Abstract
Background and aims
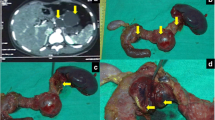
There is only little information about the spontaneous course of large pancreatic serous tumours. We followed up a white woman with a giant serous microcystic adenoma over more than 20 years.
Case report
At first clinical presentation, in 1986, the tumour measured 4.5 cm in diameter. Two years later, it measured 6 cm and was considered as non-resectable at laparotomy. A biopsy was obtained, and the tumour was diagnosed as lymphangioma, based on hematoxylin and eosin-staining. During the follow-up, the tumour progressively increased in size, measuring 12 cm in diameter in 1993 and 17 cm in 2000. Thus, an average growth rate of 0.83 cm per year was calculated. Unspecific abdominal discomfort and pain were the leading clinical symptoms. A colonic resection was necessary because of compression by the tumour in 1993. Portal hypertension was detected at laparotomy. Finally, the initial biopsy specimen was re-evaluated, using immunohistochemistry, and the final diagnosis of a serous microcystic adenoma was made.
Conclusion
This unique case demonstrates that the spontaneous course of serous microcystic adenoma of the pancreas may be favourable even with huge tumour size and that immunohistochemistry may prove a valuable tool for differential diagnosis of cystic pancreatic lesions. Due to their size and progressive, space-occupying growth, these biologically benign tumours may cause injury to adjacent organs and thus clinical symptoms. For this reason, curative surgical resection is the treatment of choice for this tumour entity except for small, asymptomatic lesions, which do not require intervention. When radical resection is impossible, palliative surgery may improve the quality of life for several years. The risk of malignant transformation seems to be low even in the long-term course.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Box JC, Douglas HO (2000) Management of cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. Am Surgeon 66:495–501
Sarr MG, Kendrick ML, Nagorney DM, Thompson GB, Farley DR, Farnell MB (2001) Cystic neoplasms of the pancreas: benign to malignant epithelial neoplasms. Surg Clin North Am 81:497–509
Spinelli KS, Fromwiller TE, Daniel RA, Kiely JM, Nakeeb A, Komorowski RA, Wilson SD, Pitt HA (2004) Cystic pancreatic neoplasms. Observe or operate. Ann Surg 239:651–659
Sarr MG, Murr M, Smyrk TC, Yeo CJ, Fernandez-del-Castillo C, Hawes RH, Freeny PC (2003) Primary cystic neoplasms of the pancreas: neoplastic disorders of emerging importance—current state-of-the-art and unanswered questions. J Gastrointest Surg 7:417–428
Vortmeyer AO, Lubensky IA, Fogt F, Linehan WM, Khettry U, Zhuang Z (1997) Allelic deletion and mutation of the von Hippel–Lindau (VHL) tumor suppressor gene in pancreatic microcystic adenomas. Am J Pathol 151:951–956
Hamilton SR, Aaltonen LA (eds) (2000) Pathology and genetics of tumours of the digestive system. IARC, Lyon
Horvath KD, Chabot JA (1999) An aggressive resectional approach to cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. Am J Surg 178:269–274
Cheng CK, Kanamaru T, Ueno N, Tanaka KI, Idei Y, Nishida Y, Yamamoto M (2001) A case of pancreatic serous cystadenoma obstructing the distal pancreatic duct. Oncol Rep 8:811–813
Heim D, Sutter PM, Mattli J, Matter P (1994) Rupturiertes cystadenom des pankreas. Chirurg 65:68–71
Marincek B (1995) Serous cystadenoma of the pancreas tail with extensive necrosis and fresh post-traumatic bleeding. Schweiz Rundsch Med Praxis 84:213–215
Barbe L, Levy P, Sauvanet A, Flejou JF, Belghiti J, Bernades P (1995) Serous cystadenoma of the pancreas revealed by choledochal stenosis. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 19:848–849
Abe H, Kubota K, Mori M, Miki K, Minagawa M, Noie T, Kimura W, Makuuchi M (1998) Serous cystadenoma of the pancreas with invasive growth: benign or malignant? Am J Gastroenterol 93:1963–1966
Kamei K, Funabiki T, Ochiai M, Amano H, Kasahara M, Sakamoto T (1991) Multifocal pancreatic serous cystadenoma with atypical cells and focal perineural invasion. Int J Pancreatol 10:161–172
El Nakadi B, Greuse M, Debaize JP, Salhadin A (1992) A new complication of cystic neoplasms of the pancreas: cysto-duodenal fistula. Acta Chir Belg 92:52–54
Haarmann W, Mittelkötter U, Smektala R (1997) Monströses seröses Zystadenomrezidiv des Pankreas. Zentralbl Chir 122:122–125
Ohta T, Nagakawa T, Itoh H, Fonseca L, Miyazaki I, Terada T (1993) A case of serous cystadenoma of the pancreas with focal malignant changes. Int J Pancreatol 14:283–289
Fujii H, Kubo S, Hirohashi K, Kinoshita H, Yamamoto T, Wakasa K (1998) Serous cystadenoma of the pancreas with atypical cells. Int J Pancreatol 23:165–169
Tseng JF, Warshaw AL, Sahani DV, Lauwers GY, Rattner DW, Fernandez-del Castillo C (2005) Serous cystadenoma of the pancreas: tumor growth rates and recommendations for treatment. Ann Surg 242:413–421
Klöppel G, Kosmahl M (2001) Cystic lesions and neoplasms of the pancreas. The features are becoming clearer. Pancreatology 1:648–655
Kamei K, Funabiki T, Ochiai M, Amano H, Marugami Y, Kasahara M, Sakamoto T (1992) Some considerations on the biology of pancreatic serous cystadenoma. Int J Pancreatol 11:97–104
Widmaier U, Mattfeldt T, Siech M, Beger HG (1996) Serous cystadenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Int J Pancreatol 20:135–139
Le Borgne J, de Calan L, Partensky C (1999) Cystadenomas and cystadenocarcinomas of the pancreas: a multiinstitutional retrospective study of 398 cases. French Surgical Association. Ann Surg 230:152–161
Tanaka M, Chari S, Adsay V, Fernandez-del Castillo C, Falconi M, Shimizu M, Yamaguchi K, Yamao K, Matsuno S (2006) International consensus guidelines for management of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms and mucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. Pancreatology 6:17–32
Siech M, Tripp K, Schmidt-Rohlfing B, Mattfeldt T, Widmaier U, Gansauge F, Görich J, Beger HG (1998) Cystic tumours of the pancreas: diagnostic accuracy, pathologic observations and surgical consequences. Langenbecks Arch Surg 383:56–61
Kim SG, Wu TT, Lee JH, Yun YK, Issa JP, Hamilton SR, Rashid A (2003) Comparison of epigenetic and genetic alterations in mucinous cystic neoplasm and serous microcystic adenoma of pancreas. Mod Path 16:1086–1094
Moore PS, Zamboni G, Brighenti A, Lissandrini D, Antonello D, Capelli P, Rigaud G, Falconi M, Scarpa A (2001) Molecular characterization of pancreatic serous microcystic adenomas. Evidence for a tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 10 q. Am J Pathol 158:317–321
Moore PS, Beghelli S, Zamboni G, Scarpa A (2003) Genetic abnormalities in pancreatic cancer. Molec Cancer 2:7–12
Gerdes B, Wild A, Wittenberg J, Barth P, Ramaswamy A, Kersting M, Lüttges J, Klöppel G, Bartsch DK (2003) Tumor-suppressing pathways in cystic pancreatic tumors. Pancreas 26:42–48
Lüttges J, Galehdari H, Bröcker V, Schwarte-Waldhoff I, Henne-Bruns D, Klöppel G, Schmiegel W, Hahn SA (2001) Allelic loss is often the first hit in the biallelic inactivation of the p53 and DPC4 genes during pancreatic carcinogenesis. Am J Pathol 158:1677–1683
Ishikawa T, Nakao A, Nomoto S, Hosono J, Harada A, Nonami T, Takagi H (1998) Immunohistochemical and molecular biological studies of serous cystadenoma of the pancreas. Pancreas 16:40–44
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schulz, HU., Kellner, U., Kahl, S. et al. A giant pancreatic serous microcystic adenoma with 20 years follow-up. Langenbecks Arch Surg 392, 209–213 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-006-0146-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-006-0146-1