Abstract
Purpose
Eccentric muscle actions are important to the development of muscle mass and strength and may affect bone mineral density (BMD). This study’s purpose was to determine the relative effectiveness of five different eccentric:concentric load ratios to increase musculoskeletal parameters during early adaptations to resistance training.
Methods
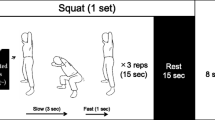
Forty male subjects performed a supine leg press and calf press training program 3 days week−1 for 8 weeks. Subjects were matched for pre-training leg press 1-repetition maximum strength (1-RM) and randomly assigned to one of five training groups. Concentric training load (% 1-RM) was constant across groups, but within groups, eccentric load was 0, 33, 66, 100, or 138 % of concentric load. Muscle mass (dual energy X-ray absorptiometry; DXA), strength (1-RM), and BMD (DXA) were measured pre- and post-training. Markers of bone metabolism were assessed pre-, mid- and post-training.
Results
The increase in leg press 1-RM in the 138 % group (20 ± 4 %) was significantly greater (P < 0.05) than the 0 % (8 ± 3 %), 33 % (8 ± 5 %) and 66 % (8 ± 4 %) groups, but not the 100 % group (13 ± 6 %; P = 0.15). All groups, except the 0 % group, increased calf press 1-RM (P < 0.05). Leg lean mass and greater trochanter BMD were increased only in the 138 % group (P < 0.05).
Conclusions
Early-phase adaptations to eccentric overload training include increases in muscle mass and site-specific increases in BMD and muscle strength which are not present or are less with traditional and eccentric underload training. Eccentric overload provides a robust musculoskeletal stimulus that may benefit bedridden patients, individuals recovering from injury or illness, and astronauts during spaceflight.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 1-RM:
-
One-repetition maximum
- ARED:
-
Advanced Resistive Exercise Device
- BMD:
-
Bone mineral density
- CSA:
-
Cross-sectional area
- DXA:
-
Dual energy X-ray absorptiometry
- iRED:
-
interim Resistive Exercise Device
- ISS:
-
International Space Station
- JSC:
-
Johnson Space Center
- LLM:
-
Leg lean mass
- NASA:
-
National Aeronautics and Space Administration
- pQCT:
-
Peripheral quantitative computed tomography
- WBLM:
-
Whole body lean mass
References
Akima H, Ushiyama J, Kubo J, Tonosaki S, Itoh M, Kawakami Y, Fukuoka H, Kanehisa H, Fukunaga T (2003) Resistance training during unweighting maintains muscle size and function in human calf. Med Sci Sports Exerc 35:655–662
Alcaraz PE, Perez-Gomez J, Chavarrias M, Blazevich AJ (2011) Similarity in adaptations to high-resistance circuit vs. traditional strength training in resistance-trained men. J Strength Cond Res 25:2519–2527
Alfredson H, Nordstrom P, Pietila T, Lorentzon R (1999) Bone mass in the calcaneus after heavy loaded eccentric calf-muscle training in recreational athletes with chronic achilles tendinosis. Calcif Tissue Int 64:450–455
Alkner BA, Tesch PA (2004) Knee extensor and plantar flexor muscle size and function following 90 days of bed rest with or without resistance exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 93:294–305
Amonette WE, Bentley JR, Lee SMC, Loehr JA, Schneider SM (2004) Ground reaction force and mechanical differences between the interim resistive exercise device (ired) and smith machine while performing a squat. NASA Technical Paper, TP-212063, Washington, D.C
Baldwin KM, White TP, Arnaud SB, Edgerton VR, Kraemer WJ, Kram R, Raab-Cullen D, Snow CM (1996) Musculoskeletal adaptations to weightlessness and development of effective countermeasures. Med Sci Sports Exerc 28:1247–1253
Bamman MM, Hunter GR, Stevens BR, Guilliams ME, Greenisen MC (1997) Resistance exercise prevents plantar flexor deconditioning during bed rest. Med Sci Sports Exerc 29:1462–1468
Bamman MM, Clarke MS, Feeback DL, Talmadge RJ, Stevens BR, Lieberman SA, Greenisen MC (1998) Impact of resistance exercise during bed rest on skeletal muscle sarcopenia and myosin isoform distribution. J Appl Physiol 84:157–163
Bassey EJ, Ramsdale SJ (1994) Increase in femoral bone density in young women following high-impact exercise. Osteoporos Int 4:72–75
Bassey EJ, Rothwell MC, Littlewood JJ, Pye DW (1998) Pre- and postmenopausal women have different bone mineral density responses to the same high-impact exercise. J Bone Miner Res 13:1805–1813
Brandenburg JP, Docherty D (2002) The effects of accentuated eccentric loading on strength, muscle hypertrophy, and neural adaptations in trained individuals. J Strength Cond Res 16:25–32
Burr DB, Martin RB (1992) Mechanisms of bone adaptation to the mechanical environment. Triangle (Sandoz) 31:59–76
Campos GE, Luecke TJ, Wendeln HK, Toma K, Hagerman FC, Murray TF, Ragg KE, Ratamess NA, Kraemer WJ, Staron RS (2002) Muscular adaptations in response to three different resistance-training regimens: Specificity of repetition maximum training zones. Eur J Appl Physiol 88:50–60
Colliander EB, Tesch PA (1990) Effects of eccentric and concentric muscle actions in resistance training. Acta Physiol Scand 140:31–39
Crameri RM, Aagaard P, Qvortrup K, Langberg H, Olesen J, Kjaer M (2007) Myofibre damage in human skeletal muscle: effects of electrical stimulation versus voluntary contraction. J Physiol 583:365–380
Crenshaw AG, Karlsson S, Styf J, Backlund T, Friden J (1995) Knee extension torque and intramuscular pressure of the vastus lateralis muscle during eccentric and concentric activities. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 70:13–19
Doan BK, Newton RU, Marsit JL, Triplett-McBride NT, Koziris LP, Fry AC, Kraemer WJ (2002) Effects of increased eccentric loading on bench press 1rm. J Strength Cond Res 16:9–13
Dudley GA, Tesch PA, Harris RT, Golden CL, Buchanan P (1991a) Influence of eccentric actions on the metabolic cost of resistance exercise. Aviat Space Environ Med 62:678–682
Dudley GA, Tesch PA, Miller BJ, Buchanan P (1991b) Importance of eccentric actions in performance adaptations to resistance training. Aviat Space Environ Med 62:543–550
Eastell R, Colwell A, Hampton L, Reeve J (1997) Biochemical markers of bone resorption compared with estimates of bone resorption from radiotracer kinetic studies in osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res 12:59–65
English KL, Loehr JA, Laughlin MA, Lee SMC, Hagan RD (2008) Reliability of strength testing using the advanced resistive exercise device and free weights. NASA Technical Paper, TP-214728, Washington, D.C
Evans RK, Negus CH, Centi AJ, Spiering BA, Kraemer WJ, Nindl BC (2012) Peripheral qct sector analysis reveals early exercise-induced increases in tibial bone mineral density. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 12:155–164
Eyre DR (1992) New biomarkers of bone resorption. J Clin Endocrinol Metabol 74:470A–470C
Ferrando AA, Tipton KD, Bamman MM, Wolfe RR (1997) Resistance exercise maintains skeletal muscle protein synthesis during bed rest. J Appl Physiol 82:807–810
Friedmann B, Kinscherf R, Vorwald S, Muller H, Kucera K, Borisch S, Richter G, Bartsch P, Billeter R (2004) Muscular adaptations to computer-guided strength training with eccentric overload. Acta Physiol Scand 182:77–88
Friedmann-Bette B, Bauer T, Kinscherf R, Vorwald S, Klute K, Bischoff D, Muller H, Weber MA, Metz J, Kauczor HU, Bartsch P, Billeter R (2010) Effects of strength training with eccentric overload on muscle adaptation in male athletes. Eur J Appl Physiol 108:821–836
Frost HM (1987a) Bone “mass” and the “mechanostat”: a proposal. Anat Rec 219:1–9
Frost HM (1987b) The mechanostat: a proposed pathogenic mechanism of osteoporoses and the bone mass effects of mechanical and nonmechanical agents. Bone Miner 2:73–85
Frost HM (1990a) Skeletal structural adaptations to mechanical usage (satmu): 1. Redefining wolff’s law: the bone modeling problem. Anat Rec 226:403–413
Frost HM (1990b) Skeletal structural adaptations to mechanical usage (satmu): 2. Redefining wolff’s law: the remodeling problem. Anat Rec 226:414–422
Frost HM (2001) From wolff’s law to the utah paradigm: insights about bone physiology and its clinical applications. Anat Rec 262:398–419
Gabriel DA, Kamen G, Frost G (2006) Neural adaptations to resistive exercise: mechanisms and recommendations for training practices. Sports Med 36:133–149
Gopalakrishnan R, Genc KO, Rice AJ, Lee SM, Evans HJ, Maender CC, Ilaslan H, Cavanagh PR (2010) Muscle volume, strength, endurance, and exercise loads during 6-month missions in space. Aviat Space Environ Med 81:91–102
Hargens AR, Parazynski S, Aratow M, Friden J (1989) Muscle changes with eccentric exercise: implications on earth and in space. Adv Myochem 2:299–312
Hather BM, Tesch PA, Buchanan P, Dudley GA (1991) Influence of eccentric actions on skeletal muscle adaptations to resistance training. Acta Physiol Scand 143:177–185
Hawkins SA, Schroeder ET, Wiswell RA, Jaque SV, Marcell TJ, Costa K (1999) Eccentric muscle action increases site-specific osteogenic response. Med Sci Sports Exerc 31:1287–1292
Higbie EJ, Cureton KJ, Warren GL 3rd, Prior BM (1996) Effects of concentric and eccentric training on muscle strength, cross-sectional area, and neural activation. J Appl Physiol 81:2173–2181
Hortobagyi T, Hill JP, Houmard JA, Fraser DD, Lambert NJ, Israel RG (1996) Adaptive responses to muscle lengthening and shortening in humans. J Appl Physiol 80:765–772
Hortobagyi T, Devita P, Money J, Barrier J (2001) Effects of standard and eccentric overload strength training in young women. Med Sci Sports Exerc 33:1206–1212
Jee WSS, Frost HM (1992) Skeletal adaptations during growth. Triangle (Sandoz) 31:77–88
Jepsen KJ, Centi A, Duarte GF, Galloway K, Goldman H, Hampson N, Lappe JM, Cullen DM, Greeves J, Izard R, Nindl BC, Kraemer WJ, Negus CH, Evans RK (2011) Biological constraints that limit compensation of a common skeletal trait variant lead to inequivalence of tibial function among healthy young adults. J Bone Miner Res 26:2872–2885
Jones DA, Rutherford OM (1987) Human muscle strength training: the effects of three different regimens and the nature of the resultant changes. J Physiol 391:1–11
Josse AR, Tang JE, Tarnopolsky MA, Phillips SM (2010) Body composition and strength changes in women with milk and resistance exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 42:1122–1130
Kohrt WM, Bloomfield SA, Little KD, Nelson ME, Yingling VR (2004) American college of sports medicine position stand: physical activity and bone health. Med Sci Sports Exerc 36:1985–1996
Kryger AI, Andersen JL (2007) Resistance training in the oldest old: consequences for muscle strength, fiber types, fiber size, and mhc isoforms. Scand J Med Sci Sports 17:422–430
Lacerte M, de Lateur BJ, Alquist AD, Questad KA (1992) Concentric versus combined concentric-eccentric isokinetic training programs: effect on peak torque of human quadriceps femoris muscle. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 73:1059–1062
Lang T, LeBlanc A, Evans H, Lu Y, Genant H, Yu A (2004) Cortical and trabecular bone mineral loss from the spine and hip in long-duration spaceflight. J Bone Miner Res 19:1006–1012
Layne JE, Nelson ME (1999) The effects of progressive resistance training on bone density: a review. Med Sci Sports Exerc 31:25–30
LeBlanc A, Lin C, Shackelford L, Sinitsyn V, Evans H, Belichenko O, Schenkman B, Kozlovskaya I, Oganov V, Bakulin A, Hedrick T, Feeback D (2000a) Muscle volume, mri relaxation times (t2), and body composition after spaceflight. J Appl Physiol 89:2158–2164
LeBlanc A, Schneider V, Shackelford L, West S, Oganov V, Bakulin A, Voronin L (2000b) Bone mineral and lean tissue loss after long duration space flight. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 1:157–160
Lee S, Shackelford L, Smith S, Guilliams M, Shepherd B, Loehr JA, Laughlin MA, Chauvin J, Hagan RD (2004a) Lean tissue mass and muscle strength: does resistive exercise during space flight prevent deconditioning? Med Sci Sports Exerc 36:S272
Lee SM, Cobb K, Loehr JA, Nguyen D, Schneider SM (2004b) Foot-ground reaction force during resistive exercise in parabolic flight. Aviat Space Environ Med 75:405–412
Loehr JA, Lee SM, English KL, Sibonga J, Smith SM, Spiering BA, Hagan RD (2011) Musculoskeletal adaptations to training with the advanced resistive exercise device. Med Sci Sports Exerc 43:146–156
Lohman T, Going S, Pamenter R, Hall M, Boyden T, Houtkooper L, Ritenbaugh C, Bare L, Hill A, Aickin M (1995) Effects of resistance training on regional and total bone mineral density in premenopausal women: A randomized prospective study. J Bone Miner Res 10:1015–1024
Martyn-St James M, Carroll S (2006) Progressive high-intensity resistance training and bone mineral density changes among premenopausal women: evidence of discordant site-specific skeletal effects. Sports Med 36:683–704
Menkes A, Mazel S, Redmond RA, Koffler K, Libanati CR, Gundberg CM, Zizic TM, Hagberg JM, Pratley RE, Hurley BF (1993) Strength training increases regional bone mineral density and bone remodeling in middle-aged and older men. J Appl Physiol 74:2478–2484
Moore AD, Lee SMC, Stenger MB, Platts SH (2010) Cardiovascular exercise in the U.S. Space program: past, present and future. Acta Astronaut 66:974–988
Morgan JL, Zwart SR, Heer M, Ploutz-Snyder R, Ericson K, Smith SM (2012) Bone metabolism and nutritional status during 30-day head-down-tilt bed rest. J Appl Physiol 113:1519–1529
Moritani T, de Vries HA (1979) Neural factors versus hypertrophy in the time course of muscle strength gain. Am J Phys Med 58:115–130
Narici M, Kayser B, Barattini P, Cerretelli P (2003) Effects of 17-day spaceflight on electrically evoked torque and cross-sectional area of the human triceps surae. Eur J Appl Physiol 90:275–282
Nickols-Richardson SM, Miller LE, Wootten DF, Ramp WK, Herbert WG (2007) Concentric and eccentric isokinetic resistance training similarly increases muscular strength, fat-free soft tissue mass, and specific bone mineral measurements in young women. Osteoporos Int 18:789–796
Norrbrand L, Fluckey JD, Pozzo M, Tesch PA (2008) Resistance training using eccentric overload induces early adaptations in skeletal muscle size. Eur J Appl Physiol 102:271–281
Oliveira AS, Caputo F, Aagaard P, Corvino RB, Goncalves M, Denadai BS (2013) Isokinetic eccentric resistance training prevents loss in mechanical muscle function after running. Eur J Appl Physiol 113:2301–2311
Ploutz LL, Tesch PA, Biro RL, Dudley GA (1994) Effect of resistance training on muscle use during exercise. J Appl Physiol 76:1675–1681
Prisby RD, Nelson AG, Latsch E (2004) Eccentric exercise prior to hindlimb unloading attenuated reloading muscle damage in rats. Aviat Space Environ Med 75:941–946
Riley DA, Bain JL, Thompson JL, Fitts RH, Widrick JJ, Trappe SW, Trappe TA, Costill DL (2000) Decreased thin filament density and length in human atrophic soleus muscle fibers after spaceflight. J Appl Physiol 88:567–572
Rittweger J, Frost HM, Schiessl H, Ohshima H, Alkner B, Tesch P, Felsenberg D (2005) Muscle atrophy and bone loss after 90 days’ bed rest and the effects of flywheel resistive exercise and pamidronate: results from the ltbr study. Bone 36:1019–1029
Roig M, O’Brien K, Kirk G, Murray R, McKinnon P, Shadgan B, Reid WD (2009) The effects of eccentric versus concentric resistance training on muscle strength and mass in healthy adults: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med 43:556–568
Ryan AS, Ivey FM, Hurlbut DE, Martel GF, Lemmer JT, Sorkin JD, Metter EJ, Fleg JL, Hurley BF (2004) Regional bone mineral density after resistive training in young and older men and women. Scand J Med Sci Sports 14:16–23
Sale DG (1988) Neural adaptation to resistance training. Med Sci Sports Exerc 20:S135–S145
Schneider SM, Amonette WE, Blazine K, Bentley J, Lee SMC, Loehr JA, Moore AD Jr, Rapley M, Mulder ER, Smith SM (2003) Training with the international space station interim resistive exercise device. Med Sci Sports Exerc 35:1935–1945
Schroeder ET, Hawkins SA, Jaque SV (2004) Musculoskeletal adaptations to 16 weeks of eccentric progressive resistance training in young women. J Strength Cond Res 18:227–235
Schuenke MD, Herman JR, Gliders RM, Hagerman FC, Hikida RS, Rana SR, Ragg KE, Staron RS (2012) Early-phase muscular adaptations in response to slow-speed versus traditional resistance-training regimens. Eur J Appl Physiol 112:3585–3595
Seger JY, Arvidsson B, Thorstensson A (1998) Specific effects of eccentric and concentric training on muscle strength and morphology in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 79:49–57
Shackelford LC, LeBlanc AD, Driscoll TB, Evans HJ, Rianon NJ, Smith SM, Spector E, Feeback DL, Lai D (2004) Resistance exercise as a countermeasure to disuse-induced bone loss. J Appl Physiol 97:119–129
Smith SM, Nillen JL, Leblanc A, Lipton A, Demers LM, Lane HW, Leach CS (1998) Collagen cross-link excretion during space flight and bed rest. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:3584–3591
Smith SM, Wastney ME, Morukov BV, Larina IM, Nyquist LE, Abrams SA, Taran EN, Shih CY, Nillen JL, Davis-Street JE, Rice BL, Lane HW (1999) Calcium metabolism before, during, and after a 3-mo spaceflight: Kinetic and biochemical changes. Am J Physiol 277:R1–R10
Smith SM, Davis-Street JE, Fesperman JV, Calkins DS, Bawa M, Macias BR, Meyer RS, Hargens AR (2003) Evaluation of treadmill exercise in a lower body negative pressure chamber as a countermeasure for weightlessness-induced bone loss: a bed rest study with identical twins. J Bone Miner Res 18:2223–2230
Smith SM, Dillon EL, DeKerlegand DE, Davis-Street JE (2004) Variability of collagen crosslinks: impact of sample collection period. Calcif Tissue Int 74:336–341
Smith SM, Wastney ME, O’Brien KO, Morukov BV, Larina IM, Abrams SA, Davis-Street JE, Oganov V, Shackelford LC (2005a) Bone markers, calcium metabolism, and calcium kinetics during extended-duration space flight on the mir space station. J Bone Miner Res 20:208–218
Smith SM, Zwart SR, Block G, Rice BL, Davis-Street JE (2005b) The nutritional status of astronauts is altered after long-term space flight aboard the international space station. J Nutr 135:437–443
Smith SM, Zwart SR, Heer M, Lee SMC, Baecker N, Meuche S, Macias BR, Shackelford LC, Schneider S, Hargens AR (2008) Wise-2005: Supine treadmill exercise within lower body negative pressure and flywheel resistive exercise as a countermeasure to bed rest-induced bone loss in women during 60-day simulated microgravity. Bone 42:572–581
Smith SM, Gardner KK, Locke J, Zwart SR (2009a) Vitamin d supplementation during antarctic winter. Am J Clin Nutr 89:1092–1098
Smith SM, Zwart SR, Heer MA, Baecker N, Evans HJ, Feiveson AH, Shackelford LC, Leblanc AD (2009b) Effects of artificial gravity during bed rest on bone metabolism in humans. J Appl Physiol 107:47–53
Smith SM, Heer MA, Shackelford L, Sibonga JD, Ploutz-Snyder L, Zwart SR (2012a) Benefits for bone from resistance exercise and nutrition in long-duration spaceflight: Evidence from biochemistry and densitometry. J Bone Miner Res 27:1896–1906
Smith SM, McCoy T, Gazda D, Morgan JL, Heer M, Zwart SR (2012b) Space flight calcium: implications for astronaut health, spacecraft operations, and earth. Nutrients 4:2047–2068
Smith SM, Zwart SR, Heer M, Hudson EK, Shackelford L, Morgan JL (2014) Men and women in space: bone loss and kidney stone risk after long-duration spaceflight. J Bone Miner Res 29(7):1639–1645
Snow-Harter C, Whalen R, Myburgh K, Arnaud S, Marcus R (1992) Bone mineral density, muscle strength, and recreational exercise in men. J Bone Miner Res 7:1291–1296
Spector ER, Smith SM, Sibonga JD (2009) Skeletal effects of long-duration head-down bed rest. Aviat Space Environ Med 80:A23–A28
Staron RS, Malicky ES, Leonardi MJ, Falkel JE, Hagerman FC, Dudley GA (1990) Muscle hypertrophy and fast fiber type conversions in heavy resistance-trained women. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 60:71–79
Staron RS, Karapondo DL, Kraemer WJ, Fry AC, Gordon SE, Falkel JE, Hagerman FC, Hikida RS (1994) Skeletal muscle adaptations during early phase of heavy-resistance training in men and women. J Appl Physiol 76:1247–1255
Tesch PA, Thorsson A, Colliander EB (1990) Effects of eccentric and concentric resistance training on skeletal muscle substrates, enzyme activities and capillary supply. Acta Physiol Scand 140:575–580
Tesch PA, Berg HE, Bring D, Evans HJ, LeBlanc AD (2005) Effects of 17-day spaceflight on knee extensor muscle function and size. Eur J Appl Physiol 93:463–468
Trappe SW, Trappe TA, Lee GA, Costill DL (2001) Calf muscle strength in humans. Int J Sports Med 22:186–191
Trappe TA, Burd NA, Louis ES, Lee GA, Trappe SW (2007) Influence of concurrent exercise or nutrition countermeasures on thigh and calf muscle size and function during 60 days of bed rest in women. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 191:147–159
Trappe S, Costill D, Gallagher P, Creer A, Peters JR, Evans H, Riley DA, Fitts RH (2009) Exercise in space: Human skeletal muscle after 6 months aboard the international space station. J Appl Physiol 106:1159–1168
Turner CH (1998) Three rules for bone adaptation to mechanical stimuli. Bone 23:399–407
Vikne H, Refsnes PE, Ekmark M, Medbo JI, Gundersen V, Gundersen K (2006) Muscular performance after concentric and eccentric exercise in trained men. Med Sci Sports Exerc 38:1770–1781
Vogt M, Hoppeler HH (2014) Eccentric exercise: mechanisms and effects when used as training regime or training adjunct. J Appl Physiol 116(11):1446–1454
Vuori I, Heinonen A, Sievanen H, Kannus P, Pasanen M, Oja P (1994) Effects of unilateral strength training and detraining on bone mineral density and content in young women: A study of mechanical loading and deloading on human bones. Calcif Tissue Int 55:59–67
Westing SH, Seger JY (1989) Eccentric and concentric torque-velocity characteristics, torque output comparisons, and gravity effect torque corrections for the quadriceps and hamstring muscles in females. Int J Sports Med 10:175–180
Westing SH, Cresswell AG, Thorstensson A (1991) Muscle activation during maximal voluntary eccentric and concentric knee extension. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 62:104–108
Zwart SR, Hargens AR, Smith SM (2004) The ratio of animal protein intake to potassium intake is a predictor of bone resorption in space flight analogues and in ambulatory subjects. Am J Clin Nutr 80:1058–1065
Zwart SR, Davis-Street JE, Paddon-Jones D, Ferrando AA, Wolfe RR, Smith SM (2005) Amino acid supplementation alters bone metabolism during simulated weightlessness. J Appl Physiol 99:134–140
Zwart SR, Hargens AR, Lee SM, Macias BR, Watenpaugh DE, Tse K, Smith SM (2007) Lower body negative pressure treadmill exercise as a countermeasure for bed rest-induced bone loss in female identical twins. Bone 40:529–537
Zwart SR, Crawford GE, Gillman PL, Kala G, Rodgers AS, Rogers A, Inniss AM, Rice BL, Ericson K, Coburn S, Bourbeau Y, Hudson E, Mathew G, Dekerlegand DE, Sams CF, Heer MA, Paloski WH, Smith SM (2009a) Effects of 21 days of bed rest, with or without artificial gravity, on nutritional status of humans. J Appl Physiol 107:54–62
Zwart SR, Oliver SM, Fesperman JV, Kala G, Krauhs J, Ericson K, Smith SM (2009b) Nutritional status assessment before, during, and after long-duration head-down bed rest. Aviat Space Environ Med 80:A15–A22
Zwart SR, Pierson D, Mehta S, Gonda S, Smith SM (2010) Capacity of omega-3 fatty acids or eicosapentaenoic acid to counteract weightlessness-induced bone loss by inhibiting nf-kappab activation: from cells to bed rest to astronauts. J Bone Miner Res 25:1049–1057
Zwart SR, Booth SL, Peterson JW, Wang Z, Smith SM (2011a) Vitamin k status in spaceflight and ground-based models of spaceflight. J Bone Miner Res 26:948–954
Zwart SR, Mehta SK, Ploutz-Snyder R, Bourbeau Y, Locke JP, Pierson DL, Smith SM (2011b) Response to vitamin d supplementation during antarctic winter is related to bmi, and supplementation can mitigate epstein-barr virus reactivation. J Nutr 141:692–697
Zwart SR, Morgan JL, Smith SM (2013a) Iron status and its relations with oxidative damage and bone loss during long-duration space flight on the international space station. Am J Clin Nutr 98:217–223
Zwart SR, Parsons H, Kimlin M, Innis SM, Locke JP, Smith SM (2013b) A 250 µg/week dose of vitamin d was as effective as a 50 µg/d dose in healthy adults, but a regimen of four weekly followed by monthly doses of 1250 µg raised the risk of hypercalciuria. Br J Nutr 110:1866–1872
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the subjects for their participation in this training study; Karen Paulder, Sydney Stein, and Leah Stroud for their assistance with exercise training and data collection; Mary Jane Maddocks of the NASA JSC Bone and Mineral Laboratory for acquisition and analysis of DXA scans; the NASA JSC Nutritional Biochemistry Laboratory for the collection and analysis of blood and urine samples; Dr. Mitzi Laughlin for statistical analysis; Drs. Brian Arenare, Todd Schlegel, and Linda Shackelford for medical monitoring; the NASA JSC Human Test Subject Facility for test subject recruitment; Jackie Reeves and Dr. Meghan Downs for editorial and technical review of the manuscript; and Linda Loerch, Dr. Jennifer Tuxhorn, and Dr. Clarence Sams for their programmatic support of this research. Finally, we will always be grateful for the mentoring, support, and friendship of our NASA JSC Exercise Physiology Laboratory lead, the late Dr. R. Donald Hagan.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical standards
The experiments described herein were conducted in compliance with the laws of the United States of America.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by William J. Kraemer.
The authors, K. L. English and J. A. Loehr, contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
English, K.L., Loehr, J.A., Lee, S.M.C. et al. Early-phase musculoskeletal adaptations to different levels of eccentric resistance after 8 weeks of lower body training. Eur J Appl Physiol 114, 2263–2280 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-014-2951-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-014-2951-5