Abstract
Purpose
Careful donor selection is important for kidney transplantations (KT) from suboptimal donors aged ≥65 years. Several tools such as histopathological assessment of preimplant biopsies have been shown to predict allograft survival and can be applied for selection. Whether the explanting surgeon’s appraisal is associated with outcomes of KTs from suboptimal donors is unknown.
Methods
We compared outcomes of KTs from ≥65-year-old deceased donors performed at our centre between 1999 and 2018 for which grading of macroscopic ‘donor arteriosclerosis’ (n=104) and ‘organ quality’ (n=208) as judged by the explanting surgeon and documented on the Eurotransplant kidney organ report was available.
Results
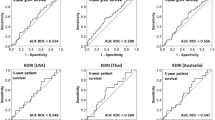
No association was observed between degree of macroscopic donor arteriosclerosis and death-censored graft survival in univariable or multivariable regression analyses. Compared to KTs from donors with no/mild arteriosclerosis, KTs from donors with moderate/severe arteriosclerosis were associated with a significantly impaired allograft function 3 months, 1 year and 3 years after transplantation (e.g. at 3 years: 176.8 µmol/l vs 137.0 µmol/l, P=0.003). Following multivariable regression analysis, these differences remained significant at 3 months and 3 years after KT. No association was observed between degree of macroscopic arteriosclerosis and mortality or primary non-function as well as no consistent association with delayed graft function and histological arteriosclerosis. Assessment of ‘organ quality’ was not associated with outcomes.
Conclusion
Our data suggest that the explanting surgeon’s assessment of donor arteriosclerosis is associated with allograft function. Larger studies and better standardization of kidney inspection after explantation are required to further explore the impact of surgeon’s appraisal in KT.


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable
References
Echterdiek F, Schwenger V, Dohler B, Latus J, Kitterer D, Heemann U, Susal C (2019) Kidneys from elderly deceased donors-is 70 the new 60? Front Immunol 10:2701. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.02701
Susal C, Kumru G, Dohler B, Morath C, Baas M, Lutz J, Unterrainer C, Arns W, Aubert O, Bara C, Beiras-Fernandez A, Bohmig GA, Bosmuller C, Diekmann F, Dutkowski P, Hauser I, Legendre C, Lozanovski VJ, Mehrabi A, Melk A, Minor T, Mueller TF, Pisarski P, Rostaing L, Schemmer P, Schneeberger S, Schwenger V, Sommerer C, Tonshoff B, Viebahn R, Viklicky O, Weimer R, Weiss KH, Zeier M, Zivcic-Cosic S, Heemann U (2020) Should kidney allografts from old donors be allocated only to old recipients? Transpl Int 33(8):849–857. https://doi.org/10.1111/tri.13628
Eurotransplant Statistics Report Library. (2021) Eurotransplant International Foundation. http://statistics.eurotransplant.org/. Accessed 24.02.2021
Rao PS, Schaubel DE, Guidinger MK, Andreoni KA, Wolfe RA, Merion RM, Port FK, Sung RS (2009) A comprehensive risk quantification score for deceased donor kidneys: the kidney donor risk index. Transplantation 88(2):231–236. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0b013e3181ac620b
Remuzzi G, Cravedi P, Perna A, Dimitrov BD, Turturro M, Locatelli G, Rigotti P, Baldan N, Beatini M, Valente U, Scalamogna M, Ruggenenti P, Dual Kidney Transplant G (2006) Long-term outcome of renal transplantation from older donors. N Engl J Med 354(4):343–352. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa052891
Remuzzi G, Grinyo J, Ruggenenti P, Beatini M, Cole EH, Milford EL, Brenner BM (1999) Early experience with dual kidney transplantation in adults using expanded donor criteria. Double Kidney Transplant Group (DKG). J Am Soc Nephrol 10(12):2591–2598
Dare AJ, Pettigrew GJ, Saeb-Parsy K (2014) Preoperative assessment of the deceased-donor kidney: from macroscopic appearance to molecular biomarkers. Transplantation 97(8):797–807. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.TP.0000441361.34103.53
Palevsky PM, Liu KD, Brophy PD, Chawla LS, Parikh CR, Thakar CV, Tolwani AJ, Waikar SS, Weisbord SD (2013) KDOQI US commentary on the 2012 KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Am J Kidney Dis 61(5):649–672. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2013.02.349
Roufosse C, Simmonds N, Clahsen-van Groningen M, Haas M, Henriksen KJ, Horsfield C, Loupy A, Mengel M, Perkowska-Ptasinska A, Rabant M, Racusen LC, Solez K, Becker JU (2018) A 2018 Reference Guide to the Banff Classification of Renal Allograft Pathology. Transplantation 102(11):1795–1814. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0000000000002366
R Core Team (2020) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Austria, Vienna
Thernau T (2020) A Package for Survival Analysis in R. R package version 3.2-7 edn
Van Buuren S, Groothuis-Oudshoorn K (2011) Mice: multivariate imputation by chained equations in R. J Statist Soft 45:1–67. https://doi.org/10.18637/jss.v045.i03
Pascual J, Zamora J, Pirsch JD (2008) A systematic review of kidney transplantation from expanded criteria donors. Am J Kidney Dis 52(3):553–586. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2008.06.005
Heilman RL, Mathur A, Smith ML, Kaplan B, Reddy KS (2016) Increasing the use of kidneys from unconventional and high-risk deceased donors. Am J Transplant 16(11):3086–3092. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.13867
Kayler LK, Mohanka R, Basu A, Shapiro R, Randhawa PS (2008) Correlation of histologic findings on preimplant biopsy with kidney graft survival. Transpl Int 21(9):892–898. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-2277.2008.00681.x
Pokorna E, Vitko S, Chadimova M, Schuck O (2000) Adverse effect of donor arteriolosclerosis on graft outcome after renal transplantation. Nephrol Dial Transplant 15(5):705–710. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/15.5.705
Cockfield SM, Moore RB, Todd G, Solez K, Gourishankar S (2010) The prognostic utility of deceased donor implantation biopsy in determining function and graft survival after kidney transplantation. Transplantation 89(5):559–566. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0b013e3181ca7e9b
Munivenkatappa RB, Schweitzer EJ, Papadimitriou JC, Drachenberg CB, Thom KA, Perencevich EN, Haririan A, Rasetto F, Cooper M, Campos L, Barth RN, Bartlett ST, Philosophe B (2008) The Maryland aggregate pathology index: a deceased donor kidney biopsy scoring system for predicting graft failure. Am J Transplant 8(11):2316–2324. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2008.02370.x
Keijbeck A, Veenstra R, Pol RA, Konijn C, Jansen N, van Goor H, Hoitsma AJ, Peutz-Kootstra CJ, Moers C (2020) The association between macroscopic arteriosclerosis of the renal artery, microscopic arteriosclerosis, organ discard, and kidney transplant outcome. Transplantation 104(12):2567–2574. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0000000000003189
Vashishtha D, McClelland RL, Ix JH, Rifkin DE, Jenny N, Allison M (2017) Relation between calcified atherosclerosis in the renal arteries and kidney function (from the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis). Am J Cardiol 120(8):1434–1439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2017.07.020
Roseman DA, Hwang SJ, Manders ES, O’Donnell CJ, Upadhyay A, Hoffmann U, Fox CS (2014) Renal artery calcium, cardiovascular risk factors, and indexes of renal function. Am J Cardiol 113(1):156–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2013.09.036
Chiu YW, Adler S, Budoff M, Takasu J, Ashai J, Mehrotra R (2010) Prevalence and prognostic significance of renal artery calcification in patients with diabetes and proteinuria. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5(11):2093–2100. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.03730410
Frei U, Noeldeke J, Machold-Fabrizii V, Arbogast H, Margreiter R, Fricke L, Voiculescu A, Kliem V, Ebel H, Albert U, Lopau K, Schnuelle P, Nonnast-Daniel B, Pietruck F, Offermann R, Persijn G, Bernasconi C (2008) Prospective age-matching in elderly kidney transplant recipients–a 5-year analysis of the Eurotransplant Senior Program. Am J Transplant 8(1):50–57. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-6143.2007.02014.x
Chavalitdhamrong D, Gill J, Takemoto S, Madhira BR, Cho YW, Shah T, Bunnapradist S (2008) Patient and graft outcomes from deceased kidney donors age 70 years and older: an analysis of the Organ Procurement Transplant Network/United Network of Organ Sharing database. Transplantation 85(11):1573–1579. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0b013e31817059a1
Bodingbauer M, Pakrah B, Steininger R, Berlakovich G, Rockenschaub S, Wekerle T, Muehlbacher F (2006) The advantage of allocating kidneys from old cadaveric donors to old recipients: a single-center experience. Clin Transplant 20(4):471–475. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-0012.2006.00508.x
Bentas W, Jones J, Karaoguz A, Tilp U, Probst M, Scheuermann E, Hauser IA, Jonas D, Gossmann J (2008) Renal transplantation in the elderly: surgical complications and outcome with special emphasis on the Eurotransplant Senior Programme. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23(6):2043–2051. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfm912
Jacobi J, Beckmann S, Heller K, Hilgers KF, Apel H, Spriewald B, Eckardt KU, Amann KU (2016) Deceased Donor Kidney Transplantation in the Eurotransplant Senior Program (ESP): a single-center experience from 2008 to 2013. Ann Transplant 21:94–104. https://doi.org/10.12659/aot.895731
Fabrizii V, Kovarik J, Bodingbauer M, Kramar R, Horl WH, Winkelmayer WC (2005) Long-term patient and graft survival in the eurotransplant senior program: a single-center experience. Transplantation 80(5):582–589. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.tp.0000168340.05714.99
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FE: study conception and design; acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data, drafting of manuscript. CT: acquisition of data, critical revision of manuscript. DK: study conception and design, critical revision of manuscript. JD: analysis and interpretation of data, critical revision of manuscript. JSB: acquisition of data, critical revision of manuscript. GP: acquisition of data, critical revision of manuscript. MO: acquisition of data, critical revision of manuscript. UH: study conception and design, critical revision of manuscript. VS: study conception and design, critical revision of manuscript. JL: study conception and design, interpretation of data, drafting and critical revision of manuscript. All authors approved the final version of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
The study was approved by the local ethics committee at the University of Tübingen (No. 632/2019 BO2) and performed according to the ethical standards of the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent to participate
Patient records/data were anonymized and de-identified prior to analysis. Data was only analysed in groups so that identification of individual patients was not possible. The ethics committee at the University of Tübingen stated that no further approval was necessary for this retrospective study.
Consent for publication
See above.
Conflict of interest
J.D. received payments from Klinikum Stuttgart – Katharinenhospital, Department of Nephrology for statistical analysis, preparation of figures and scientific writing of the statistic section of the manuscript. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Echterdiek, F., Tilgener, C., Dippon, J. et al. Impact of the explanting surgeon’s impression of donor arteriosclerosis on outcome of kidney transplantations from donors aged ≥65 years. Langenbecks Arch Surg 407, 727–737 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-021-02383-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-021-02383-7