Abstract.
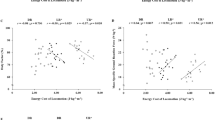
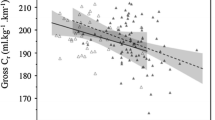
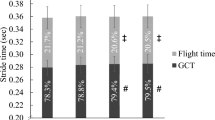
It was hypothesized that certain ground reaction force (GRF) variables are positively correlated with running economy (RE; the aerobic demand at a single speed of running). Excessive momentum changes, quantified by linear impulse measures, as well the free moment applied to the running surface could be considered potentially wasteful efforts in terms of metabolic energy requirements. Recreational runners (n=16) ran on a treadmill at 3.35 m·s–1 for physiological measurements and overground for biomechanical measurements. Correlation coefficients were calculated between RE and total vertical impulse (TVI), net impulses in three orthogonal directions, and descriptors of the free moment. The TVI and the net vertical impulse were the only GRF characteristics significantly correlated to RE (r=0.62, r=0.60, respectively). Greater overall muscle support requirements during ground contact, as represented by TVI, may have been responsible for greater aerobic demand.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heise, G., Martin, P. Are variations in running economy in humans associated with ground reaction force characteristics?. Eur J Appl Physiol 84, 438–442 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210100394
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210100394