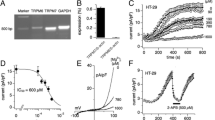
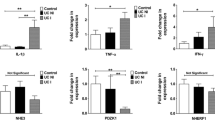
Abstract
The adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) tumor suppressor gene is mutated in almost all human colonic cancers. Disturbances in Na+ absorption have been observed in colonic cancer, and ion channels such as ether a go-go (Eag) or Ca2+-sensitive BK channels have been recognized for their oncogenic potential. APC Min/+ mice have reduced APC expression and develop multiple intestinal neoplasias (Min). Ion channels in the colonic epithelium were examined using electrophysiology and molecular techniques. APC Min/+ mice developed intestinal neoplasia and experienced a significant weight loss. Due to intestinal bleedings, the hematocrit was largely reduced and plasma aldosterone levels were enhanced. Rectal potential measurements in vivo indicated an increase in amiloride-sensitive Na+ absorption in APC Min/+ mice. Quantitative Ussing chamber studies demonstrated enhanced Na+ absorption via epithelial Na+ channels (ENaC) and suggested enhanced activity of oncogenic BK and Eag-1 channels. Patch clamp and fluorescence measurements on isolated crypts suggested enhanced K+ channel activity in the surface epithelium. ENaC-mRNA and membrane protein expression was enhanced in colonic surface epithelial cells. The data suggest that reduced expression of the APC gene with upregulation of the downstream proteins Akt and mTOR and subsequent hyperaldosteronism is paralleled by upregulation of oncogenic potassium channels and enhanced colonic Na+ absorption.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amasheh S, Barmeyer C, Koch CS, Tavalali S, Mankertz J, Epple HJ, Gehring MM, Florian P, Kroesen AJ, Zeitz M, Fromm M, Schulzke JD (2004) Cytokine-dependent transcriptional down-regulation of epithelial sodium channel in ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 126:1711–1720
Aoki K, Tamai Y, Horiike S, Oshima M, Taketo MM (2003) Colonic polyposis caused by mTOR-mediated chromosomal instability in Apc+/Delta716 Cdx2+/− compound mutant mice. Nat Genet 35:323–330
Barmeyer C, Harren M, Schmitz H, Heinzel-Pleines U, Mankertz J, Seidler U, Horak I, Wiedenmann B, Fromm M, Schulzke JD (2004) Mechanisms of diarrhea in the interleukin-2-deficient mouse model of colonic inflammation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 286:G244–G252
Bleich M, Ecke D, Schwartz B, Fraser G, Greger R (1997) Effects of the carcinogen dimethylhydrazine (DMH) on the function of rat colonic crypts. Pflügers Arch 433:254–259
Bloch M, Ousingsawat J, Simon R, Gasser TC, Mihatsch MJ, Kunzelmann K, Bubendorf L (2005) KCNMA1 gene amplification promotes tumor cell proliferation in prostate cancer. Oncogene 459:443–447
Chae KS, Martin-Caraballo M, Anderson M, Dryer SE (2005) Akt activation is necessary for growth factor-induced trafficking of functional K(Ca) channels in developing parasympathetic neurons. J Neurophysiol 93:1174–1182
Chan AO, Hui WM, Leung G, Tong T, Hung IF, Chan P, Hsu A, But D, Wong BC, Lam SK, Lam KF (2007) Patients with functional constipation do not have increased prevalence of colorectal cancer precursors. Gut 56:451–452
Davies RJ, Weidema WF, Sandle GI, Palmer L, Deschner EE, DeCosse JJ (1987) Sodium transport in a mouse model of colonic carcinogenesis. Cancer Res 47:4646–4650
Dihlmann S, Kloor M, Fallsehr C, von Knebel DM (2005) Regulation of AKT1 expression by beta-catenin/Tcf/Lef signaling in colorectal cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 26:1503–1512
Dikovskaya D, Schiffmann D, Newton IP, Oakley A, Kroboth K, Sansom O, Jamieson TJ, Meniel V, Clarke A, Nathke IS (2007) Loss of APC induces polyploidy as a result of a combination of defects in mitosis and apoptosis. J Cell Biol 176:183–195
Fodde R, Edelmann W, Yang K, van Leeuwen C, Carlson C, Renault B, Breukel C, Alt E, Lipkin M, Khan PM (1994) A targeted chain-termination mutation in the mouse Apc gene results in multiple intestinal tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:8969–8973
Fodde R, Smits R (2002) Cancer biology. A matter of dosage. Science 298:761–763
Kongkanuntn R, Bubb VJ, Sansom OJ, Wyllie AH, Harrison DJ, Clarke AR (1999) Dysregulated expression of beta-catenin marks early neoplastic change in Apc mutant mice, but not all lesions arising in Msh2 deficient mice. Oncogene 18:7219–7225
Kune GA, Kune S, Field B, Watson LF (1988) The role of chronic constipation, diarrhea, and laxative use in the etiology of large-bowel cancer. Data from the Melbourne Colorectal Cancer Study. Dis Colon Rectum 31:507–512
Kunzelmann K (2005) Ion channels and cancer. J Membr Biol 205:159–173
Land SC, McTavish N, Wilson SM (2007) Modulation of dexamethasone-evoked alpha-ENaC expression by the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). Acta Physiol 189 (S653):P08-L6-14
Lastraioli E, Guasti L, Crociani O, Polvani S, Hofmann G, Witchel H, Bencini L, Calistri M, Messerini L, Scatizzi M, Moretti R, Wanke E, Olivotto M, Mugnai G, Arcangeli A (2004) herg1 gene and HERG1 protein are overexpressed in colorectal cancers and regulate cell invasion of tumor cells. Cancer Res 64:606–611
Lee IA, Dinudom A, Kumar S, Cook DI (2007) Akt mediates the effect of insulin on epithelial sodium channels by inhibiting Nedd4-2.. J Biol Chem 282(41):29866–29873
Moran AE, Hunt DH, Javid SH, Redston M, Carothers AM, Bertagnolli MM (2004) Apc deficiency is associated with increased Egfr activity in the intestinal enterocytes and adenomas of C57BL/6J-Min/+ mice. J Biol Chem 279:43261–43272
Nathke I (2006) Cytoskeleton out of the cupboard: colon cancer and cytoskeletal changes induced by loss of APC. Nat Rev Cancer 6:967–974
Ousingsawat J, Spitzner M, Puntheeranurak S, Terracciano L, Tornillo L, Bubendorf L, Kunzelmann K, Schreiber R (2007) Expression of voltage gated potassium channels in human and mouse colonic carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 13:824–831
Pardo LA (2004) Voltage-gated potassium channels in cell proliferation. Physiology (Bethesda) 19:285–292
Pardo LA, del Camino D, Sanchez A, Alves F, Brüggemann A, Beckh S, Stühmer W (1999) Oncogenic potential of EAG K+ channels. EMBO J 18:5540–5547
Puntheeranurak S, Schreiber R, Kunzelmann K, Krishnamra N (2007) Control of ion transport in mouse proximal and distal colon by prolactin. Cell Physiol Biochem 19:77–88
Qian CN, Knol J, Igarashi P, Lin F, Zylstra U, The BT, Williams BO (2005) Cystic renal neoplasia following conditional inactivation of apc in mouse renal tubular epithelium. J Biol Chem 280:3938–3945
Rao CV, Hirose Y, Indranie C, Reddy BS (2001) Modulation of experimental colon tumorigenesis by types and amounts of dietary fatty acids. Cancer Res 61:1927–1933
Schreiber R (2005) Ca2+ signaling, intracellular pH and cell volume in cell proliferation. J Membr Biol 205:129–137
Sonnenberg A, Muller AD (1993) Constipation and cathartics as risk factors of colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. Pharmacology 47(Suppl 1):224–233
Sorensen MV, Matos JE, Praetorius HA, Sausbier M, Ruth P, Leipziger J (2005) Aldosterone up-regulates KCA 1.1 (BK) channel-mediated colonic K+ secretion. Acta Physiol 188(S651):P23
Spitzner M, Ousingsawat J, Scheidt K, Kunzelmann K, Schreiber R (2007) Role of voltage gated K+ channels for proliferation of colonic cancer cells. FASEB J 21:35–44
Su LK, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Preisinger AC, Moser AR, Luongo C, Gould KA, Dove WF (1992) Multiple intestinal neoplasia caused by a mutation in the murine homolog of the APC gene. Science 256:668–670
Valverde MA, Rojas P, Amigo J, Cosmelli D, Orio P, Bahamonde MI, Mann GE, Vergara C, Latorre R (1999) Acute activation of Maxi-K channels (hSlo) by estradiol binding to the beta subunit. Science 285:1929–1931
Wasan HS, Novelli M, Bee J, Bodmer WF (1997) Dietary fat influences on polyp phenotype in multiple intestinal neoplasia mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 94:3308–3313
Weitz J, Koch M, Debus J, Hohler T, Galle PR, Buchler MW (2005) Colorectal cancer. Lancet 365:153–165
Yao X, Kwan HY (1999) Activity of voltage-gated K+ channels is associated with cell proliferation and Ca2+ influx in carcinoma cells of colon cancer. Life Sci 65:55–62
Zhang T, Otevrel T, Gao Z, Gao Z, Ehrlich SM, Fields JZ, Boman BM (2001) Evidence that APC regulates survivin expression: a possible mechanism contributing to the stem cell origin of colon cancer. Cancer Res 61:8664–8667
Zhang Y, Wang H, Wang J, Han H, Nattel S, Wang Z (2003) Normal function of HERG K+ channels expressed in HEK293 cells requires basal protein kinase B activity. FEBS Lett 534:125–132
Acknowledgments
We thank Ernestine Tartler for her excellent technical assistance. This study was supported by DFG SCHR 752/2-2 und Wilhelm Sander-Stiftung 2005.063.1.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest exist.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the linked to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplement 1
(DOC 35 kb)
Supplement 2
(JPEG 33 kb)
Supplement 3
(DOC 27 kb)
Supplement 4
(PDF 1116 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ousingsawat, J., Spitzner, M., Schreiber, R. et al. Upregulation of colonic ion channels in APC Min/+ mice. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 456, 847–855 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-008-0451-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-008-0451-3