Abstract
Introduction
While resistance exercise (RE) is known to be beneficial for overall health, one bout of RE acutely increases aortic stiffness and pulse pressure (PP). Increases in aortic stiffness and PP in a setting of aging has been shown to detrimentally impact cognitive function. This study examined whether increased aortic stiffness and PP from an acute bout of RE is associated with cognitive function.
Methods
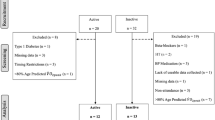
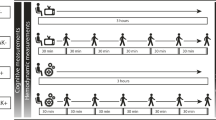
Thirty-five participants (21 ± 2 years) underwent cognitive testing before and after either an acute bout of RE or a non-exercise time-control condition. Cognitive function was assessed as reaction time and accuracy during memory recognition, attention (Flanker) and working memory (N-back) tasks. Aortic stiffness and PP were measured via pulse wave velocity (PWV) and pulse wave analysis, respectively, using a brachial oscillometric device.
Results
There were significant increases in aortic PWV and aortic PP following RE (p < 0.05) with no change in PWV or PP following the non-exercise control condition (p > 0.05). There was no change in accuracy metrics (% hits) across conditions for any cognitive task (p > 0.05). There was a condition-by-time interaction for reaction time for the memory task (p < 0.05) driven by a significant decrease in reaction times following RE (p < 0.05) with no change in reaction time following the non-exercise control (p > 0.05).
Conclusion
Functional increases in aortic stiffness and pulse pressure following acute RE occur in the absence of detrimental changes in cognitive function in young, healthy adults.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- BP:
-
Blood pressure
- CON:
-
Control condition
- DBP:
-
Diastolic blood pressure
- HR:
-
Heart rate
- MOCA:
-
Montreal Cognitive Assessment
- Pb:
-
Backward wave pressure
- Pf:
-
Forward wave pressure
- PP:
-
Pulse pressure
- PWV:
-
Pulse wave velocity
- RE:
-
Resistance exercise
- RIx:
-
Wave reflection index
- RM:
-
Repetition maximum
- RT:
-
Reaction time
References
Augustine JA, Nunemacher KN, Heffernan KS (2018) Menstrual phase and the vascular response to acute resistance exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 118:937–946
Brush CJ, Olson RL, Ehmann PJ, Osovsky S, Alderman BL (2016) Dose-response and time course effects of acute resistance exercise on executive function. J Sport Exerc Psychol 38:396–408
Chang YK, Labban JD, Gapin JI, Etnier JL (2012) The effects of acute exercise on cognitive performance: a meta-analysis. Brain Res 1453:87–101
Chang H, Kim K, Jung YJ, Kato M (2017) Effects of acute high-Intensity resistance exercise on cognitive function and oxygenation in prefrontal cortex. J Exerc Nutr Biochem 21:1–8
Cooper LL, Mitchell GF (2016) Aortic stiffness, cerebrovascular dysfunction, and memory. Pulse (Basel Switz) 4:69–77
DeVan AE, Anton MM, Cook JN, Neidre DB, Cortez-Cooper MY, Tanaka H (2005) Acute effects of resistance exercise on arterial compliance. J Appl Physiol (Bethesda Md 1985) 98:2287–2291
Dunsky A, Abu-Rukun M, Tsuk S, Dwolatzky T, Carasso R, Netz Y (2017) The effects of a resistance vs. an aerobic single session on attention and executive functioning in adults. PLoS One 12:e0176092
Hametner B, Wassertheurer S, Kropf J, Mayer C, Eber B, Weber T (2013) Oscillometric estimation of aortic pulse wave velocity: comparison with intra-aortic catheter measurements. Blood Press Monit 18:173–176
Hashimoto T, Tsukamoto H, Takenaka S, Olesen ND, Petersen LG, Sorensen H, Nielsen HB, Secher NH, Ogoh S (2018) Maintained exercise-enhanced brain executive function related to cerebral lactate metabolism in men. FASEB J Off Publ Fed Am Soc Exp Biol 32:1417–1427
Heffernan KS, Augustine JA, Lefferts WK, Spartano NL, Hughes WE, Jorgensen RS, Gump BB (2018) Arterial stiffness and cerebral hemodynamic pulsatility during cognitive engagement in younger and older adults. Exp Gerontol 101:54–62
Lefferts WK, Augustine JA, Heffernan KS (2014) Effect of acute resistance exercise on carotid artery stiffness and cerebral blood flow pulsatility. Front Physiol 5:101
Lefferts WK, Hughes WE, Heffernan KS (2015) Effect of acute high-intensity resistance exercise on optic nerve sheath diameter and ophthalmic artery blood flow pulsatility. J Hum Hypertens 29:744–748
Ludyga S, Gerber M, Brand S, Holsboer-Trachsler E, Puhse U (2016) Acute effects of moderate aerobic exercise on specific aspects of executive function in different age and fitness groups: a meta-analysis. Psychophysiology 53:1611–1626
McMorris T, Hale BJ (2012) Differential effects of differing intensities of acute exercise on speed and accuracy of cognition: a meta-analytical investigation. Brain Cogn 80:338–351
Mitchell GF, van Buchem MA, Sigurdsson S, Gotal JD, Jonsdottir MK, Kjartansson O, Garcia M, Aspelund T, Harris TB, Gudnason V, Launer LJ (2011) Arterial stiffness, pressure and flow pulsatility and brain structure and function: the age, gene/environment susceptibility—Reykjavik study. Brain J Neurol 134:3398–3407
Miyachi M (2013) Effects of resistance training on arterial stiffness: a meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med 47:393–396
Nakamura N, Muraoka I (2018) Resistance training augments cerebral blood flow pulsatility: cross-sectional study. Am J Hypertens 31:811–817
Ogoh S, Tsukamoto H, Hirasawa A, Hasegawa H, Hirose N, Hashimoto T (2014) The effect of changes in cerebral blood flow on cognitive function during exercise. Physiol Rep 2:e12163
Pase MP, Himali JJ, Mitchell GF, Beiser A, Maillard P, Tsao C, Larson MG, DeCarli C, Vasan RS, Seshadri S (2016) Association of aortic stiffness with cognition and brain aging in young and middle-aged adults: the Framingham third generation cohort study. Hypertension 67:513–519
Pierce DR, Doma K, Leicht AS (2018) Acute effects of exercise mode on arterial stiffness and wave reflection in healthy young adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Physiol 9:73
Pontifex MB, Hillman CH, Fernhall B, Thompson KM, Valentini TA (2009) The effect of acute aerobic and resistance exercise on working memory. Med Sci Sports Exerc 41:927–934
Tarumi T, Gonzales MM, Fallow B, Nualnim N, Pyron M, Tanaka H, Haley AP (2013) Central artery stiffness, neuropsychological function, and cerebral perfusion in sedentary and endurance-trained middle-aged adults. J Hypertens 31:2400–2409
Tarumi T, Gonzales MM, Fallow B, Nualnim N, Lee J, Pyron M, Tanaka H, Haley AP (2015) Cerebral/peripheral vascular reactivity and neurocognition in middle-age athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc 47:2595–2603
Tsai CL, Wang CH, Pan CY, Chen FC, Huang TH, Chou FY (2014) Executive function and endocrinological responses to acute resistance exercise. Front Behav Neurosci 8:262
Tsukamoto H, Suga T, Takenaka S, Takeuchi T, Tanaka D, Hamaoka T, Hashimoto T, Isaka T (2017) An acute bout of localized resistance exercise can rapidly improve inhibitory control. PLoS One 12:e0184075
van Sloten TT, Protogerou AD, Henry RM, Schram MT, Launer LJ, Stehouwer CD (2015) Association between arterial stiffness, cerebral small vessel disease and cognitive impairment: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 53:121–130
Weber T, Wassertheurer S, Rammer M, Maurer E, Hametner B, Mayer CC, Kropf J, Eber B (2011) Validation of a brachial cuff-based method for estimating central systolic blood pressure. Hypertension 58:825–832
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MW was instrumental in assisting with study design, IRB/ethics submission, participant recruitment, and data collection. SP assisted with data collection and wrote large portions of a manuscript initial draft. WL supervised all data collection and assisted with data interpretation, analyses, and manuscript preparation. JD assisted with data interpretation, analyses, tables, figures, and heavy editorial contributions on the manuscript. KH helped conceptualize the study, study design, initial piloting, initial data collection (with additional monitoring of data collection throughout to ensure high quality data acquisition), data interpretation, and preparation of the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Communicated by Keith Phillip George.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Palmiere, S., Wade, M., DeBlois, J.P. et al. Aortic stiffness, central pulse pressure and cognitive function following acute resistance exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 118, 2203–2211 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-018-3948-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-018-3948-2