Abstract
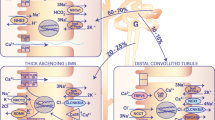
The thick ascending limb of Henle’s loop is a nephron segment that is vital to the formation of dilute and concentrated urine. This ability is accomplished by a consortium of functionally coupled proteins consisting of the apical Na+:K+:2Cl− co-transporter, the K+ channel, and basolateral Cl− channel that mediate electroneutral salt absorption. In thick ascending limbs, salt absorption is importantly regulated by the calcium-sensing receptor. Genetic or pharmacological disruption impairing the function of any of these proteins results in Bartter syndrome. The thick ascending limb is also an important site of Ca2+ and Mg2+ absorption. Calcium-sensing receptor activation inhibits cellular Ca2+ absorption induced by parathyroid hormone, as well as passive paracellular Ca2+ transport. The present review discusses these functions and their genetic and molecular regulation.





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Binding to the same recognition site as an endogenous agonist.
TAL apical membranes express 30- and 70-pS channels, and high-conductance, Ca2+-activated maxi K+ channels. ROMK, the 30-pS channel is absent from apical membranes of ROMK-null mice. The 70-pS channel mediates 80% of the apical K+ conductance. Current thinking suggests that the 70-pS K+ channel is a heterotetramer that includes ROMK, which may be a pore-containing subunit of the 70-pS K+ channels. ROMK1 is expressed in cortical collecting ducts, whereas ROMK2 is present in TAL [13].
Such a problem may contribute to or account for the findings of Desfleurs, who found that increasing basolateral calcium inhibited net calcium absorption without altering Na, Cl, K, or Mg transport by single perfused mouse CALs, [36]. CaSR activation was achieved by increasing basolateral calcium. The CAL, however, is highly permeable to calcium and elevating calcium asymmetrically at the serosal surface increases calcium backflux and results in diminished net calcium absorption regardless of an effect on the CaSR [14]. Under these conditions, it is not possible to distinguish a non-specific effect of diminished driving force from a specific action that can be attributed to the CaSR.
References
Abdullah HI, Pedraza PL, McGiff JC, Ferreri NR (2008) CaR activation increases TNF production by mTAL cells via a Gi-dependent mechanism. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 294:F345–F354
Adachi M, Asakura Y, Sato Y, Tajima T, Nakajima T, Yamamoto T, Fujieda K (2007) Novel SLC12A1 (NKCC2) mutations in two families with Bartter syndrome type 1. Endocr J 54:1003–1007
Amlal H, Legoff C, Vernimmen C, Paillard M, Bichara M (1996) Na+–K+ (NH4 +)–2Cl− cotransport in medullary thick ascending limb: control by PKA, PKC, and 20-HETE. Am J Physiol 271:C455–C463
Arthur JM, Collinsworth GP, Gettys TW, Quarles LD, Raymond JR (1997) Specific coupling of a cation-sensing receptor to G protein a-subunits in MDCK cells. Am J Physiol 273:F129–F135
Asano T, Takata K, Katagiri H, Ishihara H, Inukai K, Anai M, Hirano H, Yazaki Y, Oka Y (1993) The role of N-glycosylation in the targeting and stability of GLUT1 glucose transporter. FEBS Lett 324:258–261
Attmane-Elakeb A, Mount DB, Sibella V, Vernimmen C, Hebert SC, Bichara M (1998) Stimulation by in vivo and in vitro metabolic acidosis of expression of rBSC-1, the Na+–K+(NH4 +)–2Cl− cotransporter of the rat medullary thick ascending limb. J Biol Chem 273:33681–33691
Attmane-Elakeb A, Sibella V, Vernimmen C, Belenfant X, Hebert SC, Bichara M (2000) Regulation by glucocorticoids of expression and activity of rBSC1, the Na+–K+(NH4 +)–2Cl− cotransporter of medullary thick ascending limb. J Biol Chem 275:33548–33553
Bai M, Trivedi S, Brown EM (1998) Dimerization of the extracellular CaSR (CaR) on the cell surface of CaR-transfected HEK293 cells. J Biol Chem 273:23605–23610
Bartter FC, Pronove P, Gill JR Jr., MacCardle RC (1998) Hyperplasia of the juxtaglomerular complex with hyperaldosteronism and hypokalemic alkalosis. A new syndrome. 1962. J Am Soc Nephrol 9:516–528
Benziane B, Demaratez S, Defontaine N, Zaarour N, Cheval L, Bourgeois S, Klein C, Froissart M, Blanchard A, Pailard M, Gamba G, Houillier P, Laghmani K (2007) NKCC2 surface expression in mammalian cells: down-regulation by novel interaction with aldolase B. J Biol Chem 282:33817–33830
Besseghir K, Trimble ME, Stoner L (1986) Action of ADH on isolated medullary thick ascending limb of the Brattleboro rat. Am J Physiol 251:F271–F277
Bettinelli A, Ciarmatori S, Cesareo L, Tedeschi S, Ruffa G, Appiani AC, Rosini A, Grumieri G, Mercuri B, Sacco M, Leozappa G, Binda S, Cecconi M, Navone C, Curcio C, Syren ML, Casari G (2000) Phenotypic variability in Bartter syndrome type I. PediatrNephrol 14:940–945
Boim MA, Ho K, Shuck ME, Bienkowski MJ, Block JH, Slightom JL, Yang Y, Brenner BM, Hebert SC (1995) ROMK inwardly rectifying ATP-sensitive K+ channel. II. Cloning and distribution of alternative forms. Am J Physiol 268:F1132–1140
Bourdeau JE, Burg MB (1979) Voltage dependence of calcium transport in the thick ascending limb of Henle’s loop. Am J Physiol 236:F357–F364
Brown EM (1991) Extracellular Ca2+ sensing, regulation of parathyroid cell function, and role of Ca2+ and other ions as extracellular (first) messengers. Physiol Rev 71:371–411
Brown EM (2007) The CaSR: physiology, pathophysiology and CaR-based therapeutics. Subcell Biochem 45:139–167
Brown EM, Fuleihan Ge-H, Chen CJ, Kifor O (1990) A comparison of the effects of divalent and trivalent cations on parathyroid hormone release, 3′,5′-cyclic-adenosine monophosphate accumulation, and the levels of inositol phosphates in bovine parathyroid cells. Endocrinology 127:1064–1071
Brown EM, Gamba G, Riccardi D, Lombardi M, Butters R, Kifor O, Sun A, Hediger MA, Hebert SC (1993) Cloning, expression, and characterization of the bovine parathyroid Ca2+ sensing receptor (BOPCAR). J Am Soc Nephrol 4:704
Brown EM, Gamba G, Riccardi D, Lombardi M, Butters R, Kifor O, Sun A, Hediger MA, Lytton J, Hebert SC (1993) Cloning and characterization of an extracellular Ca2+-sensing receptor from bovine parathyroid. Nature 366:575–580
Brown EM, MacLeod RJ (2001) Extracellular calcium sensing and extracellular calcium signaling. Physiol Rev 81:239–297
Burg MB (1982) Thick ascending limb of Henle’s loop. Kidney Int 22:454–464
Burg MB, Green N (1973) Function of the thick ascending limb of Henle’s loop. Am J Physiol 224:659–668
Butters RR Jr., Chattopadhyay N, Nielsen P, Smith CP, Mithal A, Kifor O, Bai M, Quinn S, Goldsmith P, Hurwitz S, Krapcho K, Busby J, Brown EM (1997) Cloning and characterization of a CaSR from the hypercalcemic New Zealand white rabbit reveals unaltered responsiveness to extracellular calcium. J Bone Miner Res 12:568–579
Castrop H, Lorenz JN, Hansen P, Friis U, Mizel D, Oppermann M, Jensen B, Briggs J, Skott O, Schnermann J (2005) Contribution of the basolateral isoform of the Na,K,2Cl-cotransporter (NKCC1/BSC2) to renin secretion. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 289:F1185–F1192
Chang W, Shoback D (2004) Extracellular Ca2+-sensing receptors—an overview. Cell Calcium 35:183–196
Chen CJ, Barnett JV, Congo DA, Brown EM (1989) Divalent cations suppress 3′,5′-adenosine monophosphate accumulation by stimulating a pertussis toxin-sensitive guanine nucleotide-binding protein in cultured bovine parathyroid cells. Endocrinology 124:233–239
Cheng SX, Geibel JP, Hebert SC (2004) Extracellular polyamines regulate fluid secretion in rat colonic crypts via the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor. Gastroenterology 126:148–158
Conigrave AD, Quinn SJ, Brown EM (2000) L-amino acid sensing by the extracellular Ca2+-sensing receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:4814–4819
Conklin BR, Bourne HR (1994) Homeostatic signals. Marriage of the flytrap and the serpent. Nature 367:22
Contreras AM, Ramirez M, Cueva L, Alvarez S, de Loza R, Gamba G (1994) Low serum albumin and the increased risk of amikacin nephrotoxicity. Rev Invest Clin 46:37–43
Culpepper RM, Andreoli TE (1984) PGE2, forskolin, and cholera toxin interactions in modulating NaCl transport in mouse mTALH. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 247:F784–792
Cutler CP, Cramb G (2008) Differential expression of absorptive cation-chloride-cotransporters in the intestinal and renal tissues of the European eel (Anguilla anguilla). Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 149:63–73
de Jesus Ferreira MC, Bailly C (1998) Extracellular Ca2+ decreases chloride reabsorption in rat CTAL by inhibiting cAMP pathway. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 275:F198–F203
de Jesus Ferreira MC, Helies-Toussaint C, Imbert-Teboul M, Bailly C, Verbavatz JM, Bellanger AC, Chabardes D (1998) Co-expression of a Ca2+-inhibitable adenylyl cyclase and of a Ca2+-sensing receptor in the cortical thick ascending limb cell of the rat kidney. Inhibition of hormone-dependent cAMP accumulation by extracellular Ca2+. J Biol Chem 273:15192–15202
Delpire E, Rauchman MI, Beier DR, Hebert SC, Gullans SR (1994) Molecular cloning and chromosome localization of a putative basolateral Na+–K+–2Cl− cotransporter from mouse inner medullary collecting duct (mIMCD-3) cells. J Biol Chem 269:25677–25683
Desfleurs E, Wittner M, Simeone S, Pajaud S, Moine G, Rajerison R, Di Stefano A (1998) CaSR: regulation of electrolyte transport in the thick ascending limb of Henle’s loop. Kidney Blood Press Res 21:401–412
Dimke H, Flyvbjerg A, Bourgeois S, Thomsen K, Frokiaer J, Houillier P, Nielsen S, Frische S (2007) Acute growth hormone administration induces antidiuretic and antinatriuretic effects and increases phosphorylation of NKCC2. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 292:F723–F735
Ecelbarger CA, Terris J, Hoyer JR, Nielsen A, Wade JB, Knepper MA (1996) Localization and regulation of the rat renal Na+–K+–2Cl− cotransporter, BSC1. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 271:F619–F628
Edwards BR, Sutton RAL, Dirks JH (1974) Effect of calcium infusion on renal tubular reabsorption in the dog. Am J Physiol 227:13–18
Escalante B, Erlij D, Falck JR, McGiff JC (1991) Effect of cytochrome P450 arachidonate metabolites on ion transport in rabbit kidney loop of Henle. Science 251:799–802
Eveloff J, Calamia J (1986) Effect of osmolarity on cation fluxes in medullary thick ascending limb cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 250:F176–F180
Eveloff J, Warnock DK (1987) Activation of ion transport system during cell volume regulation. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 252:F1–F10
Fernandez-Llama P, Ecelbarger CA, Ware JA, Andrews P, Lee AJ, Turner R, Nielsen S, Knepper MA (1999) Cyclooxygenase inhibitors increase Na–K–2Cl cotransporter abundance in thick ascending limb of Henle’s loop. Am J Physiol 277:F219–F226
Ferreri NR, McGiff JC, Vio CP, Carroll MA (2003) TNFα regulates renal COX-2 in the rat thick ascending limb (TAL). Thromb Res 110:277–280
Fitzpatrick LA, Brandi ML, Aurbach GD (1986) Calcium-controlled secretion is effected through a guanine nucleotide regulatory protein in parathyroid cells. Endocrinology 119:2700–2703
Formenti A, De Simoni A, Arrigoni E, Martina M (2001) Changes in extracellular Ca2+ can affect the pattern of discharge in rat thalamic neurons. J Physiol 535:33–45
Fraser SA, Gimenez I, Cook N, Jennings I, Katerelos M, Katsis F, Levidiotis V, Kemp BE, Power DA (2007) Regulation of the renal-specific Na+–K+–2Cl− co-transporter NKCC2 by AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). Biochem J 405:85–93
Friedman PA (1998) Codependence of renal calcium and sodium transport. Annu Rev Physiol 60:179–197
Friedman PA, Gesek FA (1993) Calcium transport in renal epithelial cells. Am J Physiol 264:F181–F198
Friedman PA, Gesek FA, Coutermarsh BA, Kennedy SM (1994) PKA and PKC activation is required for PTH-stimulated calcium uptake by distal convoluted tubule cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 5:715
Fukuyama S, Okudaira S, Yamazato S, Yamazato M, Ohta T (2003) Analysis of renal tubular electrolyte transporter genes in seven patients with hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis. Kidney Int 64:808–816
Gagnon E, Bergeron MJ, Brunet GM, Daigle ND, Simard CF, Isenring P (2003) Molecular mechanisms of Cl transport by the renal Na–K–Cl cotransporter: identification of an intracellular locus that may form part of a high affinity Cl-binding site. J Biol Chem 279:5648–5654
Gagnon E, Forbush B, Flemmer AW, Gimenez I, Caron L, Isenring P (2002) Functional and molecular characterization of the shark renal Na–K–Cl cotransporter: novel aspects. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 283:F1046–F1055
Gamba G (2005) Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of the electroneutral cation-chloride cotransporters. Physiol Rev 85:423–493
Gamba G, Miyanoshita A, Lombardi M, Lytton J, Lee WS, Hediger MA, Hebert SC (1994) Molecular cloning, primary structure and characterization of two members of the mammalian electroneutral sodium–(potassium)–chloride cotransporter family expressed in kidney. J Biol Chem 269:17713–17722
Geering K, Theulaz F, Verrey M, Hauptle T, Rossier BC (1989) A role for the β-subunit in the expression of functional Na+–K+-ATPase in Xenopus oocytes. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 257:C851–C858
Gether U (2000) Uncovering molecular mechanisms involved in activation of G protein-coupled receptors. Endocrine Rev 21:90–113
Gimenez I, Forbush B (2003) Short-term stimulation of the renal Na–K–Cl cotransporter (NKCC2) by vasopressin involves phosphorylation and membrane translocation of the protein. J Biol Chem 278:26946–26951
Gimenez I, Forbush B (2005) Regulatory phosphorylation sites in the N-terminus of the renal Na–K–Cl cotransporter (NKCC2). Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 289:F1341–F1345
Gimenez I, Forbush B (2007) The residues determining differences in ion affinities among the alternative splice variants F, A, and B of the mammalian Renal Na–K–Cl cotransporter (NKCC2). J Biol Chem 282:6540–6547
Gimenez I, Isenring P, Forbush B III (2002) Spatially distributed alternative splice variants of the renal Na–K–Cl cotransporter exhibit dramatically different affinities for the transported ions. J Biol Chem 277:8767–8770
Gonzalez-Perret S, Kim K, Ibarra C, Damiano AE, Zotta E, Batelli M, Harris PC, Reisin IL, Arnaout MA, Cantiello HF (2001) Polycystin-2, the protein mutated in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), is a Ca2+-permeable nonselective cation channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:1182–1187
Good DW (1994) Ammonium transport by the thick ascending limb of Henle’s loop. Annu Rev Physiol 56:623–647
Greger R (1981) Chloride reabsorption in the rabbit cortical thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle. A sodium dependent process. Pflugers Arch 390:38–43
Greger R, Schlatter E (1981) Presence of luminal K+, a prerequisite for active NaCl transport in the cortical thick ascending limb of Henle’s loop of rabbit kidney. Pflugers Arch 392:92–94
Greger R, Schlatter E (1983) Properties of the basolateral membrane of the cortical thick ascending limb of Henle’s loop of rabbit kidney. A model for secondary active chloride transport. Pflugers Arch 396:325–334
Greger R, Schlatter E (1983) Properties of the lumen membrane of the cortical thick ascending limb of Henle’s loop of rabbit kidney. Pflugers Arch 396:315–324
Greger R, Schlatter E, Lang F (1983) Evidence for electroneutral sodium chloride cotransport in the cortical thick ascending limb of Henle’s loop of rabbit kidney. Pflugers Arch 396:308–314
Haas M, Dunham PB, Forbush IB (1991) [3H]Bumetanide binding to mouse kidney membranes: identification of corresponding membrane proteins. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 260:C791–C804
Hall DA, Varney DM (1980) Effect of vasopressin on electrical potential difference and chloride transport in mouse medullary thick ascending limb of Henle’s loop. J Clin Invest 66:792–802
Hamill OP, McBride DW Jr. (1996) The pharmacology of mechanogated membrane ion channels. Pharmacol Rev 48:231–252
Hammerland LG, Krapcho KJ, Garrett JE, Alasti N, Hung BCP, Simin RT, Levinthal C, Nemeth EF, Fuller FH (1999) Domains determining ligand specificity for Ca2+ receptors. Mol Pharmacol 55:642–648
Handlogten ME, Shiraishi N, Awata H, Huang C, Miller RT (2000) Extracellular Ca2+-sensing receptor is a promiscuous divalent cation sensor that responds to lead. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 279:F1083–F1091
Harrington PE, Fotsch C (2007) Calcium sensing receptor activators: calcimimetics. Curr Med Chem 14:3027–3034
Hebert SC, Culpepper RM, Andreoli TE (1981) NaCl transport in mouse medullary thick ascending limbs. I. Functional nephron heterogeneity and ADH-stimulated NaCl cotransport. Am J Physiol 241:F412–F431
Hebert SC, Culpepper RM, Andreoli TE (1981) NaCl transport in mouse medullary thick ascending limbs. I. Functional nephron heterogeneity and ADH-stimulated NaCl cotransport. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 241:F412–F431
Hebert SC, Culpepper RM, Andreoli TE (1981) NaCl transport in mouse medullary thick ascending limbs. II. ADH enhancement of transcellular NaCl cotransport; origin of transepithelial voltage. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 241:F432–F442
Hebert SC, Culpepper RM, Andreoli TE (1981) NaCl transport in mouse medullary thick ascending limbs. III. Modulation of ADH effect by peritubular osmolality. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 241:F443–F451
Hofer AM, Brown EM (2003) Extracellular calcium sensing and signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:530–538
Hu J, Spiegel AM (2007) Structure and function of the human calcium-sensing receptor: insights from natural and engineered mutations and allosteric modulators. J Cell Mol Med 11:908–922
Huang C, Handlogten ME, Miller RT (2002) Parallel activation of phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase and phospholipase C by the extracellular CaSR. J Biol Chem 277:20293–20300
Huang C, Hujer KM, Wu Z, Miller RT (2004) The Ca2+-sensing receptor couples to Gα12/13 to activate phospholipase D in Madin–Darby canine kidney cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 286:C22–C30
Huang C, Miller RT (2007) Regulation of renal ion transport by the CaSR: an update. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 16:437–443
Igarashi P, Vanden Heuver GB, Payne JA, Forbush IB (1995) Cloning, embryonic expression, and alternative splicing of a murine kidney-specific Na–K–Cl cotransporter. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 269:F406–F418
Ji W, Foo JN, O’Roak BJ, Zhao H, Larson MG, Simon DB, Newton-Cheh C, State MW, Levy D, Lifton RP (2008) Rare independent mutations in renal salt handling genes contribute to blood pressure variation. Nat Genet 40:592–599
Kaplan MR, Plotkin MD, Lee WS, Xu ZC, Lytton J, Hebert SC (1996) Apical localization of the Na–K–Cl cotransporter, rBSC1, on rat thick ascending limbs. Kidney Int 49:40–47
Karim Z, Attmane-Elakeb A, Sibella V, Bichara M (2003) Acid pH increases the stability of BSC1/NKCC2 mRNA in the medullary thick ascending limb. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:2229–2236
Kawakami K, Noguchi S, Noda M, Takahashi H, Ohta T, Kawamura M, Nojima H, Nagano K, Hirose T, Inayama S, Hayashida H, Miyata T, Numa S (1985) Primary structure of the α-subunit of Torpedo californica (Na+ + K+)ATPase deduced from cDNA sequence. Nature 316:733–736
Kifor O, Diaz R, Butters R, Brown EM (1997) The Ca2+-sensing receptor (CaR) activates phospholipases C, A2, and D in bovine parathyroid and CaR-transfected, human embryonic kidney (HEK293) cells. J Bone Miner Res 12:715–725
Kim GH, Ecelbarger CA, Mitchell C, Packer RK, Wade JB, Knepper MA (1999) Vasopressin increases Na–K–2Cl cotransporter expression in thick ascending limb of Henle’s loop. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 276:F96–F103
Knepper MA, Packer R, Good DW (1989) Ammonium transport in the kidney. Physiol Rev 69:179–249
Kurtz CL, Karolyi L, Seyberth HW, Koch MC, Vargas R, Feldmann D, Vollmer M, Knoers NV, Madrigal G, Guay-Woodford LM (1997) A common NKCC2 mutation in Costa Rican Bartter’s syndrome patients: evidence for a founder effect. J Am Soc Nephrol 8:1706–1711
Lalioti MD, Zhang J, Volkman HM, Kahle KT, Hoffmann KE, Toka HR, Nelson-Williams C, Ellison DH, Flavell R, Booth CJ, Lu Y, Geller DS, Lifton RP (2006) Wnk4 controls blood pressure and potassium homeostasis via regulation of mass and activity of the distal convoluted tubule. Nat Genet 38:1124–1132
Mamillapalli R, VanHouten J, Zawalich W, Wysolmerski J (2008) Switching of G-protein usage by the calcium-sensing receptor reverses its effect on parathyroid hormone-related protein secretion in normal versus malignant breast cells. J Biol Chem 283:24435–24447
Massry SG, Coburn JW, Chapman LW, Kleeman CR (1968) Role of serum Ca, parathyroid hormone, and NaCl infusion on renal Ca and Na clearances. Am J Physiol 214:1403–1409
McDonough AA, Geering K, Farley RA (1990) The sodium pump needs its β subunit. FASEB J 4:1598–1605
Meade P, Hoover RS, Plata C, Vazquez N, Bobadilla NA, Gamba G, Hebert SC (2003) cAMP-dependent activation of the renal-specific Na+–K+–2Cl− cotransporter is mediated by regulation of cotransporter trafficking. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 284:F1145–F1154
Moriguchi T, Urushiyama S, Hisamoto N, Iemura S, Uchida S, Natsume T, Matsumoto K, Shibuya H (2005) WNK1 regulates phosphorylation of cation-chloride-coupled cotransporters via the STE20-related kinases, SPAK and OSR1. J Biol Chem 280:42685–42693
Motoyama HI, Friedman PA (2002) CaSR regulation of PTH-dependent calcium absorption by mouse cortical ascending limbs. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 283:F399–F406
Mount DB, Baekgard A, Hall AE, Plata C, Xu J, Beier DR, Gamba G, Hebert SC (1999) Isoforms of the Na–K–2Cl transporter in murine TAL I. Molecular characterization and intrarenal localization. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 276:F347–F358
Mun HC, Franks AH, Culverston EL, Krapcho K, Nemeth EF, Conigrave AD (2004) The venus fly trap domain of the extracellular Ca2+-sensing receptor is required for l-amino acid sensing. J Biol Chem 279:51739–51744
Mupanomunda MM, Tian B, Ishioka N, Bukoski RD (2000) Renal interstitial Ca2+. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 278:F644–F669
Nemeth EF, Fox J (1999) Calcimimetic compounds: a direct approach to controlling plasma levels of parathyroid hormone in hyperparathyroidism. Trends Endocrinol Metab 10:66–71
Nemeth EF, Heaton WH, Miller M, Fox J, Balandrin MF, Van Wagenen BC, Colloton M, Karbon W, Scherrer J, Shatzen E, Rishton G, Scully S, Qi M, Harris R, Lacey D, Martin D (2004) Pharmacodynamics of the type II calcimimetic compound cinacalcet HCl. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 308:627–635
Ohki G, Miyoshi T, Murata M, Ishibashi K, Imai M, Suzuki M (2000) A calcium-activated cation current by an alternatively spliced form of Trp3 in the heart. J Biol Chem 275:39055–39060
Oppermann M, Mizel D, Kim SM, Chen L, Faulhaber-Walter R, Huang Y, Li C, Deng C, Briggs J, Schnermann J, Castrop H (2007) Renal function in mice with targeted disruption of the A isoform of the Na–K–2Cl co-transporter. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:440–448
Ortiz PA (2006) cAMP increases surface expression of NKCC2 in rat thick ascending limbs: role of VAMP. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290:F608–F616
Pace AJ, Gama L, Breitwieser GE (1999) Dimerization of the CaSR occurs within the extracellular domain and is eliminated by Cys→Ser mutations at Cys101 and Cys236. J Biol Chem 274:11629–11634
Paredes A, Plata C, Rivera M, Moreno E, Vazquez N, Munoz-Clares R, Hebert SC, Gamba G (2006) Activity of the renal Na+:K+:2Cl− cotransporter is reduced by mutagenesis of N-glycosylation sites: role for protein surface charge in Cl− transport. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290:F1094–F1102
Parfitt AM, Kleerekoper M (1980) Clinical disorders of calcium, phosphorous, and magnesium metabolism. In: Maxwell MH, Kleeman CR (eds) Clinical disorders of fluid and electrolyte metabolism. McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York, pp 947–1151
Payne JA, Forbush IB (1994) Alternatively spliced isoforms of the putative renal Na–K–Cl cotransporter are differentially distributed within the rabbit kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:4544–4548
Plata C, Meade P, Hall AE, Welch RC, Vazquez N, Hebert SC, Gamba G (2001) Alternatively spliced isoform of the apical Na–K–Cl cotransporter gene encodes a furosemide sensitive Na–Cl cotransporter. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 280:F574–F582
Plata C, Meade P, Vazquez N, Hebert SC, Gamba G (2002) Functional properties of the apical Na+–K+–2Cl− cotransporter isoforms. J Biol Chem 277:11004–11012
Plata C, Mount DB, Rubio V, Hebert SC, Gamba G (1999) Isoforms of the Na–K–2Cl cotransporter in murine TAL. II. Functional characterization and activation by cAMP. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 276:F359–F366
Pollak MR, Brown EM, Chou Y-HW, Hebert SC, Marx SJ, Steinmann B, Levi T, Seidman CE, Seidman JG (1993) Mutations in the human Ca2+-sensing receptor gene cause familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia and neonatal severe hyperparathyroidism. Cell 75:1297–1303
Pollak MR, Seidman CE, Brown EM (1996) Three inherited disorders of calcium sensing. Medicine 75:115–123
Ponce-Coria J, San Cristobal P, Kahle KT, Vazquez N, Pacheco-Alvarez D, De Los HP, Juarez P, Munoz E, Michel G, Bobadilla NA, Gimenez I, Lifton RP, Hebert SC, Gamba G (2008) Regulation of NKCC2 by a chloride-sensing mechanism involving the WNK3 and SPAK kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:8458–8463
Pressler CA, Heinzinger J, Jeck N, Waldegger P, Pechmann U, Reinalter S, Konrad M, Beetz R, Seyberth HW, Waldegger S (2006) Late-onset manifestation of antenatal Bartter syndrome as a result of residual function of the mutated renal Na+–K+–2Cl− co-transporter. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:2136–2142
Quamme GA (1982) Effect of hypercalcemia on renal tubular handling of calcium and magnesium. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 60:1275–1280
Quamme GA (1989) Control of magnesium transport in the thick ascending limb. Am J Physiol 256:F197–F210
Quinn SJ, Bai M, Brown EM (2004) pH Sensing by the calcium-sensing receptor. J Biol Chem 279:37241–37249
Reeves WB, Winters CJ, Andreoli TE (2001) Chloride channels in the loop of Henle. Annu Rev Physiol 63:631–645
Riccardi D, Hall AE, Chattopadhyay N, Xu JZ, Brown EM, Hebert SC (1998) Localization of the extracellular Ca2+/polyvalent cation-sensing protein in rat kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 274:F611–F622
Riccardi D, Hall AE, Chattopadhyay N, Xu JZ, Brown EM, Hebert SC (1998) Localization of the extracellular Ca2+ polyvalent cation-sensing protein in rat kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 274:F611–F622
Riccardi D, Lee WS, Lee K, Segre GV, Brown EM, Hebert SC (1996) Localization of the extracellular Ca2+-sensing receptor and PTH/PTHrP receptor in rat kidney. Am J Physiol 271:F951–F956
Riccardi D, Park J, Lee W-S, Gamba G, Brown EM, Hebert SC (1995) Cloning and functional expression of a rat kidney extracellular calcium/polyvalent cation-sensing receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:131–135
Rinehart J, Kahle KT, De Los HP, Vazquez N, Meade P, Wilson FH, Hebert SC, Gimenez I, Gamba G, Lifton RP (2005) WNK3 kinase is a positive regulator of NKCC2 and NCC, renal cation-Cl− cotransporters required for normal blood pressure homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:16777–16782
Rocha AS, Kokko JP (1973) Sodium chloride and water transport in the medullary thick ascending limb of Henle. Evidence for active chloride transport. J Clin Invest 52:612–623
Roman RM, Feranchak AP, Davison AK, Schwiebert EM, Fitz JG (1999) Evidence for Gd3+ inhibition of membrane ATP permeability and purinergic signaling. Am J Physiol 277:G1222–G1230
Sands JM, Naruse M, Baum M, Jo I, Hebert SC, Brown EM, Harris HW (1997) Apical extracellular calcium/polyvalent cation-sensing receptor regulates vasopressin-elicited water permeability in rat kidney inner medullary collecting duct. J Clin Invest 99:1399–1405
Sasaki S, Imai M (1980) Effects of vasopressin on water and NaCl transport across the in vitro perfused medullary thick ascending limb of Henle’s loop of mouse, rat, and rabbit kidneys. Pflugers Arch 383:215–221
Shaer AJ (2001) Inherited primary renal tubular hypokalemic alkalosis: a review of Gitelman and Bartter syndromes. Am J Med Sci 322:316–332
Shareghi GR, Agus ZS (1982) Magnesium transport in the cortical thick ascending limb of Henle’s loop of the rabbit. J Clin Invest 69:759–769
Shull GE, Lane LK, Lingrel JB (1986) Amino-acid sequence of the β-subunit of the (Na+ + K+)ATPase deduced from a cDNA. Nature 321:429–431
Shull GE, Schwartz A, Lingrel JB (1985) Amino-acid sequence of the catalytic subunit of the (Na+K+)ATPase deduced from a complementary DNA. Nature 316:691–695
Simon DB, Karet FE, Hamdan JM, Di Pietro A, Sanjad SA, Lifton RP (1996) Bartter’s syndrome, hypokalaemic alkalosis with hypercalciuria, is caused by mutations in the Na–K–2Cl cotransporter NKCC2. Nat Genet 13:183–188
Starremans PG, Kersten FF, Knoers NV, van den Heuvel LP, Bindels RJ (2003) Mutations in the human Na–K–2Cl cotransporter (NKCC2) identified in Bartter syndrome type I consistently result in nonfunctional transporters. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:1419–1426
Starremans PG, Kersten FF, van den Heuvel LP, Knoers NV, Bindels RJ (2003) Dimeric architecture of the human bumetanide-sensitive Na–K–Cl Co-transporter. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:3039–3046
Suki WN, Rouse D (1981) Hormonal regulation of calcium transport in thick ascending limb renal tubules. Am J Physiol 241:F171–F174
Suki WN, Rouse D, Ng RCK, Kokko JP (1980) Calcium transport in the thick ascending limb of Henle. Heterogeneity of function in the medullary and cortical segments. J Clin Invest 66:1004–1009
Sun A, Grossman EB, Lombardi M, Hebert SC (1991) Vasopressin alters the mechanism of apical Cl− entry from Na+:Cl− to Na+:K+:2Cl− cotransport in mouse medullary thick ascending limb. J Membr Biol 120:83–94
Takahashi N, Brooks HL, Wade JB, Liu W, Kondo Y, Ito S, Knepper MA, Smithies O (2002) Posttranscriptional compensation for heterozygous disruption of the kidney-specific NaK2Cl cotransporter gene. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:604–610
Takahashi N, Chernavvsky DR, Gomez RA, Igarashi P, Gitelman HJ, Smithies O (2000) Uncompensated polyuria in a mouse model of Bartter’s syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:5434–5439
Takaichi K, Kurokawa K (1986) High Ca2+ inhibits peptide hormone-dependent cAMP production specifically in thick ascending limbs of Henle. Miner Electrolyte Metab 12:342–346
Takaichi K, Kurokawa K (1988) Inhibitory guanosine triphosphate-binding protein-mediated regulation of vasopressin action in isolated single medullary tubules of mouse kidney. J Clin Invest 82:1437–1444
Tovar-Palacio C, Bobadilla NA, Cortes P, Plata C, De Los HP, Vazquez N, Gamba G (2004) Ion and diuretic specificity of chimeric proteins between apical Na+:K+:2Cl− and Na+:Cl− cotransporters. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 287:F570–F577
Vargas-Poussou R, Feldman D, Vollmer M, Konrad M, Kelly L, Van der Heuvel LPWJ, Tebouri L, Brandis M, Karolyi L, Hebert SC, Lemmink HH, Deschnes G, Hildebrandt F, Seyberth HW, Guay-Woodford LM, Knoers NVAM, Antignac C (1998) Novel molecular variants of the Na–K–2Cl cotransporter gene are responsible for antenatal Bartter syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 62:1332–1340
Vargas-Poussou R, Feldmann D, Vollmer M, Konrad M, Kelly L, Van den Heuvel LPWJ, Tebourbi L, Brandis M, Karolyi L, Hebert SC, Lemmink HH, Deschênes G, Hildebrandt F, Seyberth HW, Guay-Woodford LM, Knoers NVAM, Antignac C (1998) Novel molecular variants of the Na–K–2Cl cotransporter gene are responsible for antenatal Bartter syndrome. Am J Hum Genet 62:1332–1340
Vargas-Poussou R, Huang C, Hulin P, Houillier P, Jeunemaitre X, Paillard M, Planelles G, Dechaux M, Miller RT, Antignac C (2002) Functional characterization of a calcium-sensing receptor mutation in severe autosomal dominant hypocalcemia with a Bartter-like syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:2259–2266
Varrault A, Pena MSR, Goldsmith PK, Mithal A, Brown EM, Spiegel AM (1995) Expression of G protein a-subunits in bovine parathyroid. Endocrinology 136:4390–4396
Waldegger S, Jeck N, Barth P, Peters M, Vitzthum H, Wolf K, Kurtz A, Konrad M, Seyberth HW (2002) Barttin increases surface expression and changes current properties of ClC–K channels. Pflugers Arch 444:411–418
Wang D, An SJ, Wang WH, McGiff JC, Ferreri NR (2001) CaR-mediated COX-2 expression in primary cultured mTAL cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 281:F658–F664
Wang D, McGiff JC, Ferreri NR (2000) Regulation of cyclooxygenase isoforms in the renal thick ascending limb: effects of extracellular calcium. J Physiol Pharmacol 51:587–595
Wang W, Lu M, Balazy M, Hebert SC (1997) Phospholipase A2 is involved in mediating the effect of extracellular Ca2+ on apical K+ channels in rat TAL. Am J Physiol 273:F421–F429
Wang WH (2006) Regulation of ROMK (Kir1.1) channels: new mechanisms and aspects. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290:F14–F19
Wang WH, Lu M, Hebert SC (1996) Cytochrome P-450 metabolites mediate extracellular Ca2+-induced inhibition of apical K+ channels in the TAL. Am J Physiol 271:C103–C111
Ward DT (2004) Calcium receptor-mediated intracellular signalling. Cell Calcium 35:217–228
Ward DT, McLarnon SJ, Riccardi D (2002) Aminoglycosides increase intracellular calcium levels and ERK activity in proximal tubular OK cells expressing the extracellular CaSR. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:1481–1489
Watanabe S, Fukumoto S, Chang H, Takeuchi Y, Hasegawa Y, Okazaki R, Chikatsu N, Fujita T (2002) Association between activating mutations of calcium-sensing receptor and Bartter’s syndrome. Lancet 360:692–694
Welker P, Boehlick A, Mutig K, Salanova M, Kahl T, Schlueter H, Blottner D, Ponce-Coria J, Gamba G, Bachmann S (2008) Renal Na–K–Cl cotransporter activity and vasopressin-induced trafficking are lipid raft-dependent. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 295:F978–F802
Xu JC, Lytle C, Zhu TT, Payne JA, Benz Jr E, Forbush IB (1994) Molecular cloning and functional expression of the bumetanide-sensitive Na–K–Cl cotransporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:2201–2205
Yamaguchi T, Ye C, Chattopadhyay N, Sanders JL, Vassilev PM, Brown EM (2000) Enhanced expression of extracellular calcium sensing receptor in monocyte-differentiated versus undifferentiated HL-60 cells: potential role in regulation of a nonselective cation channel. Calcif Tissue Int 66:375–382
Yang T, Huang YG, Singh I, Schnermann J, Briggs JP (1996) Localization of bumetanide- and thiazide-sensitive Na–K–Cl cotransporters along the rat nephron. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 271:F931–F939
Zhang Z, Jiang Y, Quinn SJ, Krapcho K, Nemeth EF, Bai M (2002) l-Phenylalanine and NPS R-467 synergistically potentiate the function of the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor through distinct sites. J Biol Chem 277:33736–33741
Acknowledgments
Original studies described here were supported by grants DK 54171 and DK 64635 from the National Institutes of Health to PAF and GG, respectively, CONACYT grant 59992 to GG, and by a grant from the Foundation Leducq for the Transatlantic Network on Hypertension—Renal Salt Handling in the Control of Blood Pressure (GG).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This review is dedicated to the memory of Dr. Steven C. Hebert. Dr. Hebert, our colleague and friend, was a leader in elucidating the mechanism and regulation of salt and water balance by the kidney. He embodied the foresight to anticipate many of the elements contributing to renal homeostasis, an infectious enthusiasm that inspired fellows and colleagues alike, and an open and welcoming collegiality that represents all the best traits of academia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gamba, G., Friedman, P.A. Thick ascending limb: the Na+:K+:2Cl− co-transporter, NKCC2, and the calcium-sensing receptor, CaSR. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 458, 61–76 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-008-0607-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-008-0607-1