Abstract
Introduction
Recent advances support the concept of autoimmune pancreatitis as a unique systemic disease because occasional extrapancreatic lesions such as sclerosing cholangitis, sclerosing sialoadenitis, and retroperitoneal fibrosis show similar pathological features with fibrosis and abundant infiltration of IgG4-positive plasma cells, and are steroid responsive. Based on these findings, several diagnostic criteria have been proposed.
Materials and methods
Although AIP is accepted worldwide as a unique clinical entity, pathogeneic mechanism still remains unclear. To clarify it, genetic background, humoral immunity, candidates of target antigens including self-antigens and molecular mimicry from microbes, cellular immunity including regulatory T cells, complement system, and experimental models are reviewed.
Results
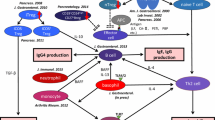
Based on these findings, we have proposed a hypothesis for the pathogenesis of AIP in the biphasic mechanism of “induction” and “progression.” In the early stage, initial response to self-antigens (LF, CA-II, CA-IV, PSTI, or α-fodrin) or molecular mimicry (Helicobacter pylori) is induced by decreased naive regulatory T cells (Tregs), and Th1 cells release proinflammatory cytokines (IFN-γ, IL-1b, IL-2, and TNF-α).
Discussion
In the chronic stage, progression is supported by increased memory Tregs and Th2 immune responses. The classical pathway of complement system may be activated by IgG1 immune complex.
Conclusion
As Tregs seem to take important roles in progression as well as induction of the disease, further studies are necessary to clarify the pathogenesis.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Anti-CA-II:
-
Carbonic anhydrase II
- AIP:
-
Autoimmune pancreatitis
- LF:
-
Lactoferrin
- AMA:
-
Anti-mitochondrial antibody
- ANA:
-
Antinuclear antibody
- CA-II:
-
Carbonic anhydrase II
- ERCP:
-
Endoscopic retrograde cholangio-pancreatography
- IFN-γ:
-
Interferon-γ
- IL-4:
-
Interleukin-4
- LF:
-
Lactoferrin
- PBC:
-
Primary biliary cirrhosis
- PSC:
-
Primary sclerosing cholangitis
- RF:
-
Rheumatoid factor
- SjS:
-
Sjögren’s syndrome
References
Sarles H, Sarles JC, Muratore R et al (1961) Chronic inflammatory sclerosis of the pancreas—an autoimmune pancreatic disease? Am J Dig Dis 6:688–698
Toki F, Kozu T, Oi I (1992) An unusual type of chronic pancreatitis showing diffuse irregular narrowing of the entire main pancreatic duct on ERC—a report of four cases. Endoscopy 24:640
Yoshida K, Toki F, Takeuchi T et al (1995) Chronic pancreatitis caused by autoimmune abnormality. Proposal of concept of autoimmune pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci 40:1561–1568
Okazaki K, Uchida K, Chiba T (2001) Recent concept of autoimmune-related pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol 36:293–302
Okazaki K (2006) In: Pour Parviz M (ed) Autoimmune pancreatitis—recent concept. Target organ toxicology series, toxicology of the pancreas. Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton, pp 459–473
Kawaguchi K, Koike M, Tsuruta K et al (1991) Lymphoplasmacytic sclerosing pancreatitis with cholangitis: a variant primary sclerosing cholangitis extensively involving pancreas. Human Pahtol 22:387–395
Pickartz T, Mayerle J, Lerch MM (2007) Autoimmune pancreatitis. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol 4:314–23
Members of the Criteria Committee for Autoimmune Pancreatitis of the Japan Pancreas Society (2002) Diagnostic criteria for autoimmune pancreatitis by the Japan Pancreas Society. J Jpn Pancreas Soc 17:587
Okazaki K, Kawa S, Kamisawa T, Naruse S, Tanaka S, Nishimori I et al (2006) Clinical diagnostic criteria of autoimmune pancreatitis: revised proposal. J Gastroenterol 41:626–31
Kim KP, Kim MH, Kim JC, Lee SS, Seo DW, Lee SK (2006) Diagnostic criteria for autoimmune chronic pancreatitis revisited. World J Gastroenterol 12:2487–96
Kim MH, Lee TY (2007) Diagnostic criteria for autoimmune pancreatitis: a proposal of revised Kim criteria. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 22:A104
Otsuki M, Chung JB, Okazaki K, Kim MH, Kamisawa T, Kawa S et al (2008) Asian diagnostic criteria for autoimmune pancreatitis: consensus of the Japan–Korea Symposium on Autoimmune Pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol 43:403–8
Chari ST, Smyrk TC, Levy MJ et al (2006) Diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis: the Mayo Clinic experience. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 4:1010–6
Chari ST, Takahashi N, Levy MJ et al (2009) A diagnostic strategy to distinguish autoimmune pancreatitis from pancreatic cancer. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 7:1097–1103
Pearson RK, Longnecker DS, Chari ST et al (2003) Controversies in clinical pancreatology: autoimmune pancreatitis: does it exist? Pancreas 27:1–13
Frulloni L, Scattolini C, Falconi M et al (2009) Autoimmune pancreatitis: differences between the focal and diffuse forms in 87 patients. Am J Gastroenterol 104:2288–94
Kawa S, Ota M, Yoshizawa K, Horiuchi A, Hamano H, Ochi Y et al (2002) HLA DRB10405-DQB10401 haplotype is associated with autoimmune pancreatitis in the Japanese population. Gastroenterology 122:1264–69
Park do H, Kim MH, Oh HB, Kwon OJ, Choi YJ, Lee SS et al (2008) Substitution of aspartic acid at position 57 of the DQbeta1 affects relapse of autoimmune pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 134:440–6
Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A, Unno H, Furuya N, Akamatsu T et al (2001) High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med 344:732–738
Uchida K, Okazaki K, Konishi Y et al (2000) Clinical analysis of autoimmune-related pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol 95:2788–2794
Okazaki K, Uchida K, Ohana M et al (2000) Autoimmune-related pancreatitis is associated with autoantibodies and Th1/Th2-type cellular immune response. Gastroenterology 118:573–581
Asada M, Nishio A, Uchida K et al (2006) Identification of a novel autoantibody against pancreatic secretory trypsin inhibitor in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreas 33:20–6
Horiuchi A, Kawa S, Hamano H, Hayashi Y, Kiyosawa K (2002) Does a lack of reactivity to alpha-fodrin indicate the existence of primary autoimmune pancreatitis? Am J Gastroenterol 97:1275–7
Muraki T, Hamano H, Ochi Y, Komatsu K, Komiyama Y, Arakura N et al (2006) Autoimmune pancreatitis and complement activation system. Pancreas 32:16–21
Tanaka S, Kobayashi T, Nakanishi K et al (2000) Corticosteroid-responsive diabetes mellitus associated with autoimmune pancreatitis. Lancet 356:910–911
Erkelens GW, Vleggaar FP, Lesterhuis W et al (1999) Sclerosing pancreato-cholangitis responsive to steroid therapy. Lancet 354:43–44
Chutaputti A, Burrell MI, Boyer JL (1995) Pseudotumor of the pancreas associated with retroperitoneal fibrosis: a dramatic response to corticosteroid therapy. Am J Gastroenterol 90:1155–1158
Petter LM, Martin JK Jr, Menke DM (1998) Localized lymphoplasmacellular pancreatitis forming a pancreatic inflammatory pseudotumor. Mayo Clin Proc 73:447–450
Uchida K, Satoi S, Miyoshi H et al (2007) Inflammatory pseudotumors of the pancreas and liver with infiltration of IgG4-positive plasma cells. Intern Med 46:1409–12
Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y et al (2003) A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. J Gastroenterol 38:982–984
Fukui T, Okazaki K, Yoshizawa H et al (2005) A case of autoimmune pancreatitis associated with sclerosing cholangitis, retroperitoneal fibrosis and Sjogren’s syndrome. Pancreatology 5:86–91
Kamisawa T, Funata N, Hayashi Y, Eishi Y, Koike M, Tsuruta K et al (2003) A new clinicopathological entity of IgG4-related autoimmune disease. J Gastroenterol 38:982–4
Yamamoto M, Takahashi H, Ohara M, Suzuki C, Naishiro Y, Yamamoto H, Shinomura Y, Imai K (2006) A new conceptualization for Mikulicz's disease as an IgG4-related plasmacytic disease. Mod Rheumatol 16:335–340
Masaki Y, Dong L, Kurose N, Kitagawa K, Morikawa Y, Yamamoto M, Takahashi H, Shinomura Y, Imai K, Saeki T, Azumi A, Nakada S, Sugiyama E, Matsui S, Origuchi T, Nishiyama S, Nishimori I, Nojima T, Yamada K, Kawano M, Zen Y, Kaneko M, Miyazaki K, Tsubota K, Eguchi K, Tomoda K, Sawaki T, Kawanami T, Tanaka M, Fukushima T, Sugai S, Umehara H (2009) Proposal for a new clinical entity, IgG4-positive multiorgan lymphoproliferative syndrome: analysis of 64 cases of IgG4-related disorders. Ann Rheum Dis 68:1310–1315
Notohara K, Burgart LJ, Yadav D, Chari S, Smyrk TC (2003) Idiopathic chronic pancreatitis with periductal lymphoplasmacytic infiltration: clinicopathologic features of 35 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 27:1119–27
Zamboni G, Luttges J, Capelli P, Frulloni L, Cavallini G, Pederzoli P et al (2004) Histopathological features of diagnostic and clinical relevance in autoimmune pancreatitis: a study on 53 resection specimens and 9 biopsy specimens. Virchows Arch 445:552–63
Okazaki K, Kawa S, Kamisawa T, Ito T, Inui K, Irie H et al (2009) Japanese clinical guidelines for autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreas 38:849–66
Inoue H, Miyatani H, Sawada Y et al (2006) A case of pancreas cancer with autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreas 33:208–9
Fukui T, Mitsuyama T, Takaoka M et al (2008) Pancreatic cancer associated with autoimmune pancreatitis in remission. Intern Med 47:151–5
Kochi Y, Yamada R, Suzuki A et al (2005) A functional variant in FCRL3, encoding Fc receptor-like 3, is associated with rheumatoid arthritis and several autoimmunities. Nat Genet 37:478–485
Umemura T, Ota M, Hamano H et al (2006) Genetic association of Fc receptor-like 3 polymorphisms with autoimmune pancreatitis in Japanese patients. Gut 55:1367–1368
Umemura T, Katsuyama Y, Hamano H et al (2009) Association analysis of toll-like receptor 4 polymorphisms with autoimmune pancreatitis. Hum Immunol 7:742–6
Chang MC, Chang YT, Tien YW, Liang PC, Jan IS, Wei SC et al (2007) T-cell regulatory gene CTLA-4 polymorphism/haplotype association with autoimmune pancreatitis. Clin Chem 53:1700–5
Umemura T, Ota M, Hamano H, Katsuyama Y, Muraki T, Arakura N, Kawa S, Kiyosawa K (2008) Association of autoimmune pancreatitis with cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 gene polymorphisms in Japanese patients. Am J Gastroenterol 103:588–94
Ueda H, Howson JM, Esposito L et al (2003) Association of the T-cell regulatory gene CTLA4 with susceptibility to autoimmune disease. Nature 423:506–11
Roitt IM (1997) Antibodies. In: Roitt IM (ed) Roitt’s essential immunology, 9th edn. Blackwell Science, London, pp 43–62
Taguchi M, Kihara Y, Nagashio Y et al (2009) Decreased production of immunoglobulin M and A in autoimmune pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol 44:1133–9
Robinson DS, Larché M, Durham SR (2004) Tregs and allergic disease. J Clin Invest 114:1389–97
Kolfschoten NM, Schuurman J, Losen M et al (2007) Anti-inflammatory activity of human IgG4 antibodies by dynamic Fab arm exchange. Science 317:1554–7
Kawa S, Kitahara K, Hamano H et al (2008) A novel immunoglobulin-immunoglobulin interaction in autoimmunity. PLoS ONE 3:e1637
Cornell LD, Chicano SL, Deshpande V et al (2007) Pseudotumors due to IgG4 immune-complex tubulointerstitial nephritis associated with autoimmune pancreatocentric disease. Am J Surg Pathol 31:1586–97
Uchiyama-Tanaka Y, Mori Y, Kimura T et al (2004) Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis associated with autoimmune-related pancreatitis. Am J Kidney Dis 43:e18–25
Kawa S, Kitahara K, Hamano H, Ozaki Y, Arakura N, Yoshizawa K et al (2008) A novel immunoglobulin-immunoglobulin interaction in autoimmunity. PLoS ONE 3(2):e1637
Nishi H, Tojo A, Onozato ML, Jimbo R, Nangaku M, Uozaki H, Hirano K et al (2007) Anti-carbonic anhydrase II antibody in autoimmune pancreatitis and tubulointerstitial nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 22:1273–5
Aparisi L, Farre A, Gomez-Cambronero L, Martinez J, De Las Heras G, Corts J et al (2005) Antibodies to carbonic anhydrase and IgG4 levels in idiopathic chronic pancreatitis: relevance for diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut 54:703–9
Nishimori I, Miyaji E, Morimoto K, Nagao K, Kamada M, Onishi S (2005) Serum antibodies to carbonic anhydrase IV in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut 54:274–81
Endo T, Takizawa S, Tanaka S, Takahashi M, Fujii H, Kamisawa T, Kobayashi T (2009) Amylase alpha-2A autoantibodies: novel marker of autoimmune pancreatitis and fulminant type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 58:732–7
Takizawa S, Endo T, Wanjia X, Tanaka S, Takahashi M, Kobayashi T (2009) HSP 10 is a new autoantigen in both autoimmune pancreatitis and fulminant type 1 diabetes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 386:192–6
Frulloni L, Lunardi C, Simone R et al (2009) Identification of a novel antibody associated with autoimmune pancreatitis. N Engl J Med 361:2135–42
Nishimori I, Bratanova T, Toshkov I, Caffrey T, Mogaki M, Shibata Y, Holingworth MA (1995) Induction of experimental autoimmune sialoadenitis by immunization of PL/J mice with carbonic anhydrase II. J Immunol 154:4865–73
Ueno Y, Ishi M, Takahashi S, Igarashi T, Toyoda T, LaRusso FN (1998) Different susceptibility of mice to immune-mediated cholangitis induced by immunization with carbonic anhydrase II. Lab Invest 78:629–37
Kountouras J, Zavos C, Gavalas E et al (2007) Challenge in the pathogenesis of autoimmune pancreatitis: potential role of Helicobacter pylori infection via molecular mimicry. Gastroenterology 133:368–369
Kountouras J, Zavos C, Chatzopoulos D (2005) A concept on the role of Helicobacter pylori infection in autoimmune pancreatitis. J Cell Mol Med 9:196–207
Guarneri F, Guarneri C, Benvenga S (3) Helicobacter pylori and autoimmune pancreatitis: role of carbonic anhydrase via molecular mimicry? J Cell Mol Med 9(3):741–4
Okazaki K (2005) Autoimmune pancreatitis: etiology, pathogenesis, clinical findings and treatment. The Japanese experience. JOP 6(1 Suppl):89–96
McGeachy MJ, Cua DJ (2007) The link between IL-23 and Th17 cell-mediated immune pathologies. Semin Immunol 19:372–6
Oukka M (2007) Interplay between pathogenic Th17 and regulatory T cells. Ann Rheum Dis 66(Suppl 3):iii87–90
Yamamoto M, Harada S, Ohara M et al (2005) Clinical and pathological differences between Mikulicz’s disease and Sjogren’s syndrome. Rheumatology 44:227–34
Zen Y, Fujii T, Harada K et al (2007) Th2 and regulatory immune reactions are increased in immunoglobin G4-related sclerosing pancreatitis and cholangitis. Hepatology 45:1538–46
Uchida K, Okazaki K, Nishi T et al (2002) Experimental immune-mediated pancreatitis in neonatally thymectomized mice immunized with carbonic anhydrase II and lactoferrin. Lab Invest 82:411–24
Ajjan RA, McIntosh RS, Waterman EA et al (1998) Analysis of the T-cell receptor Valpha repertoire and cytokine gene expression in Sjogren’s syndrome. Br J Rheumatol 37:179–185
Dienes HP, Lohse AW, Gerken G et al (1997) Bile duct epithelia as target cells in primary biliary cirrhosis and primary sclerosing cholangitis. Virchows Arch 431:119–124
Valencia X, Lipsky PE (2007) CD4+ CD25+ FoxP3+ regulatory T cells in autoimmune diseases. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol 3:619–26
Gottenberg JE, Lavie F, Abbed K et al (2005) CD4 CD25high regulatory T cells are not impaired in patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome. J Autoimmun 24:235–42
Miyoshi H, Uchida K, Taniguchi T et al (2008) Circulating Naive and CD4+ CD25 high regulatory T cells in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreas 36:133–140
Stanley JR, Amagai M (2006) Pemphigus, bullous impetigo, and the staphylococcal scalded-skin syndrome. N Engl J Med 355:1800–10
Fujii H, Nakatani K, Arita N et al (2003) Internalization of antibodies by endothelial cells via fibronectin implicating a novel mechanism in lupus nephritis. Kidney Int 64:1662–70
Aalberse RC, Stapel SO, Schuurman J, Rispens T (2009) Immunoglobulin G4: an odd antibody. Clin Exp Allergy 39:469–77
Ruiter B, Knol EF, Van Neerven RJ et al (2007) Maintenance of tolerance to cow’s milk in atopic individuals is characterized by high levels of specific immunoglobulin G4. Clin Exp Allergy 37:1103–10
Hussain R, Poindexter RW, Ottesen EA (1992) Control of allergic reactivity in human filariasis: predominant localization of blocking antibody to the IgG4 subclass. J Immunol 148:2731–7
Yazdanbakhsh M, van den Biggelaar A, Maizels RM (2001) Th2 responses without atopy: immunoregulation in chronic helminth infections and reduced allergic disease. Trends Immunol 22:372–7
Sakaguchi S, Fukuma K, Kuribayashi K, Masuda T (1985) Organ-specific autoimmune diseases in mice by elimination of T cell subset. 1. Evidence for the active participation of T cells in natural self-tolerance; deficit of a T cell subset as a possible cause of autoimmune disease. J Exp Med 161:72–87
Demols A, Moine OL, Desalle F, Quertinmont E, Laethem JLV, Deviere J (2000) CD4+ T cells play an important role in acute experimental pancreatitis in mice. Gastroenterology 118:582–590
Vallance BA, Hewlett BR, Snider DP, Collins SM (1998) T cell-mediated exocrine pancreatic damage in major histocompatibility complex class II-deficient mice. Gastroenterology 115:978–987
Sakaguchi Y, Inaba M, Tsuda M, Quan GK, Omae M, Ando Y et al (2008) The Wistar Bonn Kobori rat, a unique animal model for autoimmune pancreatitis with extrapancreatic exocrinopathy. Clin Exp Immunol 152:1–12
Marth T, Strober W, Kelsall BL (1996) High dose oral tolerance in ovalbumin TCR-transgenic mice: systemic neutralization of IL-12 augments TGF-beta secretion and T cell apoptosis. J Immunol 157:2348–57
Hahm KB, Im YH, Lee C, Park WT, Bang YJ, Grenn JE, Kim SJ (2000) Loss of TGF-β signaling contributes to autoimmune pancreatitis. J Clin Invest 105:1057–1065
Acknowledgments
This study was partly supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research of Ministry of Culture and Science of Japan (20590810) and Grant-in-Aid for “Research for Intractable Disease” Program from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okazaki, K., Uchida, K., Fukui, T. et al. Autoimmune pancreatitis—a new evolving pancreatic disease?. Langenbecks Arch Surg 395, 989–1000 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-010-0714-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-010-0714-2