Abstract
Background
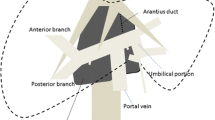
The caudate lobe is located deep in the dorsal portion of the liver. Complete resection is an extremely demanding surgery due to the limited surgical field, especially in cases with severe intra-abdominal complications. A major concern of isolated caudate lobectomy is the difficulty associated with securing the contralateral visual field during parenchymal transection. To overcome this issue, we present a new technique for isolated caudate lobectomy that uses a modified hanging maneuver.
Methods
We performed an anatomical isolated caudate lobectomy via the high dorsal resection technique using our new modified hanging maneuver in two patients with HCC in November and December 2019.
Results
Patient 1 was severely obese, so the upper abdominal cavity was occupied by a large amount of great omental fat, and fibrous adhesions were observed around the spleen. Patient 2 had undergone six preoperative treatments, and a high degree of adhesion was observed in the abdominal cavity around the liver. It was difficult to secure the surgical field due to severe abdominal complications in both cases. The total operation times in these two cases were 617 and 763 min, respectively, while the liver parenchymal dissection times of the caudate lobe were 96 and 108 min, respectively. The resection margin was negative in both patients (R0). Neither patient had any complications after surgery; both were discharged on postoperative day 14.
Conclusion
Our modified hanging maneuver is useful, particularly in cases with a narrow surgical field due to severe adhesions, bulky tumors, and/or hypertrophy of the Spiegel lobe.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- IVC:
-
Inferior vena cava
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- ICG:
-
Indocyanine green
- MCT:
-
Microwave coagulation therapy
- RFA:
-
Radiofrequency ablation
- MHV:
-
Middle hepatic vein
- LHV:
-
Left hepatic vein
- RHV:
-
Right hepatic vein
- IRHV:
-
Inferior right hepatic vein
- CPHV:
-
Caudate process hepatic vein
- RPV:
-
Right portal vein
References
Makuuchi M, Hasegawa H, Yamazaki S (1985) Ultrasonically guided subsegmentectomy. Surg Gynecol Obstet 161(4):346–350
Nakashima T, Kojiro M (1986) Pathologic characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis 6(3):259–266. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2008-1040608
Takayama T, Tanaka T, Higaki T, Katou K, Teshima Y, Makuuchi M (1994) High dorsal resection of the liver. J Am Coll Surg 179(1):72–75
Takayama T, Midorikawa Y, Higaki T, Nakayama H, Moriguchi M, Aramaki O, Yamazaki S, Aoki M, Kogure K, Makuuchi M (2019) Algorithm for resecting hepatocellular carcinoma in the caudate lobe. Ann Surg. https://doi.org/10.1097/sla.0000000000003384
Midorikawa Y, Takayama T (2012) Caudate lobectomy (segmentectomy 1) (with video). J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 19(1):48–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00534-011-0450-1
Shindoh J, Imamura H, Kokudo N (2010) Isolated sling suspension during resection of the Spiegel lobe of the liver: a safe alternative technique for difficult cases. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 17(3):359–364. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00534-010-0274-4
Kitagawa S, Murakami G, Hata F, Hirata K (2000) Configuration of the right portion of the caudate lobe with special reference to identification of its right margin. Clin Anat 13(5):321–340. https://doi.org/10.1002/1098-2353(2000)13:5<321::Aid-ca2>3.0.Co;2-r
Kumon M (2017) Anatomical study of the caudate lobe with special reference to portal venous and biliary branches using corrosion liver casts and clinical application. Liver Cancer 6(2):161–170. https://doi.org/10.1159/000454682
Lerut J, Gruwez JA, Blumgart LH (1990) Resection of the caudate lobe of the liver. Surg Gynecol Obstet 171(2):160–162
Yamamoto J, Takayama T, Kosuge T, Yoshida J, Shimada K, Yamasaki S, Hasegawa H (1992) An isolated caudate lobectomy by the transhepatic approach for hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic liver. Surgery 111(6):699–702
Colonna JO 2nd, Shaked A, Gelabert HA, Busuttil RW (1993) Resection of the caudate lobe through "bloody gultch". Surg Gynecol Obstet 176(4):401–402
Yanaga K, Matsumata T, Hayashi H, Shimada M, Urata K, Sugimachi K (1994) Isolated hepatic caudate lobectomy. Surgery 115(6):757–761
Kosuge T, Yamamoto J, Takayama T, Shimada K, Yamasaki S, Makuuchi M, Hasegawa H (1994) An isolated, complete resection of the caudate lobe, including the paracaval portion, for hepatocellular carcinoma. Arch Surg 129(3):280–284. https://doi.org/10.1001/archsurg.1994.01420270056013
Asahara T, Dohi K, Hino H, Nakahara H, Katayama K, Itamoto T, Ono E, Moriwaki K, Yuge O, Nakanishi T, Kitamoto M (1998) Isolated caudate lobectomy by anterior approach for hepatocellular carcinoma originating in the paracaval portion of the caudate lobe. J Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat Surg 5(4):416–421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s005340050066
Belghiti J, Guevara OA, Noun R, Saldinger PF, Kianmanesh R (2001) Liver hanging maneuver: a safe approach to right hepatectomy without liver mobilization. J Am Coll Surg 193(1):109–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1072-7515(01)00909-7
Kim SH, Park SJ, Lee SA, Lee WJ, Park JW, Kim CM (2006) Isolated caudate lobectomy using the hanging maneuver. Surgery 139(6):847–850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2006.01.004
Lopez-Andujar R, Montalva E, Bruna M, Jimenez-Fuertes M, Moya A, Pareja E, Mir J (2009) Step-by-step isolated resection of segment 1 of the liver using the hanging maneuver. Am J Surg 198(3):e42–e48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjsurg.2009.02.012
Makuuchi M, Yamamoto J, Takayama T, Kosuge T, Gunven P, Yamazaki S, Hasegawa H (1991) Extrahepatic division of the right hepatic vein in hepatectomy. Hepatogastroenterology 38(2):176–179
Kogure K, Kuwano H, Fujimaki N, Makuuchi M (2000) Relation among portal segmentation, proper hepatic vein, and external notch of the caudate lobe in the human liver. Ann Surg 231(2):223–228. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000658-200002000-00011
Kogure K, Ishizaki M, Nemoto M, Kuwano H, Yorifuji H, Ishikawa H, Takata K, Makuuchi M (2007) Close relation between the inferior vena cava ligament and the caudate lobe in the human liver. J Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat Surg 14(3):297–301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00534-006-1148-7
Takayama T, Makuuchi M, Kubota K, Sano K, Harihara Y, Kawarasaki H (2000) Living-related transplantation of left liver plus caudate lobe. J Am Coll Surg 190(5):635–638. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1072-7515(00)00255-6
Yamazaki S, Takayama T, Makuuchi M (2010) The technical advance and impact of caudate lobe venous reconstruction in left liver: additional safety for living-related donor liver transplantation. Transpl Int 23(4):345–349. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-2277.2009.01044.x
Hwang S, Lee SG, Ha TY, Ahn CS, Park KM, Kim KH, Lee YJ, Moon DB, Kim KK, Kim YD (2004) Simplified standardized technique for living donor liver transplantation using left liver graft plus caudate lobe. Liver Transpl 10(11):1398–1405. https://doi.org/10.1002/lt.20241
Ochiai T, Ishii H, Toma A, Ishimoto T, Yamamoto Y, Morimura R, Ikoma H, Otsuji E (2016) Modified high dorsal procedure for performing isolated anatomic total caudate lobectomy (with video). World J Surg Oncol 14:132. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-016-0896-3
Kogure K, Kuwano H, Yorifuji H, Ishikawa H, Takata K, Makuuchi M (2008) The caudate processus hepatic vein: a boundary hepatic vein between the caudate lobe and the right liver. Ann Surg 247(2):288–293. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0b013e31815efd8d
Sakamoto Y, Kokudo N, Kawaguchi Y, Akita K (2017) Clinical anatomy of the liver: review of the 19th Meeting of the Japanese Research Society of Clinical Anatomy. Liver Cancer 6(2):146–160. https://doi.org/10.1159/000449490
Couinaud C (1989) Posterior or dorsal liver. In: Couinaud C (ed) Surgical anatomy of the liver revisited. Couinaud, Claude, Paris, pp 123–134
Couinaud C (1994) The paracaval segments of the liver. J Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat Surg 1(2):145–151. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01222238
Healey JE Jr, Schroy PC (1953) Anatomy of the biliary ducts within the human liver; analysis of the prevailing pattern of branchings and the major variations of the biliary ducts. AMA Arch Surg 66(5):599–616. https://doi.org/10.1001/archsurg.1953.01260030616008
Cappelle M, Aghayan DL, van der Poel MJ, Besselink MG, Sergeant G, Edwin B, Parmentier I, De Meyere C, Vansteenkiste F, D'Hondt M (2020) A multicenter cohort analysis of laparoscopic hepatic caudate lobe resection. Langenbeck's Arch Surg 405(2):181–189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-020-01867-2
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Azusa Okuwa of SAIKOU Inc. for the figure illustrations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study conception and design: Taiji Tohyama; acquisition of data: Taiji Tohyama, Yoshimi Fujimoto, Takayoshi Murakami, Kumi Sugiu, Yasutaka Kudou, Takamasa Matsumoto; analysis and interpretation of data: Taiji Tohyama; drafting of manuscript: Taiji Tohyama; critical revision: Taiji Tohyama.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution and research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tohyama, T., Fujimoto, Y., Murakami, T. et al. Isolated caudate lobectomy using a modified hanging maneuver. Langenbecks Arch Surg 406, 927–933 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-020-02048-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-020-02048-x



