Abstract
Purpose
To provide a comprehensive evidence-based assessment of the anatomical characteristics of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve (EBSLN).
Materials and methods
A thorough systematic search was performed on the major electronic databases PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane library, and ScienceDirect to identify eligible studies. Data were extracted and pooled into a meta-analysis. The primary outcomes were the EBSLN identification rate (total number of EBSLN identified divided by the total number of dissected hemilarynges) and the prevalence of various EBSLN types.
Results
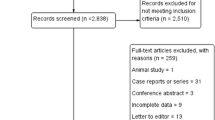
A total of 56 studies (n = 13,444 hemilarynges) were included. The overall pooled EBSLN identification rate was 89.24% (95% CI 85.49–92.49). This rate was higher for cadaveric (95.00%; 95% CI 89.73–99.35) compared to that reported in intraoperative studies (86.99%; 95% CI 82.37–91.01). Significantly higher identification rates were reported for studies in which intraoperative nerve monitoring was used (95.90%; 95% CI 94.30–97.25) compared to those which only relied on direct visual identification of the EBSLN (76.56%; 95% CI 69.34–83.08). Overall, Cernea type IIa (nerves crossing the superior thyroid artery less than 1 cm above the upper edge of the superior thyroid pole) and Friedman type 1 (nerves running their entire course superficial to the inferior pharyngeal constrictor) were the most prevalent (41.84%; 95% CI 33.28–48.08 and 50%; 95% CI 29.90–65.62, respectively). The combined prevalence of Cernea IIa and IIb (nerves crossing the superior thyroid artery below the upper edge of the superior thyroid pole) was higher in intraoperative studies compared to that in cadaveric studies (64.3% vs 49.4%). The EBSLN coursed medial to the superior thyroid artery in 70.98% (95% CI 55.14–84.68) of all cases.
Conclusion
The use of intraoperative nerve monitoring improves EBSLN identification rates. In light of the highly variable anatomical patterns displayed by the EBSLN, thorough pre-operative knowledge of its anatomy can be crucial in minimizing incidences of its iatrogenic injury.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Standring S (2008) Gray’s anatomy, anatomical basis of clinical practice, 40th edn, Chapter 56. Churchill Livingstone, London, pp 997–998
Aygün N, Uludağ M, İşgör A (2017) Contribution of intraoperative neuromonitoring to the identification of the external branch of superior laryngeal nerve. Turk J Surg 33(3):169–174
Gavid M, Dubois MD, Larivé E, Prades JM (2017) Superior laryngeal nerve in thyroid surgery: anatomical identification and monitoring. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274(9):3519–3526
Sinnatamby CS (2006) Last’s anatomy, regional and applied, 12th edn. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh Chapter 13: Pg 604
Aina EN, Hisham AN (2001) External laryngeal nerve in thyroid surgery: is the nerve stimulator necessary? Eur J Surg 167(9):662–665
Athvale PK, Bokare BD, Ekhar VR (2013) Identification and preservation of external branch of superior laryngeal nerve in thyroidectomy. Int J Phonosurg Laryngol 3(2):39–41
AbuRahma AF, Choueiri MA (2000) Cranial and cervical nerve injuries after repeat carotid endarterectomy. J Vasc Surg 32(4):649–654
Furlan J, De Magalhaes R, de Aguiar E, Shiroma S (2002) Localization of the superior laryngeal nerve during carotid endarterectomy. Surg Radiol Anat 24(3–4):190–193
Barczyński M, Konturek A, Stopa M, Honowska A, Nowak W (2012) Randomized controlled trial of visualization versus neuromonitoring of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve during thyroidectomy. World J Surg 36(6):1340–1347
Marchese-Ragona R, Restivo DA, Mylonakis I, Ottaviano G, Martini A, Sataloff RT, Staffieri (2013) The superior laryngeal nerve injury of a famous soprano, Amelita Galli-Curci. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 33(1):67
Darr EA, Tufano RP, Ozdemir S, Kamani D, Hurwitz S, Randolph G (2014) Superior laryngeal nerve quantitative intraoperative monitoring is possible in all thyroid surgeries. Laryngoscope 124(4):1035–1041
Cha YH, Moon SY, Jehoon O, Tansatit T, Yang HM (2017) Anatomy of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve in Asian population. Sci Rep 7(1):14952
Bellantone R, Boscherini M, Lombardi CP, Bossola M, Rubino F, De Crea C, Alesina P, Traini E, Cozza T, D'alatri L (2001) Is the identification of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve mandatory in thyroid operation? Results of a prospective randomized study. Surgery 130(6):1055–1059
Chintamani (2017) A tale of two nerves in thyroid surgery. Indian J Surg 79(5):375–377
Gurleyik E, Gurleyik G (2017) Intraoperative monitoring of external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve: functional identification, motor integrity, and its role on vocal cord function. J Investig Surg 22:1–6
Dedivitis RA, Guimarães AV (2005) Identification of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve during minimally invasive video-assisted thyroidectomy. Rev Bras Otorrinolaringol 71(3):326–328
Dackiw AP, Rotstein LE, Clark OH (2002) Computer-assisted evoked electromyography with stimulating surgical instruments for recurrent/external laryngeal nerve identification and preservation in thyroid and parathyroid operation. Surgery 132(6):1100–1108
Cernea CR, Ferraz AR, Furlani J, Monteiro S, Nishio S, Hojaij FC, Dutra A Jr, Marques LA, Pontes PA, Bevilacqua RG (1992) Identification of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve during thyroidectomy. Am J Surg 164(6):634–639
Cernea CR, Ferraz AR, Nishio S, Dutra A Jr, Hojaij FC, Dos Santos LR (1992) Surgical anatomy of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. Head Neck 14(5):380–383
Friedman M, LoSavio P, Ibrahim H (2002) Superior laryngeal nerve identification and preservation in thyroidectomy. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 128(3):296–303
Friedman M, Wilson MN, Ibrahim H (2009) Superior laryngeal nerve identification and preservation in thyroidectomy. Oper Tech Otolayngol Head Neck Surg 20(2):145–151
Pagedar NA, Freeman JL (2009) Identification of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve during thyroidectomy. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 135(4):360–362
Whitfield P, Morton RP, Al-Ali S (2010) Surgical anatomy of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. ANZ J Surg 80(11):813–816
Uludag M, Aygun N, Kartal K, Citgez B, Besler E, Yetkin G, Kaya C, Ozsahin H, Mihmanli M, Isgor A (2017) Contribution of intraoperative neural monitoring to preservation of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve: a randomized prospective clinical trial. Langenbeck's Arch Surg 402(6):965–976
Dionigi G, Boni L, Rovera F, Bacuzzi A, Dionigi R (2008) Neuromonitoring and video-assisted thyroidectomy: a prospective, randomized case-control evaluation. Surg Endosc 23(5):996–1003
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med 151(4):264–269
Henry BM, Tomaszewski KA, Ramakrishnan PK, Roy J, Vikse J, Loukas M, Tubbs RS, Walocha JA (2017) Development of the anatomical quality assessment (AQUA) tool for the quality assessment of anatomical studies included in meta-analyses and systematic reviews. Clin Anat 30(1):6–13
Henry BM, Tomaszewski KA, Walocha JA (2016) Methods of evidence-based anatomy: a guide to conducting systematic reviews and meta-analysis of anatomical studies. Ann Anat 205:16–21
Higgins JP, Green S (2011) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. The Cochrane Collaboration, Chapter 9:277–278
Aina EN, Hisham AN (2001) External laryngeal nerve in thyroid surgery: recognition and surgical implications. ANZ J Surg 71(4):212–214
Aleksova L, Ali MM, Chakarov DI, Yozgyur ZM (2018) Identification of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve during thyroid surgery. Folia Med 60(1):154–157
Cernea CR, Nishio S, Hojaij FC (1995) Identification of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve (EBSLN) in large goiters. Am J Otolaryngol 16(5):307–311
Chuang FJ, Chen JY, Shyu JF, Su CH, Shyr YM, Wu CW, Lui WY, Lee CS, Chen TH (2010) Surgical anatomy of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve in Chinese adults and its clinical applications. Head Neck 32(1):53–57
Dionigi G, Kim HY, Randolph GW, Wu CW, Sun H, Liu X, Barczynski M, Chiang FY (2016) Prospective validation study of Cernea classification for predicting EMG alterations of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. Surg Today 46(7):785–791
Ekhar VR, Ramkumar V, Shelkar RN, Sarode AV (2017) Identification of external branch of superior laryngeal nerve during thyroid surgery: a prospective study. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg 4(1):228–232
Estrela F, Leão HZ, Jotz GP (2011) Anatomic relation between the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve and the thyroid gland. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 77(2):249–258
Glover AR, Norlén O, Gundara JS, Morris M, Sidhu SB (2015) Use of the nerve integrity monitor during thyroid surgery aids identification of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. Ann Surg Oncol 22(6):1768–1773
Hodnett BL, Schmitt NC, Clayburgh DR, Burkowsky A, Balzer J, Thirumala PD, Duvvuri U (2015) Superior laryngeal nerve monitoring using laryngeal surface electrodes and intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring during thyroidectomy. Clin Anat 28(4):460–466
Hurtado-Lopez LM, Zaldivar-Ramírez FR (2002) Risk of injury to the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve in thyroidectomy. Laryngoscope 112(4):626–629
Hurtado-Lopez LM, Pacheco-Alvarez MI, Montes-Castillo MD, Zaldivar-Ramirez FR (2005) Importance of the intraoperative identification of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve during thyroidectomy: electromyographic evaluation. Thyroid 15(5):449–454
Hurtado-López LM, Díaz-Hernández PI, Basurto-Kuba E, Zaldívar-Ramírez FR, Pulido-Cejudo A (2016) Efficacy of intraoperative neuro-monitoring to localize the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. Thyroid 26(1):174–178
Hwang SB, Lee HY, Kim WY, Woo SU, Lee JB, Bae JW, Kim HY (2013) The anatomy of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve in Koreans. Asian J Surg 36(1):13–19
Inabnet WB, Murry T, Dhiman S, Aviv J, Lifante JC (2009) Neuromonitoring of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve during minimally invasive thyroid surgery under local anesthesia: a prospective study of 10 patients. Laryngoscope 119(3):597–601
Jonas J, Bähr R (2000) Neuromonitoring of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve during thyroid surgery. Am J Surg 179(3):234–236
Joshi RR, Rijal AS, Shrestha KK, Dhungana A, Maharjan S (2017) Identification and preservation of external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve during thyroid surgeries at NMCTH. J Coll Med Sci-Nepal 13(3):306–310
Kandil E, Mohamed SE, Deniwar A, Mohamed H, Friedlander P, Aslam R, Saeed A, Musa I, Randolph G (2015) Electrophysiologic identification and monitoring of the external branch of superior laryngeal nerve during thyroidectomy. Laryngoscope 125(8):1996–2000
Kierner AC, Aigner M, Burian M (1998) The external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve: its topographical anatomy as related to surgery of the neck. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 124(3):301–303
Lee J, Fraser S, Glover A, Sidhu S (2017) Prospective evaluation of the utility of routine neuromonitoring for an established thyroid surgical practice. ANZ J Surg 87(10):E138–E142
Loch-Wilkinson TJ, Stalberg PL, Sidhu SB, Sywak MS, Wilkinson JF, Delbridge LW (2007) Nerve stimulation in thyroid surgery: is it really useful? ANZ J Surg 77(5):377–380
Magoma G, Saidi H, Kaisha W (2012) Relation of the external laryngeal nerve to superior thyroid artery in an African population. Anat J Afr 1(1):28–30
Masuoka H, Miyauchi A, Higashiyama T, Yabuta T, Fukushima M, Ito Y, Kihara M, Kobayashi K, Yamada O, Nakayama A, Miya A (2015) Prospective randomized study on injury of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve during thyroidectomy comparing intraoperative nerve monitoring and a conventional technique. Head Neck 37(10):1456–1460
Menon RR, Murali S, Nair CG, Babu MJ, Jacob P (2017) Correlation between the Cernea classification of external branch of superior laryngeal nerve in relation to the ultrasound-based volume of thyroid gland. Indian J Endocrinol Metab 21(6):845–847
Mustafa A, Bokare B (2016) Surgical anatomy of external branch of superior laryngeal nerve (EBSLN) in thyroid surgery. Int J Biomed Adv Res 7(10):493–496
Naidoo D, Boon JM, Mieny CJ, Becker PJ, van Schoor AN (2007) Relation of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve to the superior pole of the thyroid gland: an anatomical study. Clin Anat 20(5):516–520
Ozlugedik S, Acar HI, Apaydin N, Tekdemir I, Elhan A, Comert A (2007) Surgical anatomy of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. Clin Anat 20(4):387–391
Page C, Laude M, Legars D, Foulon P, Strunski V (2004) The external laryngeal nerve: surgical and anatomic considerations. Report of 50 total thyroidectomies. Surg Radiol Anat 26(3):182–185
Patnaik U, Nilakantan A, Shrivastava T (2012) Anatomical variations of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve in relation to the inferior constrictor muscle: cadaveric dissection study. J Laryngol Otol 126(9):907–912
Patnaik U, Nilakantan A, Shrivastava T (2013) Identification of external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve in thyroid surgery: is it always possible. Thyroid 2(2)
Poyraz M, Calguner E (2001) Bilateral investigation of the anatomical relationships of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve and superior thyroid artery, and also the recurrent laryngeal nerve and inferior thyroid artery. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn 78(2–3):65–74
Pradeep PV, Jayashree B, Harshita SS (2012) A closer look at laryngeal nerves during thyroid surgery: a descriptive study of 584 nerves. Anat Res Int 2012:1–6
Rajesh PS, Kamalakshy J, Saravanan T (2017) A descriptive study on the surgical anatomy of external laryngeal nerve in patients undergoing thyroidectomies at a tertiary care center in South India. Int Surg J 4(2):519–524
Ravikumar K, Sadacharan D, Muthukumar S, Mohanpriya G, Hussain Z, Suresh RV (2016) EBSLN and factors influencing its identification and its safety in patients undergoing total thyroidectomy: a study of 456 cases. World J Surg 40(3):545–550
Seven H, Alkan Z, Cakir BO, Sam B, Uslu B, Turgut S (2003) The topographical anatomy of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve and its importance in thyroid surgery: a cadaver study. Kulak Burun Bogaz Ihtis Derg 11(6):161–165
Timmermann W, Hamelmann WH, Meyer T, Timm S, Schramm C, Hoppe F, Thiede A (2002) Identification and surgical anatomy of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. Zentralbl Chir 127(5):425–428
Uludag M, Aygun N, Kartal K, Besler E, Isgor A (2017) Is intraoperative neural monitoring necessary for exploration of the superior laryngeal nerve? Surgery 161(4):1129–1138
Wang K, Cai H, Kong D, Cui Q, Zhang D, Wu G (2017) The identification, preservation and classification of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve in thyroidectomy. World J Surg 41(10):2521–2529
Angelos P (2015) Identification of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve: an additional argument for neuromonitoring? Ann Surg Oncol 22(6):1751–1752
Hermann M, Alk G, Roka R, Glaser K, Freissmuth M (2002) Laryngeal recurrent nerve injury in surgery for benign thyroid diseases: effect of nerve dissection and impact of individual surgeon in more than 27,000 nerves at risk. Ann Surg 235(2):261–268
Barczyński M, Randolph GW, Cernea CR, Dralle H, Dionigi G, Alesina PF, Mihai R, Finck C, Lombardi D, Hartl DM, Miyauchi A (2013) External branch of the superior laryngeal nerve monitoring during thyroid and parathyroid surgery: international neural monitoring study group standards guideline statement. Laryngoscope 123:S1–S4
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
PROSPERO registration number: CRD42018098729
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheruiyot, I., Kipkorir, V., Henry, B.M. et al. Surgical anatomy of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Langenbecks Arch Surg 403, 811–823 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-018-1723-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-018-1723-9