Abstract
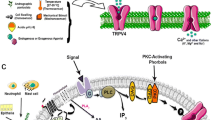
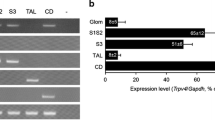
Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) was identified as the mammalian homologue of the Caenorhabditis elegans osmosensory channel protein, OSM-9. In mammals, TRPV4 is activated by a variety of stimuli including thermal stress, fatty acid metabolites, and hypotonicity. Two distinct mechanisms have been described through which TRPV4 may be activated by hypotonicity: one involves the Src family of nonreceptor protein tyrosine kinases, whereas a second is mediated via arachidonic acid metabolites. TRPV4 likely plays a role in systemic osmoregulation; accordingly, it is expressed in the blood–brain barrier-deficient osmosensory nuclei of the hypothalamus. TRPV4 is also abundantly expressed in the kidney, and its precisely demarcated distribution along the kidney tubule permits speculation about a physiological role in this tissue. TRPV4-expressing and TRPV4-negative tubule segments co-exist at all levels of the kidney, from the cortex through the inner medulla. It is conceivable that basolaterally expressed TRPV4 transmits signals arising in the interstitium (e.g, changing tonicity) to more-distal tubule segments where “fine-tuning” of the incipient urine takes place.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrade YN, Fernandes J, Vazquez E, Fernandez-Fernandez JM, Arniges M, Sanchez TM, Villalon M, Valverde MA (2005) TRPV4 channel is involved in the coupling of fluid viscosity changes to epithelial ciliary activity. J Cell Biol 168:869–874
Arniges M, Vazquez E, Fernandez-Fernandez JM, Valverde MA (2004) Swelling activated Ca2+ entry via TRPV4 channel is defective in cystic fibrosis airway epithelia. J Biol Chem 279:54062–54068
Basavappa S, Pedersen SF, Jorgensen NK, Ellory JC, Hoffmann EK (1998) Swelling-induced arachidonic acid release via the 85-kDa cPLA2 in human neuroblastoma cells. J Neurophysiol 79:1441–1449
Breton S, Beck JS, Cardinal J, Giebisch G, Laprade R (1992) Involvement and source of calcium in volume regulatory decrease of collapsed proximal convoluted tubule. Am J Physiol 263:F656–F664
Chung MK, Lee H, Caterina MJ (2003) Warm temperatures activate TRPV4 in mouse 308 keratinocytes. J Biol Chem 278:32037–32046
Cohen D (2005) TRPV4 and hypotonic stress. In: Wang D (ed) Molecular sensors for cardiovascular homeostasis. Kluwer, New York
Cohen DM (2005) SRC family kinases in cell volume regulation. Am J Physiol 288:C483–C493
Colbert HA, Bargmann CI (1995) Odorant-specific adaptation pathways generate olfactory plasticity in C. elegans. Neuron 14:803–812
Colbert HA, Smith TL, Bargmann CI (1997) OSM-9, a novel protein with structural similarity to channels, is required for olfaction, mechanosensation, and olfactory adaptation in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Neurosci 17:8259–8269
Delany NS, Hurle M, Facer P, Alnadaf T, Plumpton C, Kinghorn I, See CG, Costigan M, Anand P, Woolf CJ, Crowther D, Sanseau P, Tate SN (2001) Identification and characterization of a novel human vanilloid receptor-like protein, VRL-2. Physiol Genomics 4:165–174
Edashige K, Watanabe Y, Sato EF, Takehara Y, Utsumi K (1993) Reversible priming and protein-tyrosyl phosphorylation in human peripheral neutrophils under hypotonic conditions. Arch Biochem Biophys 302:343–7
Fernandez-Fernandez J. M, Nobles M, Currid A, Vazquez E, Valverde M. A. (2002) Maxi K+ channel mediates regulatory volume decrease response in a human bronchial epithelial cell line. Am J Physiol 283:C1705–C1714
Gao X, Wu L, O’Neil RG (2003) Temperature-modulated diversity of TRPV4 channel gating: activation by physical stresses and phorbol ester derivatives through protein kinase C-dependent and -independent pathways. J Biol Chem 278:27129–27137
Good DW (1995) Hyperosmolality inhibits bicarbonate absorption in rat medullary thick ascending limb via a protein-tyrosine kinase-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem 270:9883–9889
Guler AD, Lee H, Iida T, Shimizu I, Tominaga M, Caterina M (2002) Heatevoked activation of the ion channel, TRPV4. J Neurosci 22:6408–6414
Hilgemann DW (2004) Biochemistry. Oily barbarians breach ion channel gates. Science 304:223–224
Hisatsune C, Kuroda Y, Nakamura K, Inoue T, Nakamura T, Michikawa T, Mizutani A, Mikoshiba K (2004) Regulation of TRPC6 channel activity by tyrosine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 279:18887–18894
Jiang X, Newell EW, Schlichter LC (2003) Regulation of a TRPM7-like current in rat brain microglia. J Biol Chem 278:42867–42876
Jin X, Morsy N, Winston J, Pasricha PJ, Garrett K, Akbarali HI (2004) Modulation of TRPV1 by nonreceptor tyrosine kinase, c-Src kinase. Am J Physiol 287:C558–C563
Kahn-Kirby AH, Dantzker JL, Apicella AJ, Schafer WR, Browse J, Bargmann CI, Watts JL (2004) Specific polyunsaturated fatty acids drive TRPV-dependent sensory signaling in vivo. Cell 119:889–900
Kitahara T, Li HS, Balaban CD (2005) Changes in transient receptor potential cation channel superfamily V (TRPV) mRNA expression in the mouse inner ear ganglia after kanamycin challenge. Hear Res 201:132–144
Ko BC, Lam AK, Kapus A, Fan L, Chung SK, Chung SS (2002) Fyn and p38 signaling are both required for maximal hypertonic activation of the osmotic response element binding protein/tonicity-responsive enhancer-binding protein (OREBP/TonEBP). J Biol Chem 277:46085–46092
Lang F, Busch GL, Volkl H (1998) The diversity of volume regulatory mechanisms. Cell Physiol Biochem 8:1–45
Lee H, Iida T, Mizuno A, Suzuki M, Caterina MJ (2005) Altered thermal selection behavior in mice lacking transient receptor potential vanilloid 4. J Neurosci 25:1304–1310
Liedtke W, Choe Y, Marti-Renom MA, Bell AM, Denis CS, Sali A, Hudspeth AJ, Friedman JM, Heller S (2000) Vanilloid receptor-related osmotically activated channel (VR-OAC), a candidate vertebrate osmoreceptor. Cell 103:525–535
Liedtke W, Friedman JM (2003) Abnormal osmotic regulation in trpv4−/− mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:13698–13703
Mizuno A, Matsumoto N, Imai M, Suzuki M (2003) Impaired osmotic sensation in mice lacking TRPV4. Am J Physiol 285:C96–C101
Montell C, Birnbaumer L, Flockerzi V, Bindels RJ, Bruford EA, Caterina MJ, Clapham DE, Harteneck C, Heller S, Julius D, Kojima I, Mori Y, Penner R, Prawitt D, Scharenberg AM, Schultz G, Shimizu N, Zhu MX (2002) A unified nomenclature for the superfamily of TRP cation channels. Mol Cell 9:229–231
Negulescu PA, Munck B, Machen TE (1992) Volume-sensitive Ca influx and release from intracellular pools in gastric parietal cells. Am J Physiol 263:C584–C589
Nilius B, Vriens J, Prenen J, Droogmans G, Voets T (2004) TRPV4 calcium entry channel: a paradigm for gating diversity. Am J Physiol 286:C195–C205
Oliver D, Lien CC, Soom M, Baukrowitz T, Jonas P, Fakler B (2004) Functional conversion between A-type and delayed rectifier K+ channels by membrane lipids. Science 304:265–270
Pedersen S, Lambert IH, Thoroed SM, Hoffmann EK (2000) Hypotonic cell swelling induces translocation of the alpha isoform of cytosolic phospholipase A2 but not the gamma isoform in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Eur J Biochem 267:5531–5539
Piomelli D (2003) The molecular logic of endocannabinoid signalling. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:873–884
Sachs JR, Martin DW (1993) The role of ATP in swelling-stimulated K-Cl cotransport in human red cell ghosts. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation events are not in the signal transduction pathway. J Gen Physiol 102:551–573
Sadoshima J, Qiu ZH, Morgan JP, Izumo S (1996) Tyrosine kinase activation is an immediate and essential step in hypotonic cell swelling-induced ERK activation and c-fos gene expression in cardiac myocytes. EMBO J 15:5535–5546
Strotmann R, Harteneck C, Nunnenmacher K, Schultz G, Plant TD (2000) OTRPC4, a nonselective cation channel that confers sensitivity to extracellular osmolarity. Nat Cell Biol 2:695–702
Terreros DA, Kanli H (1992) Role of intracellular calcium in renal proximal tubule cell volume regulation. Am J Physiol 263:R1086–R1092
Thoroed SM, Lauritzen L, Lambert IH, Hansen HS, Hoffmann EK (1997) Cell swelling activates phospholipase A2 in Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Membr Biol 160:47–58
Tian W, Salanova M, Xu H, Lindsley JN, Oyama TT, Anderson S, Bachmann S, Cohen DM (2004) Renal expression of osmotically responsive cation channel TRPV4 is restricted to water-impermeant nephron segments. Am J Physiol 287:F17–F24
Tilly BC, van den Berghe N, Tertoolen LG, Edixhoven MJ, de Jonge HR (1993) Protein tyrosine phosphorylation is involved in osmoregulation of ionic conductances. J Biol Chem 268:19919–19922
Todaka H, Taniguchi J, Satoh J, Mizuno A, Suzuki M (2004) Warm temperature sensitive transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) plays an essential role in thermal hyperalgesia J Biol Chem 279:35133–35138
Triggle DJ (1999) The pharmacology of ion channels: with particular reference to voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. Eur J Pharmacol 375: 311–325
Vazquez G, Wedel BJ, Kawasaki BT, Bird GS, Putney JW Jr (2004) Obligatory role of Src kinase in the signaling mechanism for TRPC3 cation channels. J Biol Chem 279:40521–40528
Vriens J, Watanabe H, Janssens A, Droogmans G, Voets T, Nilius B (2004) Cell swelling, heat, and chemical agonists use distinct pathways for the activation of the cation channel TRPV4. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:396–401
Watanabe H, Davis JB, Smart D, Jerman JC, Smith GD, Hayes P, Vriens J, Cairns W, Wissenbach U, Prenen J, Flockerzi V, Droogmans G, Benham CD, Nilius B (2002) Activation of TRPV4 channels (hVRL-2/mTRP12) by phorbol derivatives. J Biol Chem 277:13569–13577
Watanabe H, Vriens J, Suh SH, Benham CD, Droogmans G, Nilius B (2002) Heat-evoked activation of TRPV4 channels in a HEK293 cell expression system and in native mouse aorta endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 277:47044–47051
Watanabe H, Vriens J, Prenen J, Droogmans G, Voets T, Nilius B (2003) Anandamide and arachidonic acid use epoxyeicosatrienoic acids to activate TRPV4 channels. Nature 424:434–438
Wehner F, Olsen H, Tinel H, Kinne-Saffran E, Kinne RK (2003) Cell volume regulation: osmolytes, osmolyte transport, and signal transduction. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 148:1–80
Wissenbach U, Bodding M, Freichel M, Flockerzi V (2000) Trp12, a novel Trp related protein from kidney. FEBS Lett 485:127–134
Wong SM, DeBell MC, Chase HS Jr (1990) Cell swelling increases intracellular free [Ca] in cultured toad bladder cells. Am J Physiol 258:F292–F296
Woolfson R, Hillman K (2000) Causes of acute renal failure. In: Johnson R, Feehally J (eds) Comprehensive clinical nephrology. Mosby, London, pp 4, 16, 13
Wu WJ, Sha SH, Schacht J (2002) Recent advances in understanding aminoglycoside ototoxicity and its prevention. Audiol Neurootol 7:171–174
Xu H, Zhao H, Tian W, Yoshida K, Roullet JB, Cohen DM (2003) Regulation of a transient receptor potential (TRP) channel by tyrosine phosphorylation. SRC family kinase dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of TRPV4 on TYR-253 mediates its response to hypotonic stress. J Biol Chem 278:11520–11527
Zeldin DC (2001) Epoxygenase pathways of arachidonic acid metabolism. J Biol Chem 276:36059–36062
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the Department of Veterans Affairs, and the American Heart Association.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cohen, D.M. TRPV4 and the mammalian kidney. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 451, 168–175 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-005-1456-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-005-1456-9