Abstract
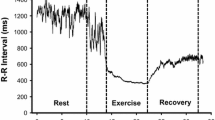
The long-term conditioning effects of physical training on cardiorespiratory interaction in 11 young healthy males were studied. Significant increases in maximum oxygen uptake (V˙O2max)(P<0.05) and decreases in heart rate (P<0.05) were achieved in all subjects following a 6-week training programme consisting of cycling for 25min each day at a work level that increased heart rate to 85% of maximum. Heart rate variability, measured as the differences between the maximum and minimum R–R interval in a respiratory cycle, increased in nine of the subjects and decreased in two. The respiratory-cycle-related high-frequency peak in the power spectral plot of R–R variability also showed significant increases in the same nine subjects and decreases in two. The latter result was similar after normalisation of the data for changes in heart rate by calculating the common coefficient of variance (CCV=HFR–R×<∮∮), where HF is the high-frequency component of the power spectral plots, using a further measure of vagal tone it was shown that, for all subjects, the R–R interval change in response to isometric contractions of the arm flexors in one respiratory cycle were significantly greater after training. These data suggest that cardiac vagal tone is increased by aerobic training for all subjects and that this is accompanied by a respiratory sinus arrhythmia (RSA) in most, but may be associated with a decrease in RSA in subjects with a very low (< 50 beats⋅min-1 heart rate.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 23 April 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Ani, M., Munir, S., White, M. et al. Changes in R–R variability before and after endurance training measured by power spectral analysis and by the effect of isometric muscle contraction. Eur J Appl Physiol 74, 397–403 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210050092
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210050092