Abstract
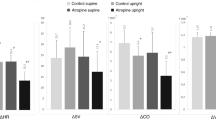
To elucidate whether combined adrenergic and parasympathetic blockade would affect the ventilatory response to exercise, especially at the initial stage (phase I), six healthy subjects performed a brief and light voluntary bilateral leg extension exercise and passive movements under the conditions of control (before the blockade) and after intravenous administration of combined β-adrenergic (propranolol, 0.2 mg · kg−1) and muscarinic (atropine, 0.04 mg · kg−1) receptor antagonists. The movements were continued only within two breaths after the onset of the motion. Ventilation increased immediately and significantly (P<0.05) within the first breath at the onset of voluntary exercise in all conditions as compared with at rest. However, the magnitude of increase in mean ventilation within two breaths at the start of exercise as against the resting value (delta ventilation) was significantly less (P<0.05) after the combined blockades (2.5 l · min−1) than in the control condition (3.7 l · min−1). Passive movements showed a similar but smaller change as compared with voluntary exercise. The heart rate response to exercise was attenuated by the combined blockade while cardiac output showed a slight change at the onset of exercise. It is concluded that phase I should occur despite the inhibited activity of the β-adrenergic and the cholinergic systems; nevertheless, the response was attenuated by the combined blockade. These results suggest a possible role of the β-adrenergic and/or cholinergic systems in the rapid increase in ventilation that occurs at the start of exercise.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 2 March 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishida, K., Hayashi, T., Moritani, T. et al. Effects of combined β-adrenergic and cholinergic blockade on the initial ventilatory response to exercise in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 76, 230–235 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210050241
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210050241