Abstract.
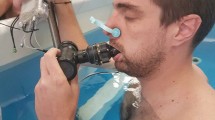
This study evaluated the subacute respiratory effects of diving, to try to separate the effects of ambient temperature from those of depth. In the first experiment 10 healthy men made a compressed-air dive to 50 m that exposed them to cold. They were compared with 10 matched control subjects who underwent the same dive profile but were exposed to a comfortable temperature. In the second experiment 16 healthy subjects made randomized cold dives to both 50 m and 10 m. Pulmonary function tests were made before, after 1 h, and 24 h after the dives. In the first experiment there was an increase in residual volume (P<0.05) and a decrease in forced expiratory volume at 1 s (FEV1), in forced vital capacity (FVC) and in mid-expiratory flow at 75% of FVC (MEF75) 1 h after the cold dives (P<0.05). In the second experiment significant increases in specific airways resistance (sR AW) (P<0.05) and decreases in FEV1 (P<0.01), in MEF75 (P<0.05), and in mid-expiratory flow at 25% of FVC (P<0.05), were obtained after the 50 m-dives, whereas sR AW increased after the 10 m-dives (P<0.05). The respiratory pattern observed 1 h after cold dives to 50 m indicated airway narrowing. The changes after cold dives to 10 m, however, were of minor magnitude. Both cold and depth seemed to contribute to the adverse effects of a single compressed-air dive on pulmonary function.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tetzlaff, K., Friege, L., Koch, A. et al. Effects of ambient cold and depth on lung function in humans after a single scuba dive. Eur J Appl Physiol 85, 125–129 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210100421
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210100421