Abstract
Purpose
Pentraxin 3 (PTX3) has been shown to be a predictor of endothelial dysfunction in patients with increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) (e.g., obesity). Circulating PTX3 concentrations are dysregulated in obese individuals and are elevated following acute aerobic exercise. High-intensity interval exercise (HIIE) has been demonstrated to be as effective as continuous moderate-intensity exercise in improving endothelial function, as indicated by brachial artery flow-mediated dilation (BAFMD), in patients with CVD. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to examine the effect of acute HIIE on plasma PTX3 and BAFMD responses in obese individuals.
Methods
Eight obese and six normal-weight young males participated in acute HIIE (4 intervals of 4 min at 80–90% of VO2max; 3 min of active recovery at 50–60% VO2max). Plasma PTX3 and BAFMD were measured prior to, immediately following exercise, and one and 2 hours into recovery.
Results
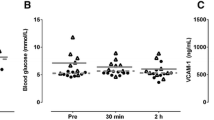
Plasma PTX3 concentrations significantly increased following HIIE, yet the PTX3 response to HIIE was significantly blunted in obese compared to normal-weight participants. While the kinetic responses of BAFMD were also significantly different in obese compared to normal-weight participants, similar increases above the baseline were observed 2 hours into recovery in both groups. Finally, plasma PTX3 concentrations were not associated with BAFMD at baseline or in response to HIIE.
Conclusion
The utilization of HIIE may serve as a time-efficient exercise prescription strategy to transiently improve endothelial function, independent of elevated plasma PTX3 concentrations, in obese individuals.




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
20 May 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-021-04701-9
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
Analyses of variance
- APMHR:
-
Age-predicted maximal heart rate
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
- AUCi:
-
Area under the curve with respect to increase
- BAFMD:
-
Brachial artery flow-mediated dilation
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- CVD:
-
Cardiovascular disease
- EDTA:
-
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- HIIE:
-
High-intensity interval exercise
- MICE:
-
Moderate-intensity continuous exercise
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- PTX3:
-
Pentraxin 3
- RPE:
-
Rating of perceived exertion
- VO2max :
-
Maximal oxygen consumption
References
American College of Sports Medicine (2013) ACSM’s guidelines for exercise testing and prescription. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Atkinson CL, Lewis NC, Carter HH, Thijssen DH, Ainslie PN, Green DJ (2015) Impact of sympathetic nervous system activity on post-exercise flow-mediated dilatation in humans. J Physiol 593(23):5145–5156
Bartlett JD, Close GL, MacLaren DPM, Gregson W, Drust B, Morton JP (2011) High-intensity interval running is perceived to be more enjoyable than moderate-intensity continuous exercise: implications for exercise adherence. J Sports Sci 29(6):547–553
Barton M (2010) Obesity and aging: determinants of endothelial cell dysfunction and atherosclerosis. Pflügers Arch 460(5):825–837
Breviario R, d”Aniello EM, Golay J (1992) Interleukin-1-inducible genes in endothelial cells Cloning of a new gene related to C-reative protein and serum amyloid P component. J Bio Chem 267(31):22190–22197
Carrizzo A, Lenzi P, Procaccini C, Damato A, Biagioni F, Ambrosio M, Amodio G, Remondelli P, Giudice CD, Izzo R, Malovini A, Formisano L, Gigantino V, Madonna M, Puca A, Trimarco B, Malovini A (2015) Pentraxin 3 induces vascular endothelial dysfunction through a P-selectin/matrix metalloproteinase-1 pathway. Circulation 131(17):1495–1505
Chatzizisis YS, Coskun AU, Jonas M, Edelman ER, Feldman CL, Stone PH (2007) Role of endothelial shear stress in the natural history of coronary atherosclerosis and vascular remodeling: molecular, cellular, and vascular behavior. J Am Coll Cardiol 49(25):2379–2393
Currie KD, McKelvie RS, MacDonald MJ (2012) Flow-mediated dilation is acutely improved after high-intensity interval exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 44(11):2057–2064
Deban L, Russo RC, Sironi M, Moalli F, Scanziani M, Zambelli V, Cuccovillo I, Bastone A, Gobbi M, Valentino S, Doni A, Garlanda C, Danese S, Salvatori G, Sassano M, Evangelista V, Rossi B, Zenaro E, Constantin G, Laudanna C, Bottazzi B, Mantovani A (2010) Regulation of leukocyte recruitment by the long pentraxin PTX3. Nature Immunol 11(4):328–334
Early KS, Stewart A, Johannsen N, Lavie C, Thomas J, Welsch M (2017) The effects of exercise training on brachial artery flow-mediated dilation. J Cardipulm Rehabil Prev 37(2):77–89
Ferrandi PJ, Fico BG, Whitehurst M, Zourdos MC, Bao F, Dodge KM, Rodriguez AL, Pena G, Huang C-J (2018) Acute high-intensity interval exercise induces comparable levels of circulating cell-free DNA and interleukin-6 in obese and normal-weight individuals. Life Sci 202:161–166
Fiuza-Luces C, Santos-Lozano A, Joyner M, Carrera-Bastos P, Picazo O, Zugaza JL, Izquierdo M, Ruilope LM, Lucia A (2018) Exercise benefits in cardiovascular disease: beyond attenuation of traditional risk factors. Nat Rev Cardio 15(12):731–743
Gillen JB, Martin BJ, MacInnis MJ, Skelly IE, Tarnopolsky MA, Gibala MJ (2016) Twelve weeks of sprint interval training improves indices of cardiometabolic health similar to traditional endurance training despite a five-fold lower exercise volume and time commitment. PLoS ONE 11(4):e0154075
Green DJ, Smith KJ (2018) Effects of exercise on vascular function, structure, and health in humans. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 8:a029819
Hallmark R, Patrie JT, Liu Z, Gaesser GA, Barrett EJ, Weltman A (2014) The effect of exercise intensity on endothelial function in physically inactive lean and obese adults. PLoS ONE 9(1):e85450
Hamburg NM, Mott MM, Bigornia SJ, Duess MA, Kluge MA, Hess DT, Apovian CM, Vita JA, Gokce N (2010) Maladaptive enlargement of the brachial artery in severe obesity is reversed with weight loss. Vasc Med 15(3):215–222
Heinrich KM, Patel PM, O’Neal JL, Heinrich BS (2014) High-intensity compared to moderate-intensity training for exercise initiation, enjoyment, adherence, and intentions: an intervention study. BMC Public Health 14(1):789
Heisz JJ, Tejada MGM, Paolucci EM, Muir C (2016) Enjoyment for high-intensity interval exercise increases during the first six weeks of training: implications for promoting exercise adherence in sedentary adults. PLoS ONE 11(12):e0168534
Imamura M, Kawasaki T, Savchenko AS, Ohashi R, Jiang S, Miyamoto K, Iwanari H, Sagara M, Tanaka T, Hamakubo T, Kodama T, Uchiyama M, Maito M (2007) Lipopolysaccharide induced expression of pentraxin 3 in human neutrophils and monocyte-derived macrophages. Cell Immunol 248(2):86–94
Jaillon S, Peri G, Delneste Y, Frémauz I, Doni A, Moalli F, Garlanda C, Romani L, Gascan H, Bellocchio S, Bozza S, Cassatella MA, Jeannin P, Mantovani A (2007) The humoral pattern recognititon pattern PTX3 is stored in neutrophil granules and localizes in extracellular traps. J Exp Med 204(4):793–804
Joyner MJ, Green DJ (2009) Exercise protects the cardiovascular system: effects beyond traditional risk factors. J Physiol 587(23):5551–5558
Kuvin JT, Patel AR, Sliney KA, Pandian NG, Rand WM, Udelson JE, Karas RH (2001) Peripheral vascular endothelial function testing as a noninvasive indicator of coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 38(7):1843–1849
Little JP, Jung ME, Wright AE, Manders RJF (2014) Effects of high-intensity interval exercise versus continuous moderate-intensity exercise on post-prandial glycemic control assessed by continuous glucose monitoring in obese adults. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 39(7):835–841
Miyaki A, Maeda S, Otsuki T, Ajisaka R (2011) Plasma pentraxin 3 concentration increases in endurance-trained men. Med Sci Sports Exerc 43(1):12–17
Miyaki A, Maeda S, Akazawa N, Tanabe Y, Ajisaka R (2012a) Habitual aerobic exercise increases plasma pentraxin 3 levels in middle aged and elderly women. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 37(5):907–911
Miyaki A, Maeda S, Choi Y, Akazawa N, Tanabe Y, So R, Tanaka K, Ajisaka R (2012b) The addition of whole-body vibration to a lifestyle modification on arterial stiffness in overweight and obese women. Artery Res 6(2):85–91
Miyaki A, Maeda S, Choi Y, Akazawa N, Eto M, Tanaka K, Ajisaka R (2013) Association of plasma PTX3 with arterial stiffness in overweight and obese individuals. Am J Hypertens 26(10):1250–1255
Munk PS, Breland UM, Aukrust P, Ueland T, Kvaløy JT, Larsen AI (2011) High intensity interval training reduces systemic inflammation in post-PCI patients. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil 18(6):850–857
Norata P, Marchesi VKP, Pulakazhi Venu VK, Pasqualini F, Anselmo A, Moalli F, Pizzitola I, Garlanda C, Mantovani A, Catapano AL (2009) Deficiency of the long pentraxin PTX3 promotes vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation 120(8):699–708
Ogawa T, Kawano Y, Imamura T, Kawakita K, Sagara M, Matsuo T, Kakitsubata Y, Ishikawa T, Kitamura K, Hatakeyama K, Asada Y, Kodama T (2010) Reciprocal contribution of pentraxin 3 and C-reactive protein to obesity and metabolic syndrome. Obesity 18(9):1871–1874
Pruessner JC, Kirschbaum C, Meinlschmid G, Hellhammer DH (2003) Two formulas for computation of the area under the curve represent measures of total hormone concentration versus time-dependent change. Psychoneuroendocrinology 28(7):916–931
Rodriguez AL, Whitehurst M, Fico BG, Dodge KM, Ferrandi PJ, Pena G, Adelman A, Huang C-J (2018) Acute high-intensity interval exercise induced greater levels of serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor in obese individuals. Exp Biol Med 243:1153–1160
Rognmo Ø, Hetland E, Helgerud J, Hoff J, Slørdahl SA (2004) High intensity aerobic interval exercise is superior to moderate intensity exercise for increasing aerobic capacity in patients with coronary artery disease. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil 11(3):216–222
Salio M, Chimenti S, De Angelis N, Molla F, Maina V, Nebuloni M, Pasqualini F, Latini R, Garlanda C, Mantovani A (2008) Cardioprotective function of the long pentraxin PTX3 in acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 117(8):1055–1064
Sandstad J, Stensvold D, Hoff M, Nes BM, Arbo I, Bye A (2015) The effects of high intensity interval training in women with rheumatic disease: a pilot study. Eur J Appl Physiol 115(10):2081–2089
Singhai A (2005) Endothelial dysfunction: role in obesity-related disorders and the early original of CVD. Proc Nutr Soc 64(1):15–22
Slusher AL, Huang C-J (2016) Association of pentraxin 3 with insulin resistance and glucose response following maximal aerobic exercise in obese and normal-mass individuals. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 94(7):734–738
Slusher AL, Mock JT, Whitehurst M, Maharaj A, Huang C-J (2015) The impact of obesity on pentraxin 3 and inflammatory milieu to acute aerobic exercise. Metabolism 64(2):323–329
Slusher AL, Mischo AB, Acevedo EO (2016) Pentraxin 3 is an anti-inflammatory protein associated with lipid-induced interleukin 10 in vitro. Cytokine 86:36–40
Slusher AL, Huang C-J (2017) The potential role of aerobic exercise-induced pentraxin 3 on obesity-related inflammation and metabolic dysregulation. Mediators Inflamm 2017:1092738
Slusher AL, Zúñiga TM, Acevedo EO (2018a) Aerobic fitness alters the capacity of mononuclear cells to produce pentraxin 3 following maximal exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 118(7):1515–1526
Slusher AL, Whitehurst M, Maharaj A, Dodge KM, Fico BG, Mock JT, Huang C-J (2018b) Plasma pentraxin 3 and glucose kinetics to acute high-intensity interval exercise versus continuous moderate-intensity exercise in healthy men. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 43(12):1233–1238
Slusher AL, Zúñiga TM, Acevedo EO (2019) Inflamm-Aging is associated with lower plasma PTX3 concentrations and an impaired capacity of PBMCs to express hTERT following LPS stimulation. Med Inflammation 2019:2324193
Thijssen DHJ, Bruno RM, van Mil ACCM, Holder SM, Faita F, Greyling A, Zock PL, Taddei S, Deanfield JE, Luscher T, Green DJ, Ghiadoni L (2019) Expert consensus and evidence-based recommendations for the assessment of flow-mediated dilation in humans. Eur Heart J 40(30):2534–2547
Tsukamoto H, Suga T, Takenaka S, Tanaka D, Takeuchi T, Hamaoka T, Isaka T, Hashimoto T (2016) Greater impact of acute high-intensity interval exercise on post-exercise executive function compared to moderate-intensity continuous exercise. Physiol Beha 155:224–230
Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, Casey DE Jr, Collins KJ, Himmelferb C, DePalma SM, Gidding S, Jamerson KA, Jones DW, MacLaughlin EJ, Muntner P, Ovbiagele B, Smith SC Jr, Spencer CC, Stafford RS, Taler SJ, Thomas RJ, Williams KA Sr, Williamson JD, Wright JT Jr (2018) 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/ PCNA Guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: executive summary: a report for the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on clinical practice guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol 71(19):21–2269
Williams MR, Westerman RA, Kingwell BA, Paige J, Blombery PA, Sudhir K, Komesaroff PA (2001) Variations in endothelial function and arterial compliance during the menstrual cycle. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86(11):5389–5395
Yasunaga T, Ikeda S, Koga S, Nakata T, Yoshida T, Masuda N, Kohno S, Maemura K (2014) Plasma pentraxin 3 is a more potent predictor of endothelial dysfunction than high-sensitive C-reactive protein. Int Heart J 55(2):160–164
Zempo-Miyaki A, Fujie S, Sato K, Hasegawa N, Sanada K, Maeda S, Hamaoka T, Iemitus M (2016) Elevated pentraxin 3 level at the early state of exercise training is associated with reduction of arterial stiffness in middle-aged and older adults. J Hum Hypertens 30(9):521–526
Zempo-Miyaki A, Kumagai H, Yoshikawa T, Myoenzono K, So R, Otsuki T, Tanaka K, Maeda S (2019) Pentraxin 3 increases in adult overweight and obese men after weight loss by dietary modification with exercise training. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 44(2):111–117
Zhu W, Zeng J, Yin J, Zhang F, Wu H, Yan S, Wang S (2010) Both flow-mediated vasodilation procedures and acute exercise improve endothelial function in obese young men. Eur J Appl Physiol 108(4):727–732
Zlibut A, Bocsan IC, Agoston-Coldea L (2019) Pentraxin-3 and endothelial dysfunction. Adv Clin Chem 91:153–179
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Florida Atlantic University Department of Exercise Science and Health Promotion for supporting the completion of this work. In addition, we thank those who donated their time to participate in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: BGF and C-JH; Data collection: BGF, KMD, PJF, AAR, GP, C-JH; Data analysis and interpretations: ALS, BGF, KMD, RSG, AAR, C-JH; Manuscript writing and revisions: ALS, BGF, KMD, RSG, and C-JH; Final approval: ALS, BGF, KMD, RSG, PJF, AAR, GP, and C-JH.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare that they have no conflict of interest, financial, or otherwise.
Additional information
Communicated by Massimo pagani.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this article was revised: Modifications have been made to the title and text. Full information regarding the corrections made can be found in the erratum/correction for this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Slusher, A.L., Fico, B.G., Dodge, K.M. et al. Impact of acute high-intensity interval exercise on plasma pentraxin 3 and endothelial function in obese individuals—a pilot study. Eur J Appl Physiol 121, 1567–1577 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-021-04632-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-021-04632-5