Abstract.
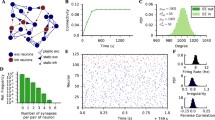
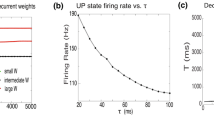
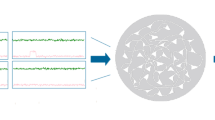
While learning and development are well characterized in feedforward networks, these features are more difficult to analyze in recurrent networks due to the increased complexity of dual dynamics – the rapid dynamics arising from activation states and the slow dynamics arising from learning or developmental plasticity. We present analytical and numerical results that consider dual dynamics in a recurrent network undergoing Hebbian learning with either constant weight decay or weight normalization. Starting from initially random connections, the recurrent network develops symmetric or near-symmetric connections through Hebbian learning. Reciprocity and modularity arise naturally through correlations in the activation states. Additionally, weight normalization may be better than constant weight decay for the development of multiple attractor states that allow a diverse representation of the inputs. These results suggest a natural mechanism by which synaptic plasticity in recurrent networks such as cortical and brainstem premotor circuits could enhance neural computation and the generation of motor programs.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 27 April 1998 / Accepted in revised form: 16 March 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hua, S., Houk, J. & Mussa-Ivaldi, F. Emergence of symmetric, modular, and reciprocal connections in recurrent networks with Hebbian learning. Biol Cybern 81, 211–225 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004220050557
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004220050557