Abstract.
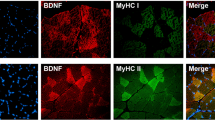
The presence of the GLUT3 glucose transporter protein in human muscle cells is a matter of debate. The present study was designed to establish whether GLUT3 is expressed in mature human skeletal muscle fibres and, if so, whether its expression changes under different conditions, such as metabolic stress (obesity, obese non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus), hypertrophy (training), de- and reinnervation (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis) or regeneration (polymyositis). We used an immunohistochemical approach to detect and localise GLUT3. GLUT3 immunoreactivity was not detectable in adult skeletal muscle fibres, nor did metabolic stress, training or de- and re-innervation induce GLUT3 expression, while a few GLUT3 expressing fibres were seen in some cases of polymyositis. In contrast, GLUT4 was expressed in all investigated muscle fibres. GLUT3 immunoreactivity was found in perineural and endoneural cells, indicating that GLUT3 is important for glucose transport into nerves through the perineurium. Taken together, these data suggest that GLUT3 expression is restricted to regenerating muscle fibres and nerves in adult human muscle. Although the significance of GLUT3 in adult human muscle fibres appears limited, GLUT3 may be of importance for the glucose supply in fetal muscle fibres and regenerating adult muscle fibres.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gaster, .M., Beck-Nielsen, .H. & Schrøder, .H. Regenerating human muscle fibres express GLUT3 protein. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 445, 105–114 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-002-0895-9
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-002-0895-9