Abstract.
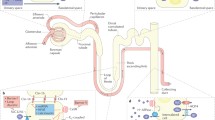
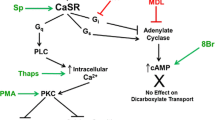
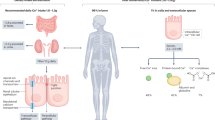
The kidney is a fundamental component of the Ca2+ homeostatic system and its ability to sense extracellular Ca2+ ([Ca2+]o) levels in the urinary filtrate and the interstitial fluid is an important ionic feedback mechanism in achieving normocalcaemia. The protein responsible for the measurement of [Ca2+]o is the extracellular Ca2+-sensing receptor (CaR), which is expressed in multiple sites along the nephron. Its cellular localization and apparent function(s) appear to depend upon the region of the nephron in which it is expressed. The renal expression of CaR will be detailed in this review and its role in integrating [Ca2+]o with the calciotropic signals responsible for Ca2+ homeostasis will be discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ward, D.T., Riccardi, D. Renal physiology of the extracellular calcium-sensing receptor. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 445, 169–176 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-002-0914-x
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-002-0914-x