Abstract
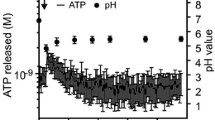
Renal epithelia can be provoked mechanically to release nucleotides, which subsequently increases the intracellular Ca2+ concentration [Ca2+]i through activation of purinergic (P2) receptors. Cultured cells often show spontaneous [Ca2+]i oscillations, a feature suggested to involve nucleotide signalling. In this study, fluo-4 loaded Madin–Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells are used as a model for quantification and characterisation of spontaneous [Ca2+]i increases in renal epithelia. Spontaneous [Ca2+]i increases occurred randomly as single cell events. During an observation period of 1 min, 10.9 ± 6.7% (n = 23) of the cells showed spontaneous [Ca2+]i increases. Spontaneous adenosine triphosphate (ATP) release from MDCK cells was detected directly by luciferin/luciferase. Scavenging of ATP by apyrase or hexokinase markedly reduced the [Ca2+]i oscillatory activity, whereas inhibition of ecto-ATPases (ARL67156) enhanced the [Ca2+]i oscillatory activity. The association between spontaneous [Ca2+]i increases and nucleotide signalling was further tested in 132–1N1 cells lacking P2 receptors. These cells hardly showed any spontaneous [Ca2+]i increases. Transfection with either hP2Y6 or hP2Y2 receptors revealed a striking degree of oscillations. Similar spontaneous [Ca2+]i increases were observed in freshly isolated, perfused mouse medullary thick ascending limb (mTAL). The oscillatory activity was reduced by basolateral apyrase and substantially lower in mTAL from P2Y2 knock out mice (0.050 ± 0.020 events per second, n = 8) compared to the wild type (0.147 ± 0.018 events per second, n = 9). These findings indicate that renal epithelia spontaneously release nucleotides leading to P2-receptor-dependent [Ca2+]i oscillations. Thus, tonic nucleotide release is likely to modify steady state renal function.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clemetson KJ, Clemetson JM (2004) Platelet receptor signalling. Hematol J 5:S159–S163
Burnstock G (2006) Purinergic signalling. Br J Pharmacol 147:S172–S181
Leipziger J (2003) Control of epithelial transport via luminal P2 receptors. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 284:F419–F432
Ralevic V, Burnstock G (1998) Receptors for purines and pyrimidines. Pharmacol Rev 50:413–492
Lazarowski ER, Boucher RC, Harden TK (2003) Mechanisms of release of nucleotides and integration of their action as P2X- and P2Y-receptor activating molecules. Mol Pharmacol 64:785–795
Abraham EH, Prat AG, Gerweck L, Seneveratne T, Arceci RJ, Kramer R, Guidotti G, Cantiello HF (1993) The multidrug resistance (mdr1) gene product functions as an ATP channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:312–316
Reisin IL, Prat AG, Abraham EH, Amara JF, Gregory RJ, Ausiello DA, Cantiello HF (1994) The cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator is a dual ATP and chloride channel. J Biol Chem 269:20584–20591
Cotrina ML, Lin JH, ves-Rodrigues A, Liu S, Li J, zmi-Ghadimi H, Kang J, Naus CC, Nedergaard M (1998) Connexins regulate calcium signaling by controlling ATP release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:15735–15740
Bao L, Locovei S, Dahl G (2004) Pannexin membrane channels are mechanosensitive conduits for ATP. FEBS Lett 572:65–68
Zegarra-Moran O, Romeo G, Galietta LJ (1995) Regulation of transepithelial ion transport by two different purinoceptors in the apical membrane of canine kidney (MDCK) cells. Br J Pharmacol 114:1052–1056
Schwiebert EM, Kishore BK (2001) Extracellular nucleotide signaling along the renal epithelium. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 280:F945–F963
Unwin RJ, Bailey MA, Burnstock G (2003) Purinergic signaling along the renal tubule: the current state of play. News Physiol Sci 18:237–241
Kishore BK, Isaac J, Fausther M, Tripp SR, Shi H, Gill PS, Braun N, Zimmermann H, Sevigny J, Robson SC (2005) Expression of NTPDase1 and NTPDase2 in murine kidney: relevance to regulation of P2 receptor signaling. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 288:F1032–F1043
Dawson TP, Gandhi R, Le HM, Kaissling B (1989) Ecto-5'-nucleotidase: localization in rat kidney by light microscopic histochemical and immunohistochemical methods. J Histochem Cytochem 37:39–47
Vallon V, Richter K, Huang DY, Rieg T, Schnermann J (2004) Functional consequences at the single-nephron level of the lack of adenosine A1 receptors and tubuloglomerular feedback in mice. Pflugers Arch 448:214–221
Hashimoto S, Huang Y, Briggs J, Schnermann J (2006) Reduced autoregulatory effectiveness in adenosine 1 receptor-deficient mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290:F888–F891
Komlosi P, Peti-Peterdi J, Fuson AL, Fintha A, Rosivall L, Bell PD (2004) Macula densa basolateral ATP release is regulated by luminal [NaCl] and dietary salt intake. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 286:F1054–F1058
Cuffe JE, Bielfeld-Ackermann A, Thomas J, Leipziger J, Korbmacher C (2000) ATP stimulates Cl- secretion and reduces amiloride-sensitive Na+ absorption in M-1 mouse cortical collecting duct cells. J Physiol 524:77–90
Lehrmann H, Thomas J, Kim SJ, Jacobi C, Leipziger J (2002) Luminal P2Y2 receptor-mediated inhibition of Na+ absorption in isolated perfused mouse CCD. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:10–18
Rouse D, Leite M, Suki WN (1994) ATP inhibits the hydrosmotic effect of AVP in rabbit CCT: evidence for a nucleotide P2u receptor. Am J Physiol 267:F289–F295
Kishore BK, Chou CL, Knepper MA (1995) Extracellular nucleotide receptor inhibits AVP-stimulated water permeability in inner medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol 269:F863–F869
Bailey MA (2004) Inhibition of bicarbonate reabsorption in the rat proximal tubule by activation of luminal P2Y1 receptors. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 287:F789–F796
Ostrom RS, Gregorian C, Insel PA (2000) Cellular release of and response to ATP as key determinants of the set-point of signal transduction pathways. J Biol Chem 275:11735–11739
Rieg T, Bundey RA, Chen Y, Deschenes G, Junger W, Insel PA, Vallon V (2007) Mice lacking P2Y2 receptors have salt-resistant hypertension and facilitated renal Na+ and water reabsorption. FASEB J (in press)
Praetorius HA, Spring KR (2001) Bending the MDCK cell primary cilium increases intracellular calcium. J Membr Biol 184:71–79
Matos JE, Robaye B, Boeynaems JM, Beauwens R, Leipziger J (2005) K+ secretion activated by luminal P2Y2 and P2Y4 receptors in mouse colon. J Physiol 564:269–279
Odgaard E, Jakobsen JK, Frische S, Praetorius J, Nielsen S, Aalkjaer C, Leipziger J (2004) Basolateral Na+-dependent HCO3 - transporter NBCn1-mediated HCO3 - influx in rat medullary thick ascending limb. J Physiol 555:205–218
Greger R, Hampel W (1981) A modified system for in vitro perfusion of isolated renal tubules. Pflugers Arch 389:175–176
Brown EM, Pollak M, Hebert SC (1998) The extracellular calcium-sensing receptor: its role in health and disease. Annu Rev Med 49:15–29
Praetorius HA, Frokiaer J, Leipziger J (2004) Transepithelial pressure pulses induce nucleotide release in polarized MDCK cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 288:F133–F141
Insel PA, Ostrom RS, Zambon AC, Hughes RJ, Balboa MA, Shehnaz D, Gregorian C, Torres B, Firestein BL, Xing M, Post SR (2001) P2Y receptors of MDCK cells: epithelial cell regulation by extracellular nucleotides. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 28:351–354
Lazarowski ER, Boucher RC, Harden TK (2000) Constitutive release of ATP and evidence for major contribution of ecto-nucleotide pyrophosphatase and nucleoside diphosphokinase to extracellular nucleotide concentrations. J Biol Chem 275:31061–31068
Farahbakhsh NA (2003) Ectonucleotidases of the rabbit ciliary body nonpigmented epithelium. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44:3952–3960
Akimova OA, Grygorczyk A, Bundey RA, Bourcier N, Gekle M, Insel PA, Orlov SN (2006) Transient activation and delayed inhibition of Na+,K+,Cl− cotransport in ATP-treated C11-MDCK cells involve distinct P2Y receptor subtypes and signaling mechanisms. J Biol Chem 524:31317–31390
Parr CE, Sullivan DM, Paradiso AM, Lazarowski ER, Burch LH, Olsen JC, Erb L, Weisman GA, Boucher RC, Turner JT (1994) Cloning and expression of a human P2U nucleotide receptor, a target for cystic fibrosis pharmacotherapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:3275–3279
Jensen ME, Odgaard E, Christensen MH, Praetorius HA, Leipziger J (2007) Flow increase triggers nucleotide release in the intact nephron. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:2062–2070
Paulais M, Baudouin-Legros M, Teulon J (1995) Extracellular ATP and UTP trigger calcium entry in mouse cortical thick ascending limbs. Am J Physiol 268:F496–F502
Kawano S, Otsu K, Kuruma A, Shoji S, Yanagida E, Muto Y, Yoshikawa F, Hirayama Y, Mikoshiba K, Furuichi T (2006) ATP autocrine/paracrine signaling induces calcium oscillations and NFAT activation in human mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Calcium 39:313–324
Scemes E, Duval N, Meda P (2003) Reduced expression of P2Y1 receptors in connexin43-null mice alters calcium signaling and migration of neural progenitor cells. J Neurosci 23:11444–11452
Missiaen L, Taylor CW, Berridge MJ (1991) Spontaneous calcium release from inositol trisphosphate-sensitive calcium stores. Nature 352:241–244
Carroll J, Swann K (1992) Spontaneous cytosolic calcium oscillations driven by inositol trisphosphate occur during in vitro maturation of mouse oocytes. J Biol Chem 267:11196–11201
Publicover NG, Horowitz NN, Sanders KM (1992) Calcium oscillations in freshly dispersed and cultured interstitial cells from canine colon. Am J Physiol 262:C589–C597
Espelt MV, Estevez AY, Yin X, Strange K (2005) Oscillatory Ca2+ signaling in the isolated Caenorhabditis elegans intestine: role of the inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor and phospholipases C beta and gamma. J Gen Physiol 126:379–392
Kono T, Nishikori T, Kataoka H, Uchio Y, Ochi M, Enomoto K (2006) Spontaneous oscillation and mechanically induced calcium waves in chondrocytes. Cell Biochem Funct 24:103–111
Kapur N, Mignery G, Banach K (2007) Cell cycle dependent calcium oscillations in mouse embryonic stem cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 292:C1510–C1518
Peti-Peterdi J (2006) Calcium wave of tubuloglomerular feedback. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 291:F473–F480
Ostrom RS, Gregorian C, Drenan RM, Gabot K, Rana BK, Insel PA (2001) Key role for constitutive cyclooxygenase-2 of MDCK cells in basal signaling and response to released ATP. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 281:C524–C531
Kishore BK, Judge JP, Sun R, Nelson RD (2006) Manifestation of renal phenotypes in mice with genetic deletion of P2Y2 receptors. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:30A(Abstract)
Thomas AP, Bird GS, Hajnoczky G, Robb-Gaspers LD, Putney JW Jr (1996) Spatial and temporal aspects of cellular calcium signaling. FASEB J 10:1505–1517
Yip KP (2002) Coupling of vasopressin-induced intracellular Ca2+ mobilization and apical exocytosis in perfused rat kidney collecting duct. J Physiol 538:891–899
Deetjen P, Thomas J, Lehrmann H, Kim SJ, Leipziger J (2000) The luminal P2Y receptor in the isolated perfused mouse cortical collecting duct. J Am Soc Nephrol 11:1798–1806
Uhlen P, Laestadius A, Jahnukainen T, Soderblom T, Backhed F, Celsi G, Brismar H, Normark S, Aperia A, Richter-Dahlfors A (2000) Alpha-haemolysin of uropathogenic E. coli induces Ca2+ oscillations in renal epithelial cells. Nature 405:694–697
Hanley PJ, Musset B, Renigunta V, Limberg SH, Dalpke AH, Sus R, Heeg KM, Preisig-Muller R, Daut J (2004) Extracellular ATP induces oscillations of intracellular Ca2+ and membrane potential and promotes transcription of IL-6 in macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:9479–9484
Ihara H, Hirukawa K, Goto S, Togari A (2005) ATP-stimulated interleukin-6 synthesis through P2Y receptors on human osteoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 326:329–334
Douillet CD, Robinson WP III, Milano PM, Boucher RC, Rich PB (2006) Nucleotides induce IL-6 release from human airway epithelia via P2Y2 and p38 MAPK-dependent pathways. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 291:L734–L746
Yoshida H, Kobayashi D, Ohkubo S, Nakahata N (2006) ATP stimulates interleukin-6 production via P2Y receptors in human HaCaT keratinocytes. Eur J Pharmacol 540:1–9
Inoue K, Hosoi J, Denda M (2007) Extracellular ATP has stimulatory effects on the expression and release of IL-6 via purinergic receptors in normal human epidermal keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol 127:362–371
Acknowledgement
We thank the following foundations for their support: The Danish Medical Research Foundation. Grundforskningsfonden. Nyreforeningens forskningsfond, The Aarhus University Research Foundation, Eva og Henry Frænkels Mindefond, The A.P. Møller Foundation for the Advancement of Medical Science and R.I.E. König-Petersen Forskningsfond for Nyresygdomme. The Water and Salt Research Center at the University of Aarhus is established and supported by the Danish National Research Foundation (Danmarks Grundforskningsfond). We thank Jean-Marie Boeynaems, Universite Libre de Bruxelles, Belgium, and Robert Nicholas, University of North Carolina, NC, USA, for the kind provision of P2-receptor transfected cells.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
C. S. Geyti and E. Odgaard contributed equally to the publication.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geyti, C.S., Odgaard, E., Overgaard, M.T. et al. Slow spontaneous [Ca2+]i oscillations reflect nucleotide release from renal epithelia. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 455, 1105–1117 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-007-0366-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-007-0366-4