Abstract
Purpose
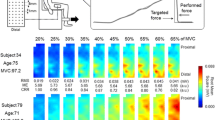
The aim of the present study was to compare spatial electromyographic potential distribution during force production between healthy young female and male using multi-channel surface electromyography (multi-SEMG).
Methods
Thirty healthy subjects (15 females) performed sustained isometric knee extension at 10% maximal voluntary contraction (MVC) task for 120 s. Multi-SEMG signals from the vastus lateralis muscle were detected and the modified entropy, coefficient of variation (CV), and correlation coefficient determined.
Results
The modified entropy and CV showed significant interaction and difference between females and males at all time points during the 10% MVC task. The correlation coefficient in females was significantly lower at 90 and 120 s than that of males.
Conclusions
The multi-SEMG potential distribution pattern in females showed more varied motor unit recruitment during sustained low-intensity isometric contraction than that of males. Variations in motor unit recruitment may result from recruitment and/or de-recruitment of motor units.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- ARV:
-
Average rectified value
- CV:
-
Coefficient of variation
- EMG:
-
Electromyogram
- multi-SEMG:
-
Multi-channel surface electromyography
- MVC:
-
Maximal voluntary contraction
- VL:
-
Vastus lateralis
References
Barnes WS (1980) The relationship between maximum isometric strength and intramuscular circulatory occlusion. Ergonomics 23:351–357. doi:10.1080/00140138008924748
Beck TW, DeFreitas JM, Stock MS (2010) Cross-talk among monopolar surface electromyographic signals from the superficial quadriceps femoris muscles. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol 50:245–250
Chanaud CM, Macpherson JM (1991) Functionally complex muscles of the cat hindlimb. III. Differential activation within biceps femoris during postural perturbations. Exp Brain Res 85:271–280
Enoka RM (2012) Muscle fatigue-from motor units to clinical symptoms. J Biomech 45:427–433. doi:10.1016/j.jbiomech.2011.11.047
Esbjörnsson-Liljedahl M, Sundberg CJ, Norman B, Jansson E (1999) Metabolic response in type I and type II muscle fibers during a 30-s cycle sprint in men and women. J Appl Physiol 87:1326–1332
Falla D, Arendt-Nielsen L, Farina D (2008) Gender-specific adaptations of upper trapezius muscle activity to acute nociceptive stimulation. Pain 138:217–225. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2008.04.004
Falla D, Andersen H, Danneskiold-Samsøe B, Arendt-Nielsen L, Farina D (2010) Adaptations of upper trapezius muscle activity during sustained contractions in women with fibromyalgia. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 20:457–464. doi:10.1016/j.jelekin.2009.07.002
Farina D, Leclerc F, Arendt-Nielsen L, Buttelli O, Madeleine P (2008) The change in spatial distribution of upper trapezius muscle activity is correlated to contraction duration. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 18:16–25. doi:10.1016/j.jelekin.2006.08.005
Hammarsten J, Bylund-Fellenius AC, Holm J, Scherstén T, Krotkiewski M (1980) Capillary supply and muscle fibre types in patients with intermittent claudication: relationships between morphology and metabolism. Eur J Clin Invest 10:301–305
Henneman E, Somjen G, Carpenter DO (1965) Functional significance of cell size in spinal motoneurons. J Neurophysiol 28:560–580
Holtermann A, Roeleveld K (2006) EMG amplitude distribution changes over the upper trapezius muscle are similar in sustained and ramp contractions. Acta Physiol 186:159–168. doi:10.1111/j.1748-1716.2005.01520.x
Holtermann A, Roeleveld K, Karlsson JS (2005) Inhomogeneities in muscle activation reveal motor unit recruitment. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 15:131–137. doi:10.1016/j.jelekin.2004.09.003
Holtermann A, Grönlund C, Stefan Karlsson J, Roeleveld K (2008) Spatial distribution of active muscle fibre characteristics in the upper trapezius muscle and its dependency on contraction level and duration. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 18:372–381. doi:10.1016/j.jelekin.2006.12.003
Holtermann A, Roeleveld K, Mork PJ, Grönlund C, Karlsson JS, Andersen LL, Olsen HB, Zebis MK, Sjøgaard G, Søgaard K (2009) Selective activation of neuromuscular compartments within the human trapezius muscle. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 19:896–902. doi:10.1016/j.jelekin.2008.04.016
Hunter SK (2014) Sex differences in human fatigability: mechanisms and insight to physiological responses. Acta Physiol 210:768–789. doi:10.1111/apha.12234
Hunter SK, Enoka RM (2001) Sex differences in the fatigability of arm muscles depends on absolute force during isometric contractions. J Appl Physiol 91:2686–2694
Hunter SK, Ryan DL, Ortega JD, Enoka RM (2002) Task differences with the same load torque alter the endurance time of submaximal fatiguing contractions in humans. J Neurophysiol 88:3087–3096. doi:10.1152/jn.00232.2002
Kent-Braun JA, Ng AV, Doyle JW, Towse TF (2002) Human skeletal muscle responses vary with age and gender during fatigue due to incremental isometric exercise. J Appl Physiol 93:1813–1823. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00091.2002
Kent-Braun JA, Fitts RH, Christie A (2012) Skeletal muscle fatigue. Compr Physiol 2:997–1044. doi:10.1002/cphy.c110029
Lexell J, Downham DY (1991) The occurrence of fibre-type grouping in healthy human muscle: a quantitative study of cross-sections of whole vastus lateralis from men between 15 and 83 years. Acta Neuropathol 81:377–381
Madeleine P, Leclerc F, Arendt-Nielsen L, Ravier P, Farina D (2006) Experimental muscle pain changes the spatial distribution of upper trapezius muscle activity during sustained contraction. Clin Neurophysiol 117:2436–2445. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2006.06.753
Maughan RJ, Harmon M, Leiper JB, Sale D, Delman A (1986) Endurance capacity of untrained males and females in isometric and dynamic muscular contractions. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 55:395–400
Merletti R, Holobar A, Farina D (2008) Analysis of motor units with high-density surface electromyography. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 18:879–890. doi:10.1016/j.jelekin.2008.09.002
Miller AE, MacDougall JD, Tarnopolsky MA, Sale DG (1993) Gender differences in strength and muscle fiber characteristics. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 66:254–262
Russ DW, Kent-Braun JA (2003) Sex differences in human skeletal muscle fatigue are eliminated under ischemic conditions. J Applied Physiol 94:2414–2422. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.01145.2002
Sadamoto T, Bonde-Petersen F, Suzuki Y (1983) Skeletal muscle tension, flow, pressure, and EMG during sustained isometric contractions in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 51:395–408
Simoneau JA, Bouchard C (1989) Human variation in skeletal muscle fiber-type proportion and enzyme activities. Am J Physiol 257:E567–E572
Simoneau JA, Lortie G, Boulay MR, Thibault MC, Thériault G, Bouchard C (1985) Skeletal muscle histochemical and biochemical characteristics in sedentary male and female subjects. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 63:30–35
Watanabe K, Kouzaki M, Merletti R, Fujibayashi M, Moritani T (2012a) Spatial EMG potential distribution pattern of vastus lateralis muscle during isometric knee extension in young and elderly men. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 22:74–79. doi:10.1016/j.jelekin.2011.09.010
Watanabe K, Kouzaki M, Moritani T (2012b) Task-dependent spatial distribution of neural activation pattern in human rectus femoris muscle. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 22:251–258. doi:10.1016/j.jelekin.2011.11.004
Watanabe K, Miyamoto T, Tanaka Y, Fukuda K, Moritani T (2012c) Type 2 diabetes mellitus patients manifest characteristic spatial EMG potential distribution pattern during sustained isometric contraction. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 97:468–473. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2012.03.004
Watanabe K, Kouzaki M, Moritani T (2015) Spatial EMG potential distribution of biceps brachii muscle during resistance training and detraining. Eur J Appl Physiol 115:2661–2670. doi:10.1007/s00421-015-3237-2
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all the subjects who volunteered to participate in this study. This study was supported in part by research grants from JSPS KAKENHI (Grant Numbers 24500586 and 15K01369).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest and that no companies or manufacturers will benefit from the results of this study.
Additional information
Communicated by Toshio Moritani.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nishikawa, Y., Watanabe, K., Takahashi, T. et al. Sex differences in variances of multi-channel surface electromyography distribution of the vastus lateralis muscle during isometric knee extension in young adults. Eur J Appl Physiol 117, 583–589 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-017-3559-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-017-3559-3