Abstract
Background and aims
Gastrointestinal motility is reduced during sepsis but the pathomechanism involved is poorly understood. We investigated the expression of substance P (SP) and vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) in the myenteric plexus during peritonitis in human small bowel.
Materials and methods
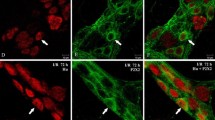
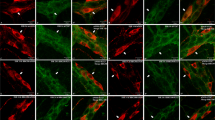
Tissue samples of the small bowel were gathered from healthy patients and from patients with peritonitis. Immunohistochemistry for myeloperoxidase (MPO), SP, and VIP was performed in whole mount sections. To determine the level of inflammation, MPO-positive cells were counted in the circular muscle layer. SP and VIP immunoreactivity was analyzed in myenteric plexus neurons. The area of positive immunoreactivity for either neuropeptide within the plexus was analyzed and set in relation to the total area of the plexus and consecutively expressed as percentage.
Results
During peritonitis, MPO-positive cells significantly increased by approximately fourfold as compared to healthy tissue. The immunoreactivity for SP was significantly reduced by approximately 80% in myenteric plexus neurons during peritonitis. In contrast, the immunoreactivity for VIP significantly increased by nearly twofold during peritonitis.
Conclusions
During peritonitis, the inflammatory reaction within the gut is increased. The neuropeptide expression in myenteric plexus neurons was observed as shifting towards increased expression of VIP, known to inhibit intestinal motility, and towards decreased expression of the prokinetic neuropeptide SP.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bauer AJ, Schwarz NT, Moore BA, Turler A, Kalff JC (2002) Ileus in critical illness: mechanisms and management. Curr Opin Crit Care 8:152–157
Schumpelick V, Ambacher T, Riesener KP (1999) Current therapy of injuries of the colon and retroperitoneum. Chirurg 70:1269–1277
Faber MD, Yee J (2006) Diagnosis and management of enteric disease and abdominal catastrophe in peritoneal dialysis patients with peritonitis. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 13:271–279
Eskandari MK, Kalff JC, Billiar TR, Lee KK, Bauer AJ (1999) LPS-induced muscularis macrophage nitric oxide suppresses rat jejunal circular muscle activity. Am J Physiol 277:G478–G486
O’Dwyer ST, Michie HR, Ziegler TR, Revhaug A, Smith RJ, Wilmore DW (1988) A single dose of endotoxin increases intestinal permeability in healthy humans. Arch Surg 123:1459–1464
Kalff JC, Carlos TM, Schraut WH, Billiar TR, Simmons RL, Bauer AJ (1999) Surgically induced leukocytic infiltrates within the rat intestinal muscularis mediate postoperative ileus. Gastroenterology 117:378–387
Mantyh PW, Catton M, Maggio JE, Vigna SR (1991) Alterations in receptors for sensory neuropeptides in human inflammatory bowel disease. Adv Exp Med Biol 298:253–283
Borovikova LV, Ivanova S, Zhang M, Yang H, Botchkina GI, Watkins LR, Wang H, Abumrad N, Eaton JW, Tracey KJ (2000) Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nature 405:458–462
van Westerloo DJ, Giebelen IA, Florquin S, Daalhuisen J, Bruno MJ, de Vos AF, Tracey KJ, van der PT (2005) The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway regulates the host response during septic peritonitis. J Infect Dis 191:2138–2148
Llewellyn-Smith IJ, Furness JB, Murphy R, O’Brien PE, Costa M (1984) Substance P-containing nerves in the human small intestine. Distribution, ultrastructure, and characterization of the immunoreactive peptide. Gastroenterology 86:421–435
Jensen J, Holmgren S (1994) The gastrointestinal canal. In: Burnstock G (ed) The autonomic nervous system, comparative physiology and evolution of the autonomic nervous system. Harwood Academic, Chur, Switzerland, pp 119–167
Dunn DL (1993) Infection. In: Greenfield LJ (ed) Scientific principles and practice. Lippincott, Philadelphia, pp 148–170
Reinhart K, Brunkhorst FM, Bone HG, Gerlach H, Gründling M, Kreymann G, Kujath P, Marggraf G, Mayer K, Meier-Hellmann A, Peckelsen C, Putensen C, Quintel M, Ragaller M, Rossaint R, Stüber F, Weiler N, Welte T, Werdan K (2006) Diagnose und Therapie der Sepsis. Med Welt 57:23–38
Kalff JC, Schraut WH, Simmons RL, Bauer AJ (1998) Surgical manipulation of the gut elicits an intestinal muscularis inflammatory response resulting in postsurgical ileus. Ann Surg 228:652–663
Glatzle J, Leutenegger CM, Mueller MH, Kreis ME, Raybould HE, Zittel TT (2004) Mesenteric lymph collected during peritonitis or sepsis potently inhibits gastric motility in rats. J Gastrointest Surg 8:645–652
Delgado M, Ganea D (2001) Inhibition of endotoxin-induced macrophage chemokine production by VIP and PACAP in vitro and in vivo. Arch Physiol Biochem 109:377–382
Ekblad E, Bauer AJ (2004) Role of vasoactive intestinal peptide and inflammatory mediators in enteric neuronal plasticity. Neurogastroenterol Motil 16(Suppl 1):123–128
Olsson C, Holmgren S (2001) The control of gut motility. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 128:481–503
Holzer P, Holzer-Petsche U (1997) Tachykinins in the gut, part II. Roles in neural excitation, secretion and inflammation. Pharmacol Ther 73:219–263
Miller LJ (1999) Gastrointestinal hormones and receptors. In: Yamada T (ed) Textbook of gastroenterology. Lippincott, New York, pp 35–66
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Best abstracts — Surgical Forum 2007
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jacob, P., Mueller, M.H., Hahn, J. et al. Alterations of neuropeptides in the human gut during peritonitis. Langenbecks Arch Surg 392, 267–271 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-007-0168-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-007-0168-3