Abstract
Purpose
Left-sided gallbladder (LSGB) is a rare congenital anomaly in the gallbladder, which is defined as a gallbladder located on the left side of the falciform ligament without situs inversus. We retrospectively analyzed 13 patients diagnosed with LSGB in a single center to confirm the safety of laparoscopic cholecystectomy (LC) and reviewed the anatomical implications in those patients.
Methods
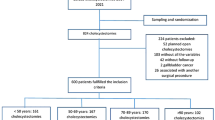
Of the 4910 patients who underwent LC for the treatment of gallbladder disease between August 2007 and December 2019, 13 (0.26%) were diagnosed as having LSGB. We retrospectively analyzed these 13 patients for general characteristics, perioperative outcomes, and other variations through the perioperative imaging workups.
Results
All patients underwent LC for gallbladder disease. In all cases, the gallbladder was located on the left side of the falciform ligament. The operation was successfully performed with standard four-trocar technique, confirming “critical view of safety (CVS)” as usual without two cases (15.4%). In one case, which had an intraoperative complication and needed choledochojejunostomy because of common bile duct injury, there was an associated variation with early common bile duct bifurcation. The other patient underwent an open conversion technique because of severe fibrosis in the Calot’s triangle. Furthermore, on postoperative computed tomography, abnormal intrahepatic portal venous branching was found in all cases.
Conclusions
Although LSGB is usually encountered by chance during surgery, it can be successfully managed through LC with CVS. However, surgeons who find LSGB have to make efforts to be aware of the high risk of bile duct injury and possibility of associated anomalies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wakabayashi G, Iwashita Y, Hibi T, Takada T, Strasberg SM, Asbun HJ, Endo I, Umezawa A, Asai K, Suzuki K (2018) Tokyo Guidelines 2018: surgical management of acute cholecystitis: safe steps in laparoscopic cholecystectomy for acute cholecystitis (with videos). J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 25:73–86
Okamoto K, Suzuki K, Takada T, Strasberg SM, Asbun HJ, Endo I, Iwashita Y, Hibi T, Pitt HA, Umezawa A (2018) Tokyo Guidelines 2018: flowchart for the management of acute cholecystitis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 25:55–72
Overby DW, Apelgren KN, Richardson W, Fanelli R (2010) SAGES guidelines for the clinical application of laparoscopic biliary tract surgery. Surg Endosc 24:2368–2386
Townsend CM, Beauchamp RD, Evers BM, Mattox KL (2017) Sabiston textbook of surgery: the biological basis of modern surgical practice. Elsevier
Nagai M, Kubota K, Kawasaki S, Takayama T (1997) Are left-sided gallbladders really located on the left side? Ann Surg 225:274
Lee D-H, Kim D, Park YH, Kim JS (2019) Clinical significance and characteristics of left-sided gallbladder: case series study of 10 patients. Ann Surg Treat Res 97:302–308
Hsu S-L, Chen T-Y, Huang T-L, Sun C-K, Concejero AM, Tsang LL-C, Cheng Y-F (2007) Left-sided gallbladder: its clinical significance and imaging presentations. World J Gastroenterol 13:6404
Si-Youn R, Poong-Man J (2008) Left-sided gallbladder with right-sided ligamentum teres hepatis: rare associated anomaly of exomphalos. J Pediatr Surg 43:1390–1395
Iskandar ME, Radzio A, Krikhely M, Leitman IM (2013) Laparoscopic cholecystectomy for a left-sided gallbladder. World J Gastroenterol 19:5925
Pereira R, Singh T, Avramovic J, Baker S, Eslick GD, Cox MR (2019) Left-sided gallbladder: a systematic review of a rare biliary anomaly. ANZ J Surg 89:1392–1397
Strong RW, Fawcett J, Hatzifotis M, Hodgkinson P, Lynch S, O’Rourke T, Slater K, Yeung S (2013) Surgical implications of a left-sided gallbladder. Am J Surg 206:59–63
Zografos GC, Lagoudianakis EE, Grosomanidis D, Koronakis N, Tsekouras D, Chrysikos J, Filis K, Manouras A (2009) Management of incidental left-sided gallbladder. JSLS 13:273
Abongwa HK, De Simone B, Alberici L, Iaria M, Perrone G, Tarasconi A, Baiocchi G, Portolani N, Di Saverio S, Sartelli M (2017) Implications of left-sided gallbladder in the emergency setting: retrospective review and top tips for safe laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 27:220–227
Strasberg SM, Brunt LM (2010) Rationale and use of the critical view of safety in laparoscopic cholecystectomy. J Am Coll Surg 211:132–138
Gross RE (1936) Congenital anomalies of the gallbladder: a review of one. hundred and forty-eight cases, with report of a double gallbladder. Arch Surg 32:131–162
Archer SB, Brown DW, Smith CD, Branum GD, Hunter JG (2001) Bile duct injury during laparoscopic cholecystectomy: results of a national survey. Ann Surg 234:549
Ludwig K, Bernhardt J, Steffen H, Lorenz D (2002) Contribution of intraoperative cholangiography to incidence and outcome of common bile duct injuries during laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Surg Endosc 16:1098–1104
Flum DR, Flowers C, Veenstra DL (2003) A cost-effectiveness analysis of intraoperative cholangiography in the prevention of bile duct injury during laparoscopic cholecystectomy. J Am Coll Surg 196:385–393
Moo-Young TA, Picus DD, Teefey S, Strasberg SM (2010) Common bile duct injury following laparoscopic cholecystectomy in the setting of sinistroposition of the galladder and biliary confluence: a case report. J Gastrointest Surg 14:166
Kim E-J, Lee J-H, Song S-Y, Lee K-G, Park H-K, Lee K-S (2010) Left-sided gallbladder with intrahepatic portal vein anomalies: a single center experiences. Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 14:241–247
Idu M, Jakimowicz J, Iuppa A, Cuschieri A (1996) Hepatobiliary anatomy in patients with transposition of the gallbladder: implications for safe laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Br J Surg 83:1442–1443
Schachner A (1916) Anomalies of the gall-bladder and bile-passages: with the report of a double gall-bladder and a floating gall-bladder. Ann Surg 64:419
Korn O, Csendes A, Bastías J (1988) Anomalies of extrahepatic biliary duct and gallbladder associated with intestinal malrotation: a case report. Surgery 103:496–498
Almodhaiberi H, Hwang S, Cho Y-J, Kwon Y, Jung B-H, Kim M-H (2015) Customized left-sided hepatectomy and bile duct resection for perihilar cholangiocarcinoma in a patient with left-sided gallbladder and multiple combined anomalies. Korean J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 19:30–34
Shimizu T, Hayashi M, Inoue Y, Komeda K, Asakuma M, Hirokawa F, Miyamoto Y, Snawder BJ, Tanaka K, Uchiyama K (2012) Living-donor liver transplantation from donor with a left-sided gallbladder with portal vein anomaly. Transplantation 94:e60–e61
Abe T, Kajiyama K, Harimoto N, Gion T, Shirabe K, Nagaie T (2012) Resection of metastatic liver cancer in a patient with a left-sided gallbladder and intrahepatic portal vein and bile duct anomalies: a case report. Int J Surg Case Rep 3:147–150
Hwang S, Lee SG, Park KM, Lee YJ, Ahn CS, Kim KH, Moon DB, Ha TY, Cho SH, Oh KB (2004) Hepatectomy of living donors with a left-sided gallbladder and multiple combined anomalies for adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation. Liver Transpl 10:141–146
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This retrospective study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of the Hanyang University Hospital, Seoul, Republic of Korea, and all research conducted adhered to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki (IRB No. 2018-09-019).
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung, Y.K., Choi, D. & Lee, K.G. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy for left-sided gallbladder. Langenbecks Arch Surg 407, 207–212 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-021-02263-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-021-02263-0