Abstract
Purpose
This study was designed to compare the long-term outcome of patients treated with conservative versus surgical treatment for acute sigmoid diverticulitis (SD).
Patients and methods
Consecutive admissions of all patients with acute SD were prospectively recruited from January 2004 to June 2007. In June 2008, all patients were contacted using a standardized questionnaire. Outcomes were compared based on initial therapy (conservative vs. surgical). Furthermore, multiple logistic regression was used to identify risk factors for recurrence of SD.
Results
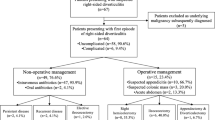
A total of 210 patients were included in the study. One hundred fifty-three patients were reached for follow-up: 70 (45.8%) presented with their first episode, and 83 (54.2%) had a prior history of SD. The median follow-up was 32 months (range 12–52). Thirteen (32.5%) of 40 conservatively treated patients and four (3.5%) of 113 surgically treated patients had a recurrence of SD (p < 0.001) during follow-up. One patient (2.5%) required emergency surgery after conservative treatment due to free perforation (p = 0.567). Treatment groups did not differ in age, gender, and inflammatory parameters, but conservatively treated patients had a significantly higher comorbidity (>2 disorders; p = 0.038) and less frequently a severe SD (p = 0.022) at the index admission. Recurrent episode of SD, covered perforated SD, and conservative treatment were identified as risk factors for recurrence of SD on multiple logistic regression.
Conclusions
Surgical treatment of acute SD is more effective in preventing an eventual relapse of SD than conservative treatment, particularly in patients with recurrent and severe diverticulitis. The necessity for an emergency operation during follow-up is low and did not differ between the two treatment groups. The initial clinical presentation of SD is not a strong predictor of recurrence.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jun S, Stollmann N (2002) Epidemiology of diverticular disease. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 16:529–542
Parks TG (1975) Natural history of diverticular disease of the colon. Clin Gastroenterol 4:53–69
Etzioni DA, Mack TM, Beart RW Jr, Kaiser AM (2009) Diverticulitis in the United States: 1998–2005: changing patterns of disease and treatment. Ann Surg 249(2):210–217
Roberts P, Abel M, Rosen L et al (1995) Practice parameters for sigmoid diverticulitis. The Standards Task Force American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons. Dis Colon Rectum 38:125–132
Lee YS (1986) Diverticular disease of the large bowel in Singapore. An autopsy survey. Dis Colon Rectum 29:330–335
Jacobs M, Verdeja JC, Goldstein HS (1991) Minimally invasive colon resection (laparoscopic colectomy). Surg Laparosc Endosc 1:144–150
Janes S, Meagher A, Frizelle FA (2005) Elective surgery after acute diverticulitis. Br J Surg 92:133–142
Rafferty J, Shellito P, Hyman NH, Buie WD (2006) Practice parameters for sigmoid diverticulitis. Dis Colon Rectum 49:939–944
Chapman JRM, Dozois EJM, Wolff BGM, Gullerud REB, Larson DRM (2006) Diverticulitis: a progressive disease? Do multiple recurrences predict less favorable outcomes? Ann Surg 243:876–883
Holmer C, Lehmann KS, Engelmann S, Frericks B, Loddenkemper C, Buhr HJ, Ritz JP (2010) Microscopic findings in sigmoid diverticulitis—changes after conservative therapy. J Gastrointest Surg 14(5):812–817
Hansen O, Stock W (1999) Prophylaktische Operation bei der Divertikelkrankheit des Kolons—Stufenkonzept durch exakte Stadieneinteilung. Langenbecks Arch Chir Suppl II: 1257
Reissfelder C, Buhr HJ, Ritz JP (2006) Can laparoscopically assisted sigmoid resection provide uncomplicated management even in cases of complicated diverticulitis? Surg Endosc 20(7):1055–1059
Ritz JP, Lehmann KS, Frericks B, Stroux A, Buhr HJ, Holmer C (2010) Outcome of patients with acute sigmoid diverticulitis—multivariate analysis of risk factors for free perforation. Surgery 149:606–613
Reissfelder C, Buhr HJ, Ritz JP (2006) What is the optimal time of surgical intervention after an acute attack of sigmoid diverticulitis: early or late elective laparoscopic resection. Dis Colon Rectum 49:1842–1848
Rothenberger DA, Wiltz O (1993) Surgery for complicated diverticulitis. Surg Clin North Am 73:975–992
Antolovic D, Reissfelder C, Koch M, Mertens B, Schmidt J, Büchler MW, Weitz J (2009) Surgical treatment of sigmoid diverticulitis—analysis of predictive risk factors for postoperative infections, surgical complications, and mortality. Int J Colorectal Dis 24:577–584
Al-Sahaf O, Al-Azawi D, Fauzi MZ et al (2008) Early discharge policy of patients with acute colonic diverticulitis following initial CT scan. Int J Colorectal Dis 23:979–984
Favuzza J, Friel JC, Kelly JJ, Perugini RC, Counihan TC (2009) Benefits of laparoscopic peritoneal lavage for complicated sigmoid diverticulitis. Int J Colorectal Dis 24:797–801
Schiedeck TH, Schwandner O, Bruch HP (1998) Laparoscopic sigmoid resection in diverticulitis. Chirurg 69:846–853
Kohler L, Sauerland S, Neugebauer E (1999) Diagnosis and treatment of diverticular disease: results of a consensus development conference. The Scientific Committee of the European Association for Endoscopic Surgery. Surg Endosc 13:430–436
Schwandner O, Farke S, Fischer F, Eckmann C, Schiedeck TH, Bruch HP (2004) Laparoscopic colectomy for recurrent and complicated diverticulitis: a prospective study of 396 patients. Langenbecks Arch Surg 389:97–103
Zdichavsky M, Granderath FA, Blumenstock G, Kramer M, Küper MA, Königsrainer A (2010) Acute laparoscopic intervention for diverticular disease (AIDD): a feasible approach. Langenbecks Arch Surg 395(1):41–48
Wong WD, Wexner SD, Lowry A, Vernava A 3rd, Burnstein M et al (2000) Practice parameters for the treatment of sigmoid diverticulitis—supporting documentation. The Standards Task Force. The American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons. Dis Colon Rectum 43:290–297
Germer CT, Buhr HJ (2002) Sigmoid diverticulitis. Surgical indications and timing. Chirurg 73:681–689
Ritz JP, Lehmann KS, Loddenkemper C, Frericks B, Buhr HJ, Holmer C (2010) Preoperative CT staging in sigmoid diverticulitis—does it correlate with intraoperative and histological findings? Langenbecks Arch Surg 395(8):1009–1015
Broderick-Villa G, Burchette RJ, Collins JC, Abbas MA, Haigh PI (2005) Hospitalization for acute diverticulitis does not mandate routine elective colectomy. Arch Surg 140(6):576–581
Guzzo J, Hyman N (2004) Diverticulitis in young patients: is an aggressive approach really justified? Dis Colon Rectum 47:1187–1191
Ritz JP, Lehmann KS, Stroux A, Buhr HJ, Holmer C (2011) Sigmoid diverticulitis in young patients—a more aggressive disease than in older patients? J Gastrointest Surg 15(4):667–674
Kotzampassakis N, Pittet O, Schmidt S, Denys A, Demartines N, Calmes JM (2010) Presentation and treatment outcome of diverticulitis in younger adults: a different disease than in older patients? Dis Colon Rectum 53(3):333–338
Peppas G, Bliziotis IA, Oikonomaki D, Falagas ME (2007) Outcomes after medical and surgical treatment of diverticulitis: a systematic review of the available evidence. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 22(9):1360–1368
Greenberg AS, Gal R, Coben RM, Cohen S, Dimarino AJ Jr (2005) A retrospective analysis of medical or surgical therapy in young patients with diverticulitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 21:1225–1229
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holmer, C., Lehmann, K.S., Engelmann, S. et al. Long-term outcome after conservative and surgical treatment of acute sigmoid diverticulitis. Langenbecks Arch Surg 396, 825–832 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-011-0815-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-011-0815-6