Abstract
Purpose
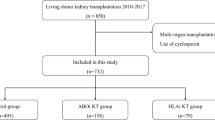
Since 2004, ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation (ABOi KTx) became an established procedure to expand the living donor pool in Germany. Currently, ABOi KTx comprises > 20% of all living donor KTx. Up to September 2015, > 100 ABOi KTx were performed in Freiburg. Regarding lymphocele formation, only scarce data exist.
Methods
Between April 2004 and September 2015, 106 consecutive ABOi and 277 consecutive ABO-compatible kidney transplantations (ABOc KTx) were performed. Two ABOi and 117 ABOc recipients were excluded due to differences in immunosuppression. One hundred-four ABOi and 160 ABOc KTx patients were analyzed concerning lymphocele formation.
Results
The incidence of lymphoceles in ABOi KTx was 25.2% and 10.6% in ABOc KTx (p = 0.003). A major risk factor appeared the frequency of ≥ 8 preoperative immunoadsorption and/or plasmapheresis sessions (OR 5.61, 95% CI 2.31–13.61, p < 0.001). Particularly, these ABOi KTx recipients had a distinctly higher risk of developing lymphocele (40.0% vs. 19.2%, p = 0.044). IA/PE sessions on day of transplantation (no lymphocele 20.0% vs. lymphocele 28.6%, p = 0.362) or postoperative IA/PE sessions (no lymphocele 25.7% vs. lymphocele 24.1%, p = 1.0) showed no influence on formation of lymphoceles.
Conclusion
In ABOi KTx, the incidence of lymphocele formation is significantly increased compared to ABOc KTx and leads to more frequent surgical reinterventions without having an impact on graft survival.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABOc:
-
blood group compatible
- ABOi:
-
blood group incompatible
- BMI:
-
body mass index
- CMV:
-
cytomegalovirus
- DJ:
-
double-J catheter
- EC:
-
red blood cell transfusion
- IA:
-
immunoadsorption
- KTx:
-
kidney transplantation
- PP:
-
plasmapheresis
- PRA:
-
panel reactive antibody
- USRDS:
-
United States Renal Data System
References
Zschiedrich S, Jänigen B, Dimova D, Neumann A, Seidl M, Hils S, Geyer M, Emmerich F, Kirste G, Drognitz O, Hopt UT, Walz G, Huber TB, Pisarski P, Kramer-Zucker A (2016) One hundred ABO-incompatible kidney transplantations between 2004 and 2014: a single-center experience. Nephrol Dial Transplant 31:663–671
Zschiedrich S, Kramer-Zucker A, Jänigen B, Seidl M, Emmerich F, Pisarski P, Huber TB (2015) An update on ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation. Transpl Int 28:387–397
Takahashi K, Saito K (2006) Present status of ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation in Japan. Xenotransplantation 13:118–122
Genberg H, Kumlien G, Wennberg L, Berg U, Tydèn G (2008) ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation using antigen-specific immunoadsorption and rituximab: a 3-year follow-up. Transplantation 85:1745–1754
Wilpert J, Geyer M, Pisarski P et al (2010) Long-term outcome of ABO-incompatible living donor kidney transplantation based on antigen-specific desensitization. An observational comparative analysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 25:3778–3786
Tydèn G, Kumlien G, Fehrman I (2003) Successful ABO-incompatible kidney transplantations without splenectomy using antigen-specific immunoadsorption and rituximab. Transplantation 76:730–731
Renner FC, Czekalinska B, Kemkes-Matthes B, Feustel A, Stertmann WA, Padberg W, Weimer R (2010) Postoperative bleeding after ABO-incompatible living donor kidney transplantation. Transplant Proc 42:4164–4166
De Weerd AE, Van Agteren M, Leebeek FW, Ijzermans JN, Weimar W, Betjes MG (2015) ABO-incompatible kidney transplant recipients have a higher bleeding risk after antigen-specific immunoadsorption. Transplant Int 28:25–33
Schaefer B, Tönshoff B, Schmidt J, Golriz M, Mehrabi A, Gombos P, Morath C, Wühl E, Schaefer F, Schmitt CP (2013) Bleeding complications in pediatric ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation. Pediatr Nephrol 28:327–332
Hwang JK, Kim SI, Choi BS, Yang CW, Kim YS, Moon IS, Kim JI (2011) Short-term results of ABO-incompatible living donor kidney transplantation: comparison with ABO-compatible grafts. J Korean Surg Soc 81:10–18
Lentine KL, Axelrod D, Klein C, Simpkins C, Xiao H, Schnitzler MA, Tuttle-Newhall JE, Dharnidharka VR, Brennan DC, Segev DL (2014) Early clinical complications after ABO incompatible live donor kidney transplantation: a national study of Medicare-insured recipients. Transplantation 98:54–65
Schwartz J, Stegall MD, Kremers WK, Gloor J (2006) Complications, resource utilization, and cost of ABO-incompatible living donor kidney transplantation. Transplantation 82:155–163
Park WY, Kang SS, Park SB, Park UJ, Kim HT, Cho WH, Han S (2016) Comparison of clinical outcomes between ABO-compatible and ABO-incompatible spousal donor kidney transplantation. Kidney Res Clin Pract 35:50–54
Sivakumaran P, Vo AA, Villicana R et al (2009) Therapeutic plasma exchange for desensitization prior to transplantation in ABO-incompatible renal allografts. J Clin Apher 24:155–160
Kim MH, Jun KW, Hwang JK, Kim JI, Chung BH, Choi BS, Kim YS, Yang CW, Moon IS (2015) Risk factors for postoperative bleeding in ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation. Clin Transpl 29:365–372
Conrad S, Schneider AW, Gonnermann D, Ganama A, Tenschert W, Huland W (1994) Urologic complications after kidney transplantation. Experiences in a center with 539 recipients. Urol A 33:392–400
Reek C, Tenschert W, Fernandez S, Meyer-Moldenhauer WH, Huland H (1997) Untersuchung zum Auftreten von Lymphozelen nach allogener Nierentransplantation und deren Therapie. Urol A 36:313–317
Hamza A, Fischer K, Koch E, Wicht A, Zacharias M, Loertzer H, Fornara P (2006) Diagnostics and therapy of lymphoceles after kidney transplantation. Transplant Proc 38:701–706
Humar A, Matas AJ (2005) Surgical complications after kidney transplantation. Semin Dial 18:505–510
Naciri Bennani H, Abdulrahman Z, Allal A et al (2016) Early post-transplant complications following ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation. J Nephropathol 5:19–27
Song SH, Lee J, Kim BS, Kim S, Lee JG, Jeong HJ, Kim YS, Kim MS, Kim HO, Kim SI, Huh KH (2017) Successful launch of an ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation program to overcome the shortage of compatible living donors: experience at a single center. Clin Nephrol 88:117–123
Barba J, Rosell D, Rincon JE et al (2012) New immunosuppressive therapies and surgical complications after renal transplantation. Transplant Proc 44:1275–1280
Koch M, Wiech T, Marget M, Peine S, Thude H, Achilles EG, Fischer L, Lehnhardt A, Thaiss F, Nashan B (2015) De novo mTOR inhibitor-based immunosuppression in ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation. Clin Transpl 29:1021–1028
Lopau K, Syamken K, Rubenwolf P, Riedmiller H, Wanner C (2010) Impact of mycophenolate mofetil on wound complications and lymphoceles after kidney transplantation. Kidney Blood Press Res 33:52–59
Barba J, Algarra R, Romero L, Tienza A, Velis JM, Robles JE, Zudaire JJ, Pascual I (2013) Recipient and donor risk factors for surgical complications following kidney transplantation. Scand J Urol 47:63–71
Orlic L, Mikolasevic I, Jakopcic I, Grskovic A, Jelic Pranjic I, Racki S, Stimac D (2015) Body mass index: short- and long-term impact on kidney transplantation. Int J Clin Pract 69:1357–1365
Røine E, Bjork IT, Øyen O (2010) Targeting risk factors for impaired wound healing and wound complications after kidney transpantation. Tranplant Proc 42:2542–2546
Goel M, Flechner SM, Zhou L et al (2004) The influence of various maintenance immunosuppressive drugs on lymphocele formation and treatment after kidney transplantation. J Urol 171:1788–1792
Mokos I, Basic-Jukic N, Kastelan Z, Kes P, Pasini J (2010) Influence of long-term dialysis treatment on operative complications after renal transplantation. Transplant Proc 42:2531–2533
Pillot P, Bardonnaud N, Lillaz J, Delorme G, Chabannes E, Bernardini S, Guichard G, Bittard H, Kleinclauss F (2012) Risk factors for surgical complications after renal transplantation and impact on patient and graft survival. Transplant Proc 44:2803–2808
Thölking G, Koch R, Pavenstädt H, Schuette-Nuetgen K, Busch V, Wolters H, Kelsch R, Reuter S, Suwelack B (2015) Antigen-specific versus non-antigen-specific immunoadsorption in ABO-incompatible renal transplantation. PLoS One 10:e0131465
Zietek Z, Iwan-Zietek I, Sulikowski T et al (2011) The outcomes of treatment and the etiology of lymphoceles with a focus on hemostasis in kidney recipients: a preliminary report. Transplant Proc 43:3008–3012
Lundin C, Bersztel A, Wahlberg J, Wadström J (2002) Low molecular weight heparin prophylaxis increases the incidence of lymphocele after kidney transplantation. Ups J Med Sci 107:9–15
Koessler J, Kobsar A, Kuhn S, Koessler A, Yilmaz P, Weinig E, Putz E, Boeck M, Klinker E (2015) The effect of immunoadsorption with the Immusorba TR-350 column on coagulation compared to plasma exchange. Vox Sang 108:46–51
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Erika Graf (IMBI Freiburg) for the very helpful statistical consultation enhancing clarity of data presentation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BMJ: study conception and design, drafting of manuscript, interpretation of data, transplant surgeon. CS: acquisition of data. TG: analysis of data. OT: critical revision of manuscript. CL: critical revision of manuscript. SFF: critical revision of manuscript. SZ: study conception and design, critical revision of manuscript. PP: critical revision of manuscript, principal transplant surgeon.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The registry and the study were approved by the ethics committee of the University Medical Center Freiburg and in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
All patients of the Freiburg living donor kidney program gave informed consent for collecting and storing their data in our living donor transplant registry for analysis for research purposes.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jänigen, B.M., Salabè, C., Glatz, T. et al. Single cohort study: ABO-incompatible kidney transplant recipients have a higher risk of lymphocele formation. Langenbecks Arch Surg 404, 999–1007 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-019-01812-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-019-01812-y