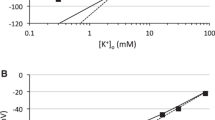
Abstract
[K+]e increase accompanies many pathological states in the CNS and evokes changes in astrocyte morphology and glial fibrillary acidic protein expression, leading to astrogliosis. Changes in the electrophysiological properties and volume regulation of astrocytes during the early stages of astrocytic activation were studied using the patch-clamp technique in spinal cords from 10-day-old rats after incubation in 50 mM K+. In complex astrocytes, incubation in high K+ caused depolarization, an input resistance increase, a decrease in membrane capacitance, and an increase in the current densities (CDs) of voltage-dependent K+ and Na+ currents. In passive astrocytes, the reversal potential shifted to more positive values and CDs decreased. No changes were observed in astrocyte precursors. Under hypotonic stress, astrocytes in spinal cords pre-exposed to high K+ revealed a decreased K+ accumulation around the cell membrane after a depolarizing prepulse, suggesting altered volume regulation. 3D confocal morphometry and the direct visualization of astrocytes in enhanced green fluorescent protein/glial fibrillary acidic protein mice showed a smaller degree of cell swelling in spinal cords pre-exposed to high K+ compared to controls. We conclude that exposure to high K+, an early event leading to astrogliosis, caused not only morphological changes in astrocytes but also changes in their membrane properties and cell volume regulation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderova M, Antonova T, Petrik D, Neprasova H, Chvatal A, Sykova E (2004) Voltage-dependent potassium currents in hypertrophied rat astrocytes after a cortical stab wound. Glia 48:311–326
Anderova M, Kubinova S, Mazel T, Chvatal A, Eliasson C, Pekny M, Sykova E (2001) Effect of elevated K(+), hypotonic stress, and cortical spreading depression on astrocyte swelling in GFAP-deficient mice. Glia 35:189–203
Bonthius DJ, Lothman EW, Steward O (1995) The role of extracellular ionic changes in upregulating the mRNA for glial fibrillary acidic protein following spreading depression. Brain Res 674:314–328
Bordey A, Hablitz JJ, Sontheimer H (2000) Reactive astrocytes show enhanced inwardly rectifying K+ currents in situ. Neuroreport 11:3151–3155
Bordey A, Lyons SA, Hablitz JJ, Sontheimer H (2001) Electrophysiological characteristics of reactive astrocytes in experimental cortical dysplasia. J Neurophysiol 85:1719–1731
Bordey A, Sontheimer H (2000) Ion channel expression by astrocytes in situ: comparison of different CNS regions. Glia 30:27–38
Chvatal A, Anderova M, Sykova E (2004) Analysis of K+ accumulation reveals privileged extracellular region in the vicinity of glial cells in situ. J Neurosci Res 78:668–682
Chvatal A, Anderova M, Ziak D, Sykova E (1999) Glial depolarization evokes a larger potassium accumulation around oligodendrocytes than around astrocytes in gray matter of rat spinal cord slices. J Neurosci Res 56:493–505
Chvatal A, Pastor A, Mauch M, Sykova E, Kettenmann H (1995) Distinct populations of identified glial cells in the developing rat spinal cord slice: ion channel properties and cell morphology. Eur J Neurosci 7:129–142
D’Ambrosio R, Maris DO, Grady MS, Winn HR, Janigro D (1999) Impaired K(+) homeostasis and altered electrophysiological properties of post-traumatic hippocampal glia. J Neurosci 19:8152–8162
Del Bigio MR, Omara F, Fedoroff S (1994) Astrocyte proliferation in culture following exposure to potassium ion. Neuroreport 5:639–641
Ferroni S, Nobile M, Caprini M, Rapisarda C (2000) pH modulation of an inward rectifier chloride current in cultured rat cortical astrocytes. Neuroscience 100:431–438
Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ (1981) Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch 391:85–100
Hinterkeuser S, Schroder W, Hager G, Seifert G, Blumcke I, Elger CE, Schramm J, Steinhauser C (2000) Astrocytes in the hippocampus of patients with temporal lobe epilepsy display changes in potassium conductances. Eur J Neurosci 12:2087–2096
Inagaki M, Nakamura Y, Takeda M, Nishimura T, Inagaki N (1994) Glial fibrillary acidic protein: dynamic property and regulation by phosphorylation. Brain Pathol 4:239–243
Jabs R, Paterson IA, Walz W (1997) Qualitative analysis of membrane currents in glial cells from normal and gliotic tissue in situ: down-regulation of Na+ current and lack of P2 purinergic responses. Neuroscience 81:847–860
Kimelberg HK, Rutledge E, Goderie S, Charniga C (1995) Astrocytic swelling due to hypotonic or high K+ medium causes inhibition of glutamate and aspartate uptake and increases their release. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 15:409–416
Kofuji P, Newman EA (2004) Potassium buffering in the central nervous system. Neuroscience 129:1045–1056
Koller H, Schroeter M, Jander S, Stoll G, Siebler M (2000) Time course of inwardly rectifying K(+) current reduction in glial cells surrounding ischemic brain lesions. Brain Res 872:194–198
Kressin K, Kuprijanova E, Jabs R, Seifert G, Steinhauser C (1995) Developmental regulation of Na+ and K+ conductances in glial cells of mouse hippocampal brain slices. Glia 15:173–187
Lascola CD, Kraig RP (1996) Whole-cell chloride currents in rat astrocytes accompany changes in cell morphology. J Neurosci 16:2532–2545
Lee YB, Du S, Rhim H, Lee EB, Markelonis GJ, Oh TH (2000) Rapid increase in immunoreactivity to GFAP in astrocytes in vitro induced by acidic pH is mediated by calcium influx and calpain I. Brain Res 864:220–229
MacFarlane SN, Sontheimer H (1997) Electrophysiological changes that accompany reactive gliosis in vitro. J Neurosci 17:7316–7329
Macfarlane SN, Sontheimer H (1998) Spinal cord astrocytes display a switch from TTX-sensitive to TTX-resistant sodium currents after injury-induced gliosis in vitro. J Neurophysiol 79:2222–2226
Matthias K, Kirchhoff F, Seifert G, Huttmann K, Matyash M, Kettenmann H, Steinhauser C (2003) Segregated expression of AMPA-type glutamate receptors and glutamate transporters defines distinct astrocyte populations in the mouse hippocampus. J Neurosci 23:1750–1758
Nolte C, Matyash M, Pivneva T, Schipke CG, Ohlemeyer C, Hanisch UK, Kirchhoff F, Kettenmann H (2001) GFAP promoter-controlled EGFP-expressing transgenic mice: a tool to visualize astrocytes and astrogliosis in living brain tissue. Glia 33:72–86
Norton WT (1999) Cell reactions following acute brain injury: a review. Neurochem Res 24:213–218
Orkand RK, Nicholls JG, Kuffler SW (1966) Effect of nerve impulses on the membrane potential of glial cells in the central nervous system of amphibia. J Neurophysiol 29:788–806
Pannicke T, Faude F, Reichenbach A, Reichelt W (2000) A function of delayed rectifier potassium channels in glial cells: maintenance of an auxiliary membrane potential under pathological conditions. Brain Res 862:187–193
Pasantes-Morales H, Schousboe A (1989) Release of taurine from astrocytes during potassium-evoked swelling. Glia 2:45–50
Pastor A, Chvatal A, Sykova E, Kettenmann H (1995) Glycine- and GABA-activated currents in identified glial cells of the developing rat spinal cord slice. Eur J Neurosci 7:1188–1198
Pekny M, Nilsson M (2005) Astrocyte activation and reactive gliosis. Glia 50:427–434
Perillan PR, Li X, Simard JM (1999) K(+) inward rectifier currents in reactive astrocytes from adult rat brain. Glia 27:213–225
Roy ML, Sontheimer H (1995) Beta-adrenergic modulation of glial inwardly rectifying potassium channels. J Neurochem 64:1576–1584
Schroder W, Hager G, Kouprijanova E, Weber M, Schmitt AB, Seifert G, Steinhauser C (1999) Lesion-induced changes of electrophysiological properties in astrocytes of the rat dentate gyrus. Glia 28:166–174
Somjen GG (1979) Extracellular potassium in the mammalian central nervous system. Annu Rev Physiol 41:159–177
Somjen GG (2001) Mechanisms of spreading depression and hypoxic spreading depression-like depolarization. Physiol Rev 81:1065–1096
Sontheimer H (1994) Voltage-dependent ion channels in glial cells. Glia 11:156–172
Sykova E (1983) Extracellular K+ accumulation in the central nervous system. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 42:135–189
Sykova E (1992) Ionic and volume changes in the microenvironment of nerve and receptor cells. Prog Sens Physiol 13:1–167
Sykova E (2005) Glia and volume transmission during physiological and pathological states. J Neural Transm 112:137–147
Sykova E, Jendelova P, Simonova Z, Chvatal A (1992) K+ and pH homeostasis in the developing rat spinal cord is impaired by early postnatal X-irradiation. Brain Res 594:19–30
Sykova E, Vargova L, Prokopova S, Simonova Z (1999) Glial swelling and astrogliosis produce diffusion barriers in the rat spinal cord. Glia 25:56–70
Vargova L, Chvatal A, Anderova M, Kubinova S, Ziak D, Sykova E (2001) Effect of osmotic stress on potassium accumulation around glial cells and extracellular space volume in rat spinal cord slices. J Neurosci Res 65:129–138
Verkhratsky A, Steinhauser C (2000) Ion channels in glial cells. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 32:380–412
Vorisek I, Sykova E (1997) Ischemia-induced changes in the extracellular space diffusion parameters, K+, and pH in the developing rat cortex and corpus callosum. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 17:191–203
Walz W (1997) Role of astrocytes in the spreading depression signal between ischemic core and penumbra. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 21:135–142
Yu SP (2003) Regulation and critical role of potassium homeostasis in apoptosis. Prog Neurobiol 70:363–386
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants 305/03/1172 and 305/06/1316 from the Grant Agency of the Czech Republic; AVOZ50390512, 1M0021620803, and LC554 from the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic; and 57/2005/C/2.LF from the Grant Agency of Charles University, Prague. The authors would like to thank Dr. Ladislav Andera for help with GFAP quantification, Mgr. Petr Pivonka for developing a program for patch-clamp data analysis, and Hana Hronova for immunohistochemical staining.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neprasova, H., Anderova, M., Petrik, D. et al. High extracellular K+ evokes changes in voltage-dependent K+ and Na+ currents and volume regulation in astrocytes. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 453, 839–849 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-006-0151-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-006-0151-9