Abstract.
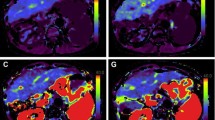
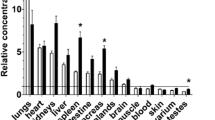
Intrahepatic shunts have an important function in the regulation of portal venous pressure in the normal rat liver. The present study determined their location, the region of confluence between the hepatic arterial and portal venous vasculatures, regions within the liver that are bypassed and the effects of hepatic arterial perfusion upon the intrahepatic redistribution of portal venous flow. Livers of male Sprague-Dawley rats were excised and perfused in vitro. Hepatic bromosulphthalein (BSP) and glucose uptake were measured in hepatic venous samples. Diversion of the hepatic arterial supply into the portal venous vasculature opened the portal venous intrahepatic shunts and resulted in a 50% reduction in portal venous glucose uptake from 29.6±1.6% to 14.9±0.9% (P<0.0001 Student's paired t-test). Portal venous injection of 15-µm-diameter microspheres also opened the intrahepatic shunts and reduced portal venous glucose uptake to 10% from 29.0±1.6% to 7.8±0.9% (P<0.0001 Student's paired t-test). No significant reductions in portal venous BSP uptake (43.0±6.9 to 48.0±4.8%) or hepatic arterial glucose uptake, from an average value of 94.0%, occurred. Therefore, cessation of hepatic arterial perfusion or portal venous injection of microspheres reduced portal venous glucose uptake without affecting BSP uptake. It is concluded that intrahepatic shunts divert perfusate away from the perivenous, sinusoidal (zone III) regions and into the hepatic venous vasculature, distal to zone III. The microsphere data indicate that confluence between the hepatic arterial and portal venous vasculatures occurs mainly in sinusoidal zone II.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alexander, B., Rogers, C. & Naftalin, R. Hepatic arterial perfusion decreases intrahepatic shunting and maintains glucose uptake in the rat liver. Pflügers Arch - Eur J Physiol 444, 291–298 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-002-0815-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-002-0815-z