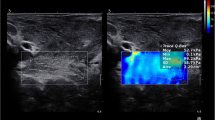
Abstract
Purpose
The present study aimed to clarify the effects of the trunk position on muscle stiffness that reflects elongation of the lumbar erector spinae and lumbar multifidus muscles using ultrasonic shear wave elastography (SWE).
Methods
The study included ten healthy men. The shear elastic modulus of the left lumbar erector spinae and lumbar multifidus muscles were evaluated using ultrasonic SWE. Measurement postures for the left lumbar erector spinae muscle were (1) prone position (Rest), (2) sitting position with the trunk flexed (Flexion), (3) the Flexion position adding right trunk lateral flexion (Flexion-Lateral Flexion), and (4) the Flexion position adding right trunk rotation (Flexion-Rotation 1). The left lumbar multifidus muscle were measured in positions (1)–(3), and (5) the Flexion position adding left trunk rotation (Flexion-Rotation 2).
Results
The shear elastic modulus of the lumbar erector spinae muscle in the Flexion-Lateral Flexion position was significantly higher than that in the Rest, Flexion, or Flexion-Rotation 1 positions. Shear elastic modulus of the lumbar multifidus muscle was similar in the Flexion, Flexion-Lateral Flexion, and Flexion-Rotation 2 positions, but significantly lower in the Rest position.
Conclusions
The results of the present study suggest that the lumbar erector spinae muscle is stretched effectively in the position adding trunk contralateral lateral flexion to flexion. The results also indicate that the lumbar multifidus muscle, which does not appear to be affected by adding trunk contralateral lateral flexion or ipsilateral rotation to flexion, is stretched effectively in the trunk flexion position.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ICC:
-
Intraclass correlation coefficient
- LBP:
-
Low back pain
- MA:
-
Moment arm
- ROI:
-
Region of interest
- SWE:
-
Shear wave elastography
References
Ateş F, Hug F, Bouillard K, Jubeau M, Frappart T, Couade M, Bercoff J, Nordez A (2015) Muscle shear elastic modulus is linearly related to muscle torque over the entire range of isometric contraction intensity. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 25:703–708
Aubry S, Risson JR, Kastler A, Barbier-Brion B, Siliman G, Runge M, Kastler B (2013) Biomechanical properties of the calcaneal tendon in vivo assessed by transient shear wave elastography. Skeletal Radiol 42:1143–1150
Bergmark A (1989) Stability of the lumbar spine. A study in mechanical engineering. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl 230:1–54
Chaffin DB, Redfern MS, Erig M, Goldstein SA (1990) Lumbar muscle size and locations from CT scans of 96 women of age 40 to 63 years. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 5, 9–16
Creze M, Nyangoh Timoh K, Gagey O, Rocher L, Bellin MF, Soubeyrand M (2017) Feasibility assessment of shear wave elastography to lumbar back muscles: a radioanatomic study. Clin Anat 30:774–780
Dumas GA, Poulin MJ, Roy B, Gagnon M, Jovanovic M (1991) Orientation and moment arms of some trunk muscles. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 16, 293–303
Hangai M, Kaneoka K, Kuno S, Hinotsu S, Sakane M, Mamizuka N, Sakai S, Ochiai N (2008) Factors associated with lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration in the elderly. Spine J 8:732–740
Hangai M, Kaneoka K, Hinotsu S, Shimizu K, Okubo Y, Miyakawa S, Mukai N, Sakane M, Ochiai N (2009) Lumbar intervertebral disk degeneration in athletes. Am J Sports Med 37:149–155
Jorgensen MJ, Marras WS, Granata KP, Wiand JW (2001) MRI-derived moment-arms of the female and male spine loading muscles. Clin Biomech (Bristol Avon) 16:182–193
Kaneoka K, Shimizu K, Hangai M, Okuwaki T, Mamizuka N, Sakane M, Ochiai N (2007) Lumbar intervertebral disk degeneration in elite competitive swimmers: a case control study. Am J Sports Med 35:1341–1345
Kelly JP, Koppenhaver SL, Michener LA, Proulx L, Bisagni F, Cleland JA (2018) Characterization of tissue stiffness of the infraspinatus, erector spinae, and gastrocnemius muscle using ultrasound shear wave elastography and superficial mechanical deformation. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 38:73–80
Koo TK, Guo JY, Cohen JH, Parker KJ (2013) Relationship between shear elastic modulus and passive muscle force: an ex-vivo study. J Biomech 46:2053–2059
Lin YH, Chen CS, Cheng CK, Chen YH, Lee CL, Chen WJ (2001) Geometric parameters of the in vivo tissues at the lumbosacral joint of young Asian adults. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 26:2362–2367
MacDonald DA, Moseley GL, Hodges PW (2006) The lumbar multifidus: does the evidence support clinical beliefs? Man Ther 11:254–263
Maganaris CN, Baltzopoulos V, Sargeant AJ (2000). In vivo measurement-based estimations of the human Achilles tendon moment arm. Eur J Appl Physiol 83:363–369
Maïsetti O, Hug F, Bouillard K, Nordez A (2012) Characterization of passive elastic properties of the human medial gastrocnemius muscle belly using supersonic shear imaging. J Biomech 45:978–984
Masaki M, Aoyama T, Murakami T, Yanase K, Ji X, Tateuchi H, Ichihashi N (2017) Association of low back pain with muscle stiffness and muscle mass of the lumbar back muscles, and sagittal spinal alignment in young and middle-aged medical workers. Clin Biomech (Bristol Avon) 49:128–133
McGill SM, Santaguida L, Stevens J (1993) Measurement of the trunk musculature from T5 to L5 using MRI scans of 15 young males corrected for muscle fibre orientation. Clin Biomech (Bristol Avon) 8:171–178
Moga PJ, Erig M, Chaffin DB, Nussbaum MA (1993) Torso muscle moment arms at intervertebral levels T10 through L5 from CT scans on eleven male and eight female subjects. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 18:2305–2309
Moore A, Mannion J, Moran RW (2015) The efficacy of surface electromyographic biofeedback assisted stretching for the treatment of chronic low back pain: a case-series. J Bodyw Mov Ther 19:8–16
Moreau B, Vergari C, Gad H, Sandoz B, Skalli W, Laporte S (2016) Non-invasive assessment of human multifidus muscle stiffness using ultrasound shear wave elastography: a feasibility study. Proc Inst Mech Eng H 230:809–814
Oliveira CB, Maher CG, Pinto RZ, Traeger AC, Lin CC, Chenot JF van, Tulder M, Koes BW (2018) Clinical practice guidelines for the management of non-specific low back pain in primary care: an updated overview. Eur Spine J 27:2791–2803
Sherman KJ, Cherkin DC, Cook AJ, Hawkes RJ, Deyo RA, Wellman R, Khalsa PS (2010) Comparison of yoga versus stretching for chronic low back pain: protocol for the Yoga Exercise Self-care (YES) trial. Trials 11:36
Umegaki H, Ikezoe T, Nakamura M, Nishishita S, Kobayashi T, Fujita K, Tanaka H, Ichihashi N (2015) The effect of hip rotation on shear elastic modulus of the medial and lateral hamstrings during stretching. Man Ther 20:134–137
Umehara J, Ikezoe T, Nishishita S, Nakamura M, Umegaki H, Kobayashi T, Fujita K, Ichihashi N (2015) Effect of hip and knee position on tensor fasciae latae elongation during stretching: an ultrasonic shear wave elastography study. Clin Biomech (Bristol Avon) 30:1056–1059
Umehara J, Hasegawa S, Nakamura M, Nishishita S, Umegaki H, Tanaka H, Fujita K, Kusano K, Ichihashi N (2017a) Effect of scapular stabilization during cross-body stretch on the hardness of infraspinatus, teres minor, and deltoid muscles: an ultrasonic shear wave elastography study. Musculoskelet Sci Pract 27:91–96
Umehara J, Nakamura M, Fujita K, Kusano K, Nishishita S, Araki K, Tanaka H, Yanase K, Ichihashi N (2017b) Shoulder horizontal abduction stretching effectively increases shear elastic modulus of pectoralis minor muscle. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 26:159–1165
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B) 15H03043. The authors wish to thank all of the individuals who participated in the present study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors conceived and designed the research. MM, XJ, and TY conducted experiments. MM and XJ analyzed data. MM, HT, and NI wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest. No funding sources were used for the present study.
Additional information
Communicated by Bénédicte Schepens.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masaki, M., Ji, X., Yamauchi, T. et al. Effects of the trunk position on muscle stiffness that reflects elongation of the lumbar erector spinae and multifidus muscles: an ultrasonic shear wave elastography study. Eur J Appl Physiol 119, 1085–1091 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-019-04098-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-019-04098-6