Abstract
Objective
The objective of this paper is to prove lymph node infestation by Echinococcus multilocularis and provide evidence for systematic lymph node dissection in curative resections for alveolar echinococcosis (AE).
Background
Human AE is a life threatening parasitic condition, usually caused by an intrahepatic infiltrative and destructive growth of the larvae E. multilocularis. WHO guidelines provide radical hepatic resection for curative treatment. However, the current norms do not consider dissection of regional lymph nodes. No report to date has visualized concurrent lymph node infestation.
Methods
Radical excision of infested liver including regional lymph nodes with subsequent histological examination was carried out in a patient suffering from AE. The literature was reviewed and a revised state-of-the-art treatment of AE deduced.
Results
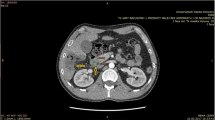
Upon inspection the liver displayed macroscopic features of AE, in contrast to the regional lymph nodes which appeared unsuspicious. Further histological analysis confirmed regional lymph node infestation of E. multilocularis.
Conclusions
This is the first publication on histological evidence of E. multilocularis in regional hepatic lymph nodes, and thus, demonstrating dissemination from the liver. Since AE can spread through lymphatic drainage, even without causing macroscopic conspicuity, resection should not be resumed to the liver tissue only, but rather to consider the routine removal of regional lymph nodes as well. Omission of lymph node dissection can leave behind parasitic tissue and surgical procedures erroneously judged as curative.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kern P, Bardonnet K, Renner E, Auer H, Pawlowski Z, Ammann RW, Vuitton DA, Kern P (2003) European echinococcosis registry: human alveolar echinococcosis, Europe, 1982–2000. Emerg Infect Dis 9:343–349
Urdiales-Viedma M, Martos-Padilla S, Nogales-Fernandez F, Lopez-Yevenes A (1984) Lymph node changes in echinococcosis. Arch Pathol Lab Med 108:528
Reuter S, Seitz HM, Kern P, Junghanss T (2000) Extrahepatic alveolar echinococcosis without liver involvement: a rare manifestation. Infection 28:187–192. doi:10.1007/s150100050079
Uchino J, Sato N (1993) Alveolar echinococcosis of the Liver. Hokkaido University Medical Library Series Vol.30. INSS: 0385-6089. Hokkaido University School of Medicine, Sapporo, Japan
Reuter S, Buck A, Manfras B, Kratzer W, Seitz HM, Darge K, Reske SN, Kern P (2004) Structured treatment interruption in patients with alveolar echinococcosis. Hepatology 39:509–517. doi:10.1002/hep. 20078
Kern P, Wen H, Sato N, Vuitton DA, Gruener B, Shao Y, Delabrousse E, Kratzer W, Bresson-Hadni S (2006) WHO classification of alveolar echinococcosis: principles and application. Parasitol Int 55(Suppl):S283–S287. doi:10.1016/j.parint.2005.11.041
Kadry Z, Renner EC, Bachmann LM, Attigah N, Renner EL, Ammann RW, Clavien PA (2005) Evaluation of treatment and long-term follow-up in patients with hepatic alveolar echinococcosis. Br J Surg 92:1110–1116. doi:10.1002/bjs.4998
Craig P (2003) Echinococcus multilocularis. Curr Opin Infect Dis 16:437–444. doi:10.1097/00001432-200310000-00010
Lethbridge RC (1980) The biology of the oncosphere of cyclophyllidean cestodes. Helminthological Abstr A49:59–72
Uchino J, Sato N, Nakajima Y, Matsushita M, Takahashi M, Une Y (1993) XI. Treatment. In: Uchino J, Sato N (eds) Alveolar Echinococcosis of the Liver. Hokkaido University Medical Library Series, vol. 30. INSS: 0385–6089. Hokkaido University School of Medicine, Sapporo, Japan, pp 137–149
Eckert J, Thompson RC, Mehlhorn H (1983) Proliferation and metastases formation of larval Echinococcus multilocularis. I. Animal model, macroscopical and histological findings. Z Parasitenkd 69:737–748. doi:10.1007/BF00927423
Drolshammer I, Wiesmann E, Eckert J (1973) Human echinococcosis in Switzerland during the years 1956–1969. Schweiz Med Wochenschr 103:1386–1392
Mehlhorn H, Eckert J, Thompson RC (1983) Proliferation and metastases formation of larval Echinococcus multilocularis. II. Ultrastructural investigations. Z Parasitenkd 69:749–763. doi:10.1007/BF00927424
Reuter M, Kreshchenko N (2004) Flatworm asexual multiplication implicates stem cells and regeneration. Can J Zool 82:334–356. doi:10.1139/z03-219
Spiliotis M, Lechner S, Tappe D, Scheller C, Krohne G, Brehm K (2008) Transient transfection of Echinococcus multilocularis primary cells and complete in vitro regeneration of metacestode vesicles. Int J Parasitol 38:1025–1039. doi:10.1016/j.ijpara.2007.11.002
Matsuhisa T (1996) The mechanism of distant metastases of alveolar hydatid disease. Hokkaido Igaku Zasshi 71:369–376
Atkins D, Best D, Briss PA, Eccles M, Falck-Ytter Y, Flottorp S, Guyatt GH, Harbour RT, Haugh MC, Henry D, Hill S, Jaeschke R, Leng G, Liberati A, Magrini N, Mason J, Middleton P, Mrukowicz J, O'Connell D, Oxman AD, Phillips B, Schunemann HJ, Edejer TT, Varonen H, Vist GE, Williams JW Jr, Zaza S (2004) Grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 328:1490–1494. doi:10.1136/bmj.328.7454.1490
WHO/OIE (2001) Manual on echinococcosis in humans and animals: a public health problem of global concern. World Organisation for Animal Health and World Health Organisation, Paris, France
Ammann RW, Eckert J (1996) Cestodes; Echinococcus. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 25:655–689. doi:10.1016/S0889-8553(05) 70268-5
WHO Informal Working Group on Echinococcosis (1996) Guidelines for treatment of cystic and alveolar echinococcosis in humans. Bull World Health Organ 74:231–242
Bresson-Hadni S, Humbert P, Paintaud G, Auer H, Lenys D, Laurent R, Vuitton DA, Miguet JP (1996) Skin localization of alveolar echinococcosis of the liver. J Am Acad Dermatol 34:873–877. doi:10.1016/S0190-9622(96) 90068-7
Ambo M, Adachi K, Ohkawara A (1999) Postoperative alveolar hydatid disease with cutaneous-subcutaneous involvement. J Dermatol 26:343–347
Reuter S, Buck A, Grebe O, Nussle-Kugele K, Kern P, Manfras BJ (2003) Salvage treatment with amphotericin B in progressive human alveolar echinococcosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47:3586–3591. doi:10.1128/AAC.47.11.3586-3591.2003
Senturk H, Mert A, Ersavasti G, Tabak F, Akdogan M, Ulualp K (1998) Bronchobiliary fistula due to alveolar hydatid disease: report of three cases. Am J Gastroenterol 93:2248–2253
Huang J, Wu YM, Liang PC, Lee PH (2004) Alveolar hydatid disease causing total occlusion of the inferior vena cava. J Formos Med Assoc 103:633–636
Wilson JF, Rausch RL, Wilson FR (1995) Alveolar hydatid disease. Review of the surgical experience in 42 cases of active disease among Alaskan Eskimos. Ann Surg 221:315–323. doi:10.1097/00000658-199503000-00015
Acknowledgments
The authors thank D. Kocot and R.S. Reske, Department of Nuclear Medicine, University of Ulm, Ulm, Germany for contributing the FDG-PET-CT images.
The patient agreed to publication and gave written consent.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buttenschoen, K., Kern, P., Reuter, S. et al. Hepatic infestation of Echinococcus multilocularis with extension to regional lymph nodes. Langenbecks Arch Surg 394, 699–704 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-009-0481-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-009-0481-0