Abstract
Introduction
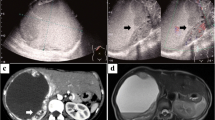
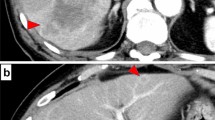
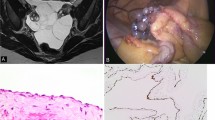
In this rare case of intrahepatic malignant mesothelioma with subsequent lymph node metastases, hepatic segmentectomy in combination with repeated lymphadenectomy resulted in prolonged survival, currently 37 months after initial diagnosis.
Discussion
Immunohistochemically, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 expressing tumor cells were surrounded by a dense D 2–40-positive lymphangiovascular network, suggesting tumor induced lymphangiogenesis correlating to 2-deoxy-2[18F]fluoro-d-glucose-positron emission tomography/computed tomography-positive recurrent intraabdominal and intrathoracic lymphatic tumor spread. Therefore, extended lymphadenectomy during primary tumor resection and combined adjuvant chemotherapy with promising anticancer agents possessing antilymphangiogenic and antimetabolite properties should be considered to prolong survival in cases of extrathoracic malignant mesothelioma. Additionally, as shown in our case, individual operative concepts and (sometimes) multiple operations can be beneficial for highly selected patients. Importantly, a case-by-case optimized antitumor regimen requires interdisciplinary expertise and consensus of all involved faculties.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CA 12–5:
-
Carbohydrate antigen 12–5
- CA 19–9:
-
Carbohydrate antigen 19–9
- CEA:
-
Carcinoembryonic antigen
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- FDG-PET:
-
2-Deoxy-2[18F]fluoro-d-glucose-positron emission tomography
- MPM:
-
Malignant pulmonary mesothelioma
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- NSCLC:
-
Nonsmall cell lung cancer
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- VEGFR1:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1
References
Sohrab S, Hinterthaner M, Stamatis G, Rödelsberger K, Woitowitz H-J, Konietzko N (2000) Das maligne Pleuramesotheliom. Dtsch Arztebl 97:A3257–A3262
Chabot JF, Beard D, Langlois AJ, Beard JW (1970) Mesotheliomas of peritoneum, epicardium, and pericardium induced by strain MC29 avian leukosis virus. Cancer Res 30:1287–1308
Carbone M, Pass HI (2006) Evolving aspects of mesothelioma carcinogenesis: SV40 and genetic predisposition. J Thorac Oncol 1:169–171. doi:10.1097/01243894-200602000-00012
Antropoli M, Freda F, Apicella A, Nunziata L, Cutolo PP, Antropoli C et al (2002) Peritoneal multicystic mesothelioma: unusual case of localization in the left lobe of the liver. Chir Ital 54:897–902
Gupta S, Gupta RK, Gujral RB, Agarwal D, Saxena R, Tandon P (1992) Peritoneal mesothelioma simulating pseudomyxoma peritonei on CT and sonography. Gastrointest Radiol 17:129–131. doi:10.1007/BF01888527
Horling EW, Albert C, Bassermann R, Stiegler H (1996) Multicystic peritoneal mesothelioma. Zentralbl Chir 121:587–590
Matsukuma S, Aida S, Hata Y, Sugiura Y, Tamai S (1996) Localized malignant peritoneal mesothelioma containing rhabdoid cells. Pathol Int 46:389–391. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1827.1996.tb03627.x
Iczkowski KA, Katz G, Zander DS, Clapp WL (2002) Malignant mesothelioma of tunica vaginalis testis: a fatal case with liver metastasis. J Urol 167:645–646. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(01) 69106-7
Chen KT, Arhelger RB, Flam MS, Hanson JH (1982) Malignant mesothelioma of tunica vaginalis testis. Urology 20:316–319. doi:10.1016/0090-4295(82) 90652-5
Gütgemann I, Standop J, Fischer HP (2006) Primary intrahepatic malignant mesothelioma of epithelioid type. Virchows Arch 448:655–658. doi:10.1007/s00428-006-0175-8
Blasi AD, Boscaino A, De Dominicis G, Marsilia GM, D’Antonio A, Nappi O (2004) Multicystic mesothelioma of the liver with secondary involvement of peritoneum and inguinal region. Int J Surg Pathol 12:87–91. doi:10.1177/106689690401200116
Imura J, Ichikawa K, Takeda J, Iwasaki Y, Tomita S, Kubota K et al (2002) Localized malignant mesothelioma of the epithelial type occurring as a primary hepatic neoplasm: a case report with review of the literature. APMIS 110:789–794. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0463.2002.t01-1-1101102.x
Leonardou P, Semelka RC, Kanematsu M, Braga L, Woosley JT (2003) Primary malignant mesothelioma of the liver: MR imaging findings. Magn Reson Imaging 21:1091–1093. doi:10.1016/S0730-725X(03) 00197-8
Churg A, Colby TV, Cagle P, Corson J, Gibbs AR, Gilks B et al (2000) The separation of benign and malignant mesothelial proliferations. Am J Surg Pathol 24:1183–1200. doi:10.1097/00000478-200009000-00001
Hirakawa S, Brown LF, Kodama S, Paavonen K, Alitalo K, Detmar M (2007) VEGF-C-induced lymphangiogenesis in sentinel lymph nodes promotes tumor metastasis to distant sites. Blood 109:1010–1017. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-05-021758
Skobe M, Hamberg LM, Hawighorst T, Schirner M, Wolf GL, Alitalo K et al (2001) Concurrent induction of lymphangiogenesis, angiogenesis, and macrophage recruitment by vascular endothelial growth factor-C in melanoma. Am J Pathol 159:893–903
Ohta Y, Shridhar V, Bright RK, Kalemkerian GP, Du W, Carbone M et al (1999) VEGF and VEGF type C play an important role in angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in human malignant mesothelioma tumours. Br J Cancer 81:54–61. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6690650
Plate K (2001) From angiogenesis to lymphangiogenesis. Nat Med 7:151–152. doi:10.1038/84579
Stacker SA, Caesar C, Baldwin ME, Thornton GE, Williams RA, Prevo R et al (2001) VEGF-D promotes the metastatic spread of tumor cells via the lymphatics. Nat Med 7:186–191. doi:10.1038/84635
Achen MG, McColl BK, Stacker SA (2005) Focus on lymphangiogenesis in tumor metastasis. Cancer Cell 7:121–127. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2005.01.017
Niki T, Iba S, Tokunou M, Yamada T, Matsuno Y, Hirohashi S (2000) Expression of vascular endothelial growth factors A, B, C, and D and their relationships to lymph node status in lung adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 6:2431–2439
Skobe M, Detmar M (2000) Structure, function, and molecular control of the skin lymphatic system. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc 5:14–19. doi:10.1046/j.1087-0024.2000.00001.x
Scavelli C, Vacca A, Di PG, Dammacco F, Ribatti D (2004) Crosstalk between angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in tumor progression. Leukemia 18:1054–1058. doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2403355
Murakami M, Zheng Y, Hirashima M, Suda T, Morita Y, Ooehara J et al (2008) VEGFR1 tyrosine kinase signaling promotes lymphangiogenesis as well as angiogenesis indirectly via macrophage recruitment. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28:658–664. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.107.150433
Cursiefen C, Chen L, Borges LP, Jackson D, Cao J, Radziejewski C et al (2004) VEGF-A stimulates lymphangiogenesis and hemangiogenesis in inflammatory neovascularization via macrophage recruitment. J Clin Invest 113:1040–1050
Aishima S, Nishihara Y, Iguchi T, Taguchi K, Taketomi A, Maehara Y et al (2008) Lymphatic spread is related to VEGF-C expression and D2–40-positive myofibroblasts in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Mod Pathol 21:256–264. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800985
Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC, Brahmer J, Schiller JH, Dowlati A et al (2006) Paclitaxel–carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 355:2542–2550. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa061884
Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W, Cartwright T, Hainsworth J, Heim W et al (2004) Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 350:2335–2342. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa032691
Li Q, Yano S, Ogino H, Wang W, Uehara H, Nishioka Y et al (2007) The therapeutic efficacy of anti vascular endothelial growth factor antibody, bevacizumab, and pemetrexed against orthotopically implanted human pleural mesothelioma cells in severe combined immunodeficient mice. Clin Cancer Res 13:5918–5925. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0501
Shih C, Chen VJ, Gossett LS, Gates SB, MacKellar WC, Habeck LL et al (1997) LY231514, a pyrrolo[2, 3-d]pyrimidine-based antifolate that inhibits multiple folate-requiring enzymes. Cancer Res 57:1116–1123
Taylor EC, Kuhnt D, Shih C, Rinzel SM, Grindey GB, Barredo J et al (1992) A dideazatetrahydrofolate analogue lacking a chiral center at C-6, N-[4-[2-(2-amino-3, 4-dihydro-4-oxo-7H-pyrrolo[2, 3-d]pyrimidin-5- yl) ethyl]benzoyl]-L-glutamic acid, is an inhibitor of thymidylate synthase. J Med Chem 35:4450–4454. doi:10.1021/jm00101a023
Vogelzang NJ, Rusthoven JJ, Symanowski J, Denham C, Kaukel E, Ruffie P et al (2003) Phase III study of pemetrexed in combination with cisplatin versus cisplatin alone in patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma. J Clin Oncol 21:2636–2644. doi:10.1200/JCO.2003.11.136
Tsiouris A, Walesby RK (2007) Malignant pleural mesothelioma: current concepts in treatment. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 4:344–352. doi:10.1038/ncponc0839
Vogelzang NJ, Porta C, Mutti L (2005) New agents in the management of advanced mesothelioma. Semin Oncol 32:336–350. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2005.02.010
Yamamuro M, Gerbaudo VH, Gill RR, Jacobson FL, Sugarbaker DJ, Hatabu H (2007) Morphologic and functional imaging of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Eur J Radiol 64:356–366. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2007.08.010
Truong MT, Marom EM, Erasmus JJ (2006) Preoperative evaluation of patients with malignant pleural mesothelioma: role of integrated CT-PET imaging. J Thorac Imaging 21:146–153. doi:10.1097/00005382-200605000-00006
Ceresoli GL, Chiti A, Zucali PA, Rodari M, Lutman RF, Salamina S et al (2006) Early response evaluation in malignant pleural mesothelioma by positron emission tomography with [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose. J Clin Oncol 24:4587–4593. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.06.8999
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to A.J. Bauer and R. S. Chanthaphavong for the editorial assistance and critical reading of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buchholz, B.M., Gütgemann, I., Fischer, HP. et al. Lymph node dissection in primary intrahepatic malignant mesothelioma: case report and implications for diagnosis and therapy. Langenbecks Arch Surg 394, 1123–1130 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-009-0476-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-009-0476-x