Abstract
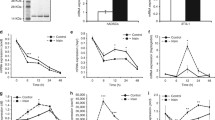
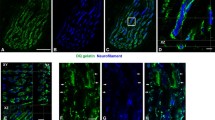
Glucocorticoids have anti-anabolic effects on many tissues and can cause muscle atrophy. However, their effects on type IV collagen gene expression and degradation in skeletal muscle have not been studied previously. Rats were treated daily with dexamethasone or saline. Half the groups of experimental and control animals were also subjected to daily endurance or uphill running exercise to determine the possible preventive effects of exercise. After an experimental period of 3 or 10 days, the extensor digitorum longus, soleus and tibialis anterior muscles were studied. Dexamethasone treatment for 10 days reduced muscle weight and type IV collagen mRNA abundance in all muscles. Gene expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) was decreased in fast muscles. However, the effects of this decrease were possibly attenuated by the simultaneous decrease in the activity of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMP-2). The amount of type IV collagen was not changed during dexamethasone treatment or exercise. The regulation of type IV collagen degradation during dexamethasone treatment varied between slow and fast muscles. Although endurance running prevented muscle atrophy, exercise could not compensate the changes observed in the regulation of type IV collagen gene expression and degradation during dexamethasone treatment.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahtikoski AM, Koskinen SOA, Virtanen P, Kovanen V, Takala TES (2003) Synthesis and degradation of type IV collagen in rat skeletal muscle during immobilization in shortened and lengthened position. Acta Physiol Scand 177:473–481
Aimes RT, Quiley JP (1995) Matrix metalloproteinase-2 is an interstitial collagenase. Inhibitor-free enzyme catalyzes the cleavage of collagen fibrils and soluble type I collagen generating the specific 3/4- and 1/4-length fragments. J Biol Chem 270:5872–5876
Chomczynski P, Mackey K (1994) One-hour downward capillary blotting of RNA at neutral pH. Anal Biochem 221:303–305
Chromiak JA, Vandenburg HH (1992) Glucocorticoid-induced skeletal muscle atrophy in vitro is attenuated by mechanical stimulation. Am J Physiol 262:C1471–C1477
Collier IE, Wilhelm SM, Eisen AZ, Marmer BL, Grant GA, Seltzer JL, Kronberger A, He C, Bauer EA, Goldberg GI (1988) H-ras oncogene-transformed human bronchial epithelial cells (TBE-1) secrete a single metalloprotease capable of degrading basement membrane collagen. J Biol Chem 263:6579–6587
Cutroneo KR, Counts DF (1975) Anti-inflammatory steroids and collagen metabolism: Glucocorticoid-mediated alterations of prolyl hydroxylase activity and collagen synthesis. Mol Pharmacol 11:632–639
Delp MC, Duan C (1996) Composition and size of type I, IIA, IID/X, and IIB fibers and citrate synthase activity of rat muscle. J Appl Physiol 80:261–270
Fimbel S, Abdelmalki A, Mayet MH, Sempore B, Koubi H, Pugeat M, Dechaud H, Favier RJ (1993) Exercise training fails to prevent glucocorticoid-induced muscle alterations in young growing rats. Pflugers Arch 424:369–376
Hantai D, Gautron J, Labat-Robert J (1983) Immunolocalization of fibronectin and other macromolecules of the intercellular matrix in the striated muscle fiber of the adult rat. Coll Relat Res 3:381–391
Kherif S, Lafuma C, Dehaupas M, Lachkar S, Fournier J-G, Verdière-Sahuqué M, Fardeau M, Alameddine HS (1999) Expression of matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 in regenerating skeletal muscle: a study in experimentally injured and mdx muscles. Dev Biol 205:158–170
Kleiner DE, Stetler-Stevenson WG (1994) Quantitative zymography: detection of picogram quantities of gelatinases. Anal Biochem 218:325–329
Koskinen SOA, Wang W, Ahtikoski AM, Kjaer M, Han XY, Komulainen J, Kovanen V, Takala TES (2001) Acute exercise induced changes in rat skeletal muscle mRNAs and proteins regulating type IV collagen content. Am J Physiol 280:R1292–R1300
Kuhl U, Öcalan M, Timpl R, Mayne R, Hay E, Mark K von der (1984) Role of the muscle fibroblasts in the deposition of type IV collagen in the basal lamina of myotubes. Differentiation 28:164–172
Kylmäniemi M, Oikarinen A, Oikarinen K, Salo T (1996) Effects of dexamethasone and cell proliferation on the expression of matrix metalloproteinases in human normal and malignant cells. J Dent Res 75: 919–926
Lieu F-K, Powers SK, Herb RA, Criswell D, Martin D, Wood C, Stainsby W, Chen C-L (1993) Exercise and glucocorticoid-induced diaphragmatic myopathy. J Appl Physiol 75:763–771
Long W, Liping W, Barrett EJ (2001) Dexamethasone inhibits the stimulation of muscle protein synthesis and PHAS-I and p70 S6-kinase phosphorylation. Am J Physiol 280:E570–E575
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, p 545
Morin I, Li WQ, Su S, Ahmad M, Zafarullah M (1999) Induction of stromelysin gene expression by tumor necrosis factor α is inhibited by dexamethasone, salicylate, and n-acetylcysteine in synovial fibroblasts. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 289:1634–40
Nava S, Gayan-Ramirez G, Rollier H, Bisschop A, Dom R, Bock V de, Decramer M (1996) Effects of acute steroid administration on ventilatory and peripheral muscles in rats. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 153:1888–1896
Oikarinen J, Pihlajaniemi T, Hämäläinen L, Kivirikko KI (1983) Cortisol decreases the cellular concentration of translatable procollagen mRNA species in cultured human skin fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta 741:297–302
Oikarinen A, Salo T, Ala-Kokko L, Tryggvason K (1987) Dexamethasone modulates the metabolism of type IV collagen and fibronectin in human basement-membrane-forming fibrosarcoma (HT-1080) cells. Biochem J 245:235–241
Oliver GW, Leferson JD, Stetler-Stevenson WG, Kleiner DE (1997) Quantitative reverse zymography: analysis of picogram amounts of metalloproteinase inhibitors using gelatinase A and B reverse zymograms. Anal Biochem 244:161–166
Risteli J, Bächinger HP, Engel J, Furthmayr H, Timpl R (1980) 7-S Collagen: characterization of an unusual basement membrane structure. Eur J Biochem 108:239–250
Risteli J, Wick G, Timpl R (1981) Immunological characterization of the 7-S domain of type IV collagens. Coll Relat Res 5:419–432
Seene T, Viru A (1982) The catabolic effect of glucocorticoids on different types of skeletal muscle fibres and its dependence upon muscle activity and interaction with anabolic steroids. J Steroid Biochem 16:249–352
Seene T, Umnova M, Alev K, Pehme A (1988) Effect of glucocorticoids on contractile apparatus of rat skeletal muscle. Steroid Biochem 29:313–317
Stetler-Stevenson WG, Krutzsch HC, Liotta LA (1989) Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP-2). J Biol Chem 262:17374–17378
Takala TES, Myllylä R, Salminen A, Anttinen H, Vihko V (1983) Increased activities of prolyl 4-hydroxylase and galactosylhydroxylysyl glucosyltransferase, enzymes of collagen biosynthesis, in skeletal muscle of endurance trained mice. Pflugers Arch 399:271–274
Trocmé C, Gaudin P, Berthier S, Barro C, Zaoui P, Morel F (1998) Human B lymphocytes synthesize the 92-kDa gelatinase, matrix metalloproteinase-9. J Biol Chem 273:20677–20684
Wilhelm SM, Collier IE, Marmer BL, Eisen AZ, Grant GA, Goldberg GI (1989) SV40-transformed human lung fibroblasts secrete a 92-kDa type IV collagenase which is identical to that secreted by normal human macrophages. J Biol Chem 264:17213–17221
Xu J, Kim G-M, Ahmed SH, Xu J, Yan P, Xu XM, Hsu CY (2001) Glucorticoid receptor-mediated suppression of activator protein-1 activation and matrix metalloproteinase expression after spinal cord injury. J Neurosci 21:92–97
Yurchenko PD, O’Rear JJ (1994) Basal lamina assembly. Curr Opin Cell Biol 6:674–681
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from Finland’s Ministry of Education and the Suomen Urheiluopistosäätiö Foundation. We are grateful to Ms. Mervi Koistinen, Ms. Tuovi Nykänen and Ms. Aila Ollikainen for their skilful technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahtikoski, A.M., Riso, EM., Koskinen, S.O.A. et al. Regulation of type IV collagen gene expression and degradation in fast and slow muscles during dexamethasone treatment and exercise. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 448, 123–130 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-003-1226-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-003-1226-5