov VT, Volkl S, Muller M, Bohla A, Klar J, Kunz-Schughart LA, Hehlgans T, Kurtz A (2004) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha activates NFkappaB to inhibit renin transcription by targeting cAMP-responsive element. J Biol Chem 279:1458–1467
Vo N, Goodman RH (2001) CREB-binding protein and p300 in transcriptional regulation. J Biol Chem 276:13505–13508
Yang T, Endo Y, Huang YG, Smart A, Briggs JP, Schnermann J (2000) Renin expression in COX-2-knockout mice on normal or low-salt diets. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 279:F819–F825
Ying L, Morris BJ, Sigmund CD (1997) Transactivation of the human renin promoter by the cyclic AMP/protein kinase A pathway is mediated by both cAMP-responsive element binding protein-1 (CREB)-dependent and CREB-independent mechanisms in Calu-6 cells. J Biol Chem 272:2412–2420
Yuan W, Pan W, Kong J, Zheng W, Szeto FL, Wong KE, Cohen R, Klopot A, Zhang Z, Li YC (2007) 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 suppresses renin gene transcription by blocking the activity of the cyclic AMP response element in the renin gene promoter. J Biol Chem 282:29821–29830
Zhou X, Davis DR, Sigmund CD (2006) The human renin kidney enhancer is required to maintain base-line renin expression but is dispensable for tissue-specific, cell-specific, and regulated expression. J Biol Chem 281:35296–35304
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft grant SFB 699/B1 to V.T.T. We gratefully acknowledge the excellent technical assistance of Dr. Anelia Todorova and Sandra Mayer.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Desch, M., Harlander, S., Neubauer, B. et al. cAMP target sequences enhCRE and CNRE sense low-salt intake to increase human renin gene expression in vivo. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 461, 567–577 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-011-0956-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-011-0956-z