Abstract
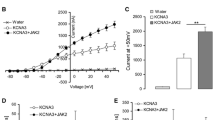
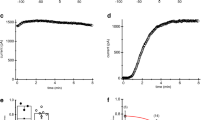
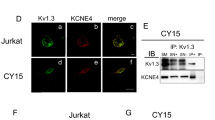
The voltage-gated K+ channel Kv1.3 is an important regulator of lymphocyte function. Activation of lymphocytes is accompanied by stimulation, whereas CD95-induced apoptosis by inhibition, of Kv1.3. The channel serves to maintain cell membrane potential, a prerequisite for signalling through the Ca2+ release-activated Ca2+ channel ICRAC. As glucocorticoids are known to regulate lymphocyte function, the present study addressed the effect of dexamethasone on voltage-gated K+ channels in Jurkat T-lymphocytes. In whole-cell patch-clamp experiments current families evoked by 200-ms potential steps every 15 s from −70 mV to values from −120 to +100 mV revealed the functional expression of voltage-gated K+ channels. Pre-treatment of Jurkat T-lymphocytes for 2–3 h with 1 µM dexamethasone led to a significant decrease of voltage-gated K+ currents. Fura-2-fluorescence measurements showed that the readdition of Ca2+ to Ca2+-depleted cells led to a rapid increase of cytosolic Ca2+ activity. This increase of Ca2+ activity was blunted by both the K+ channel blocker margatoxin (10 nM) and 24 h pre-treatment with dexamethasone (1 µM). In conclusion, dexamethasone inhibits voltage-gated K+ channels in Jurkat T-lymphocytes, an effect impeding Ca2+ entry through ICRAC.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spencer RH, Chandy KG, Gutman GA (1993) Immunological identification of the Shaker-related Kv1.3 potassium channel protein in T and B lymphocytes, and detection of related proteins in files and yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 191:201–206
Parekh AB, Penner R (1997) Store depletion and calcium influx. Physiol Rev 77:901–930
Cantrell DA (1996) T cell antigen receptor signal transduction pathways. Cancer Surv 27:165–175
Kojima H, Aizawa Y, Yanai Y, Nagaoka K, Takeuchi M, Ohta T, Ikegami H, Ikeda M, Kurimoto M (1999) An essential role for NF-kappa B in IL-18-induced IFN-gamma expression in KG-1 cells. J Immunol 162:5063–5069
Sica A, Dorman L, Viggiano V, Cippitelli M, Ghosh P, Rice N, Young HA (1997) Interaction of NF-kappaB and NFAT with the interferon-gamma promoter. J Biol Chem 272:30412–30420
Lepple-Wienhues A, Belka C, Laun T, Jekle A, Walter B, Wieland U, Welz M, Heil L, Kun J, Busch G, Weller M, Bamberg M, Gulbins E, Lang F (1999) Stimulation of CD95 (Fas) blocks T lymphocyte calcium channels through sphingomyelinase and sphingolipids. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:13795–13800
Amigorena S, Choquet D, Teillaud JL, Korn H, Fridman WH (1990) Ion channel blockers inhibit B cell activation at a precise stage of the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Possible involvement of K+ channels. J Immunol 144:2038–2045
Chandy KG, DeCoursey TE, Cahalan MD, McLaughlin C, Gupta S (1984) Voltage-gated potassium channels are required for human T lymphocyte activation. J Exp Med 160:369–385
DeCoursey TE, Chandy KG, Gupta S, Cahalan MD (1984) Voltage-gated K+ channels in human T lymphocytes: a role in mitogenesis? Nature 307:465–468
DeCoursey TE, Chandy KG, Gupta S, Cahalan MD (1987) Mitogen induction of ion channels in murine T lymphocytes. J Gen Physiol 89:405–420
Leonard RJ, Garcia ML, Slaughter RS, Reuben JP (1992) Selective blockers of voltage-gated K+ channels depolarize human T lymphocytes: mechanism of the antiproliferative effect of charybdotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:10094–10098
Lewis RS, Cahalan MD (1990) Ion channels and signal transduction in lymphocytes. Annu Rev Physiol 52:415–430
Lewis RS, Cahalan MD (1995) Potassium and calcium channels in lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol 13:623–653
Price M, Lee SC, Deutsch C (1989) Charybdotoxin inhibits proliferation and interleukin 2 production in human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:10171–10175
Gulbins E, Szabo I, Baltzer K, Lang F (1997) Ceramide-induced inhibition of T lymphocyte voltage-gated potassium channel is mediated by tyrosine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:7661–7666
Szabo I, Gulbins E, Apfel H, Zhang X, Barth P, Busch AE, Schlottmann K, Pongs O, Lang F (1996) Tyrosine phosphorylation-dependent suppression of a voltage-gated K+ channel in T lymphocytes upon Fas stimulation. J Biol Chem 271:20465–20469
Hoffman-Goetz L, Zajchowski S (1999) In vitro apoptosis of lymphocytes after exposure to levels of corticosterone observed following submaximal exercise. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 39:269–274
Shimizu T, Kawamura T, Miyaji C, Oya H, Bannai M, Yamamoto S, Weerasinghe A, Halder RC, Watanabe H, Hatakeyama K, Abo T (2000) Resistance of extrathymic T cells to stress and the role of endogenous glucocorticoids in stress associated immunosuppression. Scand J Immunol 51:285–292
Cohen JJ, Duke RC (1984) Glucocorticoid activation of a calcium-dependent endonuclease in thymocyte nuclei leads to cell death. J Immunol 132:38–42
Wyllie AH (1980) Glucocorticoid-induced thymocyte apoptosis is associated with endogenous endonuclease activation. Nature 284:555–556
Kirsch AH, Mahmood AA, Endres J, Bohra L, Bonish B, Weber K, Fox DA (1999) Apoptosis of human T-cells: induction by glucocorticoids or surface receptor ligation in vitro and ex vivo. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 13:80–89
Bansal N, Houle A, Melnykovych G (1991) Apoptosis: mode of cell death induced in T cell leukemia lines by dexamethasone and other agents. FASEB J 5:211–216
Baxter GD, Collins RJ, Harmon BV, Kumar S, Prentice RL, Smith PJ, Lavin MF (1989) Cell death by apoptosis in acute leukaemia. J Pathol 158:123–129
El Helw LM, Lorigan PC, Robinson MH, Coleman RE, Hancock BW (2000) VEDex (vincristine, epirubicin dexamethasone): an effective and well tolerated palliative chemotherapy regimen for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Int J Oncol 16:777–782
Gaynon PS, Carrel AL (1999) Glucocorticosteroid therapy in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Adv Exp Med Biol 457:593–605
Josting A, Reiser M, Wickramanayake PD, Rueffer U, Draube A, Sohngen D, Tesch H, Wolf J, Diehl V, Engert A (2000) Dexamethasone, carmustine, etoposide, cytarabine, and melphalan (dexa-BEAM) followed by high-dose chemotherapy and stem cell rescue—a highly effective regimen for patients with refractory or relapsed indolent lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 37:115–123
Garcia-Calvo M, Leonard RJ, Novick J, Stevens SP, Schmalhofer W, Kaczorowski GJ, Garcia ML (1993) Purification, characterization, and biosynthesis of margatoxin, a component of Centruroides margaritatus venom that selectively inhibits voltage-dependent potassium channels. J Biol Chem 268:18866–18874
Leonard RJ, Garcia ML, Slaughter RS, Reuben JP (1992) Selective blockers of voltage-gated K+ channels depolarize human T lymphocytes: mechanism of the antiproliferative effect of charybdotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:10094–10098
Grynkiewicz G, Poenie M, Tsien RY (1985) A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem 260:3440–3450
Webster MK, Goya L, Firestone GL (1993) Immediate-early transcriptional regulation and rapid mRNA turnover of a putative serine/threonine protein kinase. J Biol Chem 268:11482–11485
Webster MK, Goya L, Ge Y, Maiyar AC, Firestone GL (1993) Characterization of sgk, a novel member of the serine/threonine protein kinase gene family which is transcriptionally induced by glucocorticoids and serum. Mol Cell Biol 13:2031–2040
Firestone GL, Giampaolo JR, O'Keeffe BA (2003) Stimulus-dependent regulation of the serum and glucocorticoid inducible protein kinase (Sgk) transcription, subcellular localization and enzymatic activity. Cell Physiol Biochem 13:1–12
Gamper N, Fillon S, Huber SM, Feng Y, Kobayashi T, Cohen P, Lang F (2002) IGF-1 up-regulates K+ channels via PI3-kinase, PDK1 and SGK1. Pflugers Arch 443:625–634
Gamper N, Fillon S, Feng Y, Friedrich B, Lang PA, Henke G, Huber SM, Kobayashi T, Cohen P, Lang F (2002) K+ channel activation by all three isoforms of serum- and glucocorticoid-dependent protein kinase SGK. Pflugers Arch 445:60–66
Lang F, Henke G, Embark HM, Waldegger S, Palmada M, Bohmer C, Vallon V (2003) Regulation of channels by the serum and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase—implications for transport, excitability and cell proliferation. Cell Physiol Biochem 13:41–50
Wärntges S, Friedrich B, Henke G, Duranton C, Lang PA, Waldegger S, Meyermann R, Kuhl D, Speckmann EJ, Obermuller N, Witzgall R, Mack AF, Wagner HJ, Wagner A, Broer S, Lang F (2002) Cerebral localization and regulation of the cell volume-sensitive serum- and glucocorticoid-dependent kinase SGK1. Pflugers Arch 443:617–624
Lang F, Madlung J, Bock J, Lukewille U, Kaltenbach S, Lang KS, Belka C, Wagner CA, Lang HJ, Gulbins E, Lepple-Wienhues A (2000) Inhibition of Jurkat-T-lymphocyte Na+/H+-exchanger by CD95(Fas/Apo-1)-receptor stimulation. Pflugers Arch 440:902–907
Szabo I, Lepple-Wienhues A, Kaba KN, Zoratti M, Gulbins E, Lang F (1998) Tyrosine kinase-dependent activation of a chloride channel in CD95-induced apoptosis in T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:6169–6174
Lang F, Madlung J, Uhlemann AC, Risler T, Gulbins E (1998) Cellular taurine release triggered by stimulation of the Fas(CD95) receptor in Jurkat lymphocytes. Pflugers Arch 436:377–383
Lang F, Madlung J, Siemen D, Ellory C, Lepple-Wienhues A, Gulbins E (2000) The involvement of caspases in the CD95(Fas/Apo-1)- but not swelling-induced cellular taurine release from Jurkat T-lymphocytes. Pflugers Arch 440:93–99
Maeno E, Ishizaki Y, Kanaseki T, Hazama A, Okada Y (2000) Normotonic cell shrinkage because of disordered volume regulation is an early prerequisite to apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:9487–9492
Moran J, Hernandez-Pech X, Merchant-Larios H, Pasantes-Morales H (2000) Release of taurine in apoptotic cerebellar granule neurons in culture. Pflugers Arch 439:271–277
Pasantes-Morales H, Franco R, Torres-Marquez ME, Hernandez-Fonseca K, Ortega A (2000) Amino acid osmolytes in regulatory volume decrease and isovolumetric regulation in brain cells: contribution and mechanisms. Cell Physiol Biochem 10:361–370
Bock J, Szabo I, Jekle A, Gulbins E (2002) Actinomycin D-induced apoptosis involves the potassium channel Kv1.3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 295:526–531
Beauvais F, Michel L, Dubertret L (1995) Human eosinophils in culture undergo a striking and rapid shrinkage during apoptosis. Role of K+ channels. J Leukoc Biol 57:851–855
Benson RS, Heer S, Dive C, Watson AJ (1996) Characterization of cell volume loss in CEM-C7A cells during dexamethasone-induced apoptosis. Am J Physiol 270:C1190–C1203
Bortner CD, Cidlowski JA (1999) Caspase independent/dependent regulation of K+, cell shrinkage, and mitochondrial membrane potential during lymphocyte apoptosis. J Biol Chem 274:21953–21962
Ritter M, Wöll E (1996) Modification of cellular ion transport by the Ha-ras oncogene: Steps towards malignant transformation. Cell Physiol Biochem 6:245–270
Tanneur V, Ilgaz D, Duranton C, Fillon S, Gamper N, Huber SM, Lang F (2002) Time-dependent regulation of capacitative Ca2+ entry by IGF-1 in human embryonic kidney cells. Pflugers Arch 445:74–79
Deutsch C, Lee SC (1988) Cell volume regulation in lymphocytes. Renal Physiol Biochem 11:260–276
Deutsch C, Chen LQ (1993) Heterologous expression of specific K+ channels in T lymphocytes: functional consequences for volume regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:10036–10040
Grinstein S, Smith JD (1990) Calcium-independent cell volume regulation in human lymphocytes. Inhibition by charybdotoxin. J Gen Physiol 95:97–120
Lee SC, Price M, Prystowsky MB, Deutsch C (1988) Volume response of quiescent and interleukin 2-stimulated T-lymphocytes to hypotonicity. Am J Physiol 254:C286–C296
Gamper N, Huber SM, Badawi K, Lang F (2000) Cell volume-sensitive sodium channels upregulated by glucocorticoids in U937 macrophages. Pflugers Arch 441:281–286
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the technical assistance of E. Faber. This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (La 315/4-4, Le 792/3-3), a grant of the Bundesministerium für Bildung, Wissenschaft, Forschung und Technologie (Fö. 01KS9602) and the Interdisziplinäres Zentrum für Klinische Forschung der Universität Tübingen (IZKF) (S. 05.00023.2/IIB9) and of the fortune program, Tübingen.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lampert, A., Müller, M.M., Berchtold, S. et al. Effect of dexamethasone on voltage-gated K+ channels in Jurkat T-lymphocytes. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 447, 168–174 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-003-1148-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-003-1148-2