Abstract
Purpose
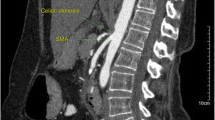
Median arcuate ligament (MAL) syndrome is a clinical syndrome caused by the compression of the celiac artery (CA) by the MAL. This study aimed to present the detailed anatomy and a step-by-step procedure of CA decompression for MAL syndrome.
Methods
The CA decompression procedure involves exposing the diaphragmatic crura and aorta, taping the left gastric artery, and dividing the compressive tissues. The MAL and ganglionic tissue, which form a broad band with multiple layers overlying the CA, comprise the compressive tissues. Therefore, the compressive tissues overlying the CA are encircled and divided one by one until the CA stenosis is released. CA decompression is confirmed with intraoperative duplex ultrasonography of the CA, with a return to normal peak systolic velocities without variation between deep inspiration and expiration.
Conclusion
This report presents the detailed anatomy and procedural steps for CA decompression in MAL syndrome.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CA:
-
Celiac artery
- CHA:
-
Common hepatic artery
- IPA:
-
Inferior phrenic artery
- LGA:
-
Left gastric artery
- MAL:
-
Median arcuate ligament
References
Kim EN, Lamb K, Relles D, Moudgill N, DiMuzio PJ, Eisenberg JA (2016) Median arcuate ligament syndrome—review of this rare disease. JAMA Surg 151(5):471–477. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamasurg.2016.0002
Sgroi MD, Kabutey N-K, Krishnam M, Fujitani RM (2015) Pancreaticoduodenal artery aneurysms secondary to median arcuate ligament syndrome may not need celiac artery revascularization or ligament release. Ann Vasc Surg 29(1):122. e1–122. e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avsg.2014.05.020
Oikawa R, Ito K, Takemura N, Mihara F, Kokudo N (2020) Arterial communication around the pancreatic tail enabled division of the gastroduodenal artery during pancreaticoduodenectomy in patient with complete celiac artery occlusion: a case report. Surg Case Rep 6(1):29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40792-020-0787-2
Cienfuegos JA, Estevez MG, Ruiz-Canela M, Pardo F, Diez-Caballero A, Vivas I, Bilbao JI, Martí-Cruchaga P, Zozaya G, Valentí V, Hernández-Lizoáin JL, Rotellar F (2018) Laparoscopic treatment of median arcuate ligament syndrome: analysis of long-term outcomes and predictive factors. J Gastrointest Surg 22(4):713–721. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-017-3635-3
Moore KL, Dalley AF (2017) Clinically oriented anatomy 8th edition. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Jimenez JC, Harlander-Locke M, Dutson EP (2012) Open and laparoscopic treatment of median arcuate ligament syndrome. J Vasc Surg 56(3):869–873. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2012.04.057
Loukas M, Hullett J, Wagner T (2005) Clinical anatomy of the inferior phrenic artery. Clin Anat 18(5):357–365. https://doi.org/10.1002/ca.20112
Vaziri K, Hungness ES, Pearson EG, Soper NJ (2009) Laparoscopic treatment of celiac artery compression syndrome: case series and review of current treatment modalities. J Gastrointest Surg 13(2):293–298. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-008-0702-9
Lipshutz B (1917) A composite study of the coeliac axis artery. Ann Surg 65(2):159–169. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000658-191702000-00006
Harjola P (1963) A rare obstruction of the coeliac artery. Report of a case. Ann Chir Gynaecol Fenn 52:547–550
Do MV, Smith TA, Bazan HA, Sternbergh W, Abbas AE, Richardson WS (2013) Laparoscopic versus robot-assisted surgery for median arcuate ligament syndrome. Surg Endosc 27(11):4060–4066. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-013-3061-x
Reilly LM, Ammar AD, Stoney RJ, Ehrenfeld WK (1985) Late results following operative repair for celiac artery compression syndrome. J Vasc Surg 2(1):79–91
Kohn GP, Bitar RS, Farber MA, Marston WA, Overby DW, Farrell TM (2011) Treatment options and outcomes for celiac artery compression syndrome. Surg Innov 18(4):338–343. https://doi.org/10.1177/1553350610397383
Roseborough GS (2009) Laparoscopic management of celiac artery compression syndrome. J Vasc Surg 50(1):124–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2008.12.078
Availability of data and material
The datasets analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to their containing information that could compromise the privacy of research participants but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Funding
Grants-in-Aid for Research from the National Center for Global Health and Medicine (30-1021 to N. T.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KI and NT contributed to the conception and design of the study. All authors contributed to the acquisition and analysis of data. KI and NT were major contributors in writing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This article satisfied the consensus of the National Center for Global Health and Medicine Research Ethics Committee/Institutional Review Board.
Consent for publication
Informed consent for using intraoperative photographs was obtained from the patient presented in this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ito, K., Takemura, N., Oikawa, R. et al. Detailed anatomy and procedure of celiac artery decompression in median arcuate ligament syndrome. Langenbecks Arch Surg 406, 1717–1722 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-021-02195-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-021-02195-9